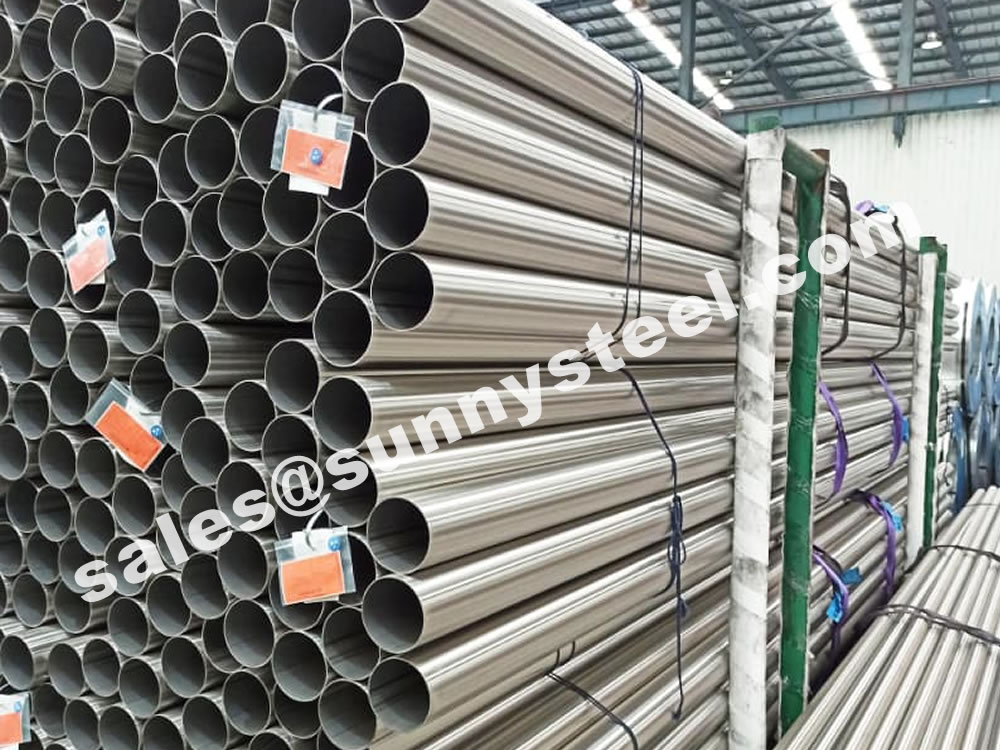
Carbon seamless steel pipes advantages are high pressure resistance, good toughness, long pipe sections and few joints.
Carbon steel seamless pipes are made by drawing a solid billet over a piercing rose to create a cylindrical hollow section without welding or a seam. They are preferred for higher pressure pipe systems and are widely used in the manufacturing of pipe fittings such as bends, elbows, and tees. They are also used in the nuclear device, gas conveyance, petrochemical, shipbuilding and boiler industries.

Seamless carbon steel pipe is a type of steel pipe that is manufactured without any welded joints or seams. It is produced by piercing a solid billet of carbon steel to create a hollow tube. The absence of a weld seam in seamless carbon steel pipes makes them stronger and more reliable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications compared to welded pipes.
Seamless carbon steel pipes are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, power generation, and refineries. They are suitable for conveying various fluids and gases, including water, oil, natural gas, and steam. The seamless construction of these pipes ensures smooth flow and reduces the risk of leaks or failures.
Seamless carbon steel pipes come in various sizes, wall thicknesses, and grades to meet different application requirements. They are often manufactured according to industry standards such as ASTM A53, ASTM A106, API 5L, and others.
Overall, seamless carbon steel pipes offer excellent strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making them a preferred choice for many critical applications in various industries.
The complex chemical and physical properties of the various grades of carbon steel pipe allow for a broad range of service usage. American Piping Products has the right grade, size and price to meet your requirements, including A/SA-106 Grade B/C and API 5L X- 42 thru X -70. A/SA-106 Grades B & C are utilized for services ranging from structural supports to steam drum headers with temperature ranges up to 800°F, while API 5L X Grades 42 thru 70 are utilized for the water and petroleum industry to transport liquids or as platforms on off-shore rigs.
Typical carbon steel pipe material grades in API 5L Grade B, X42 to X70, ASTM A106 B, ASTM A53 B, ASTM A252 Grade 3 and ASTM A333 Grade 6 etc. Octal offers various of carbon steel pipes including seamless, welded (ERW EFW, LSAW, SSAW) steel pipes for the mining industries.
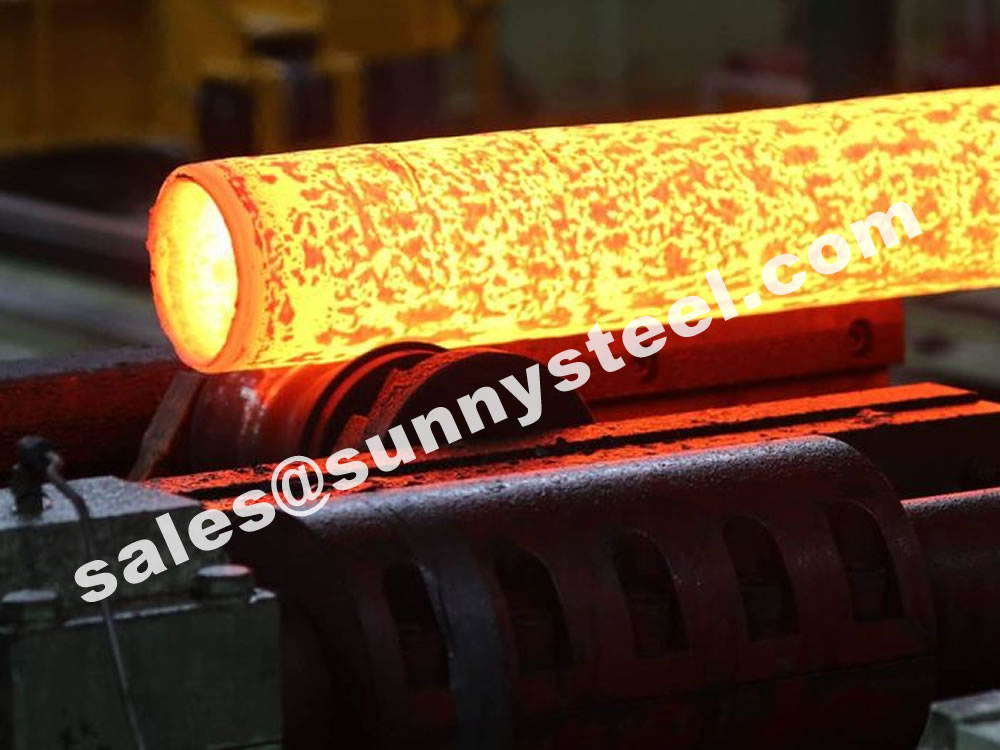












Piercing is the first process of deformation of seamless carbon steel pipe, and its function is to pass the solid tube blank out of the hollow capillary. Due to the surface defect or eccentricity (uneven wall thickness) of the threaded capillary, it is difficult to eliminate or reduce it in the subsequent deformation process. Therefore, the quality of the perforated capillary has an extremely important influence on the quality of the hot-rolled seamless steel pipe. The perforation methods of the tube blank include press punching, push rolling perforation and oblique rolling perforation.
Pressure punching is to put the heated billet or corrugated steel ingot into the circular mold, and then use the press to drive the punch to punch out the inner hole in the center of the tube blank. Generally, the area of the punched inner hole is equal to or slightly larger than the gap between the blank and the round die, so the deformation is very small, and the elongation coefficient generally does not exceed 1.1.
Push-roll piercing can be regarded as an improved form of pressure punching, that is, the fixed round die during pressure punching is changed to a pair of round-hole pass rolls, and the rolls are driven by a motor. When the roll turns to bite the tube blank into the pass and roll it, the punch fixed in the center of the pass penetrates it into the hollow capillary. For push rolling, a reverse thrust is added to the end of the billet, so it is called push rolling piercing.
The advantages of push roll perforation are as follows:
Push-rolling perforation was a method for circular continuous casting technology that was not yet mature at that time, and required square continuous casting slab perforation and tube rolling. Although it has been greatly improved compared with pressure stamping, the amount of deformation is still small, so the capillary is short and thick, and it is particularly prone to large uneven wall thickness. Therefore, after piercing, it is necessary to set up a skewed roll stretching machine to reduce the capillary wall thickness, extend the capillary length, and reduce the unevenness of the capillary wall thickness. However, with the maturity of round billet continuous casting technology, this method has been gradually replaced by cross rolling piercing.
The cross-rolling piercing is to use the circular tube billet to be bitten by two mutually inclined and co-rotating rolls, and advance in a spiral shape. The tube blank passes through the hollow capillary through the pass formed by the roller, the guide plate (or guide roller, guide plate) and the plug.
In fact, the round tube billet is bitten by the roll, rotated and compressed, deformed, and spirally advances. Before contacting the plug, the plastic deformation of the central area of the tube blank under repeated tensile and compressive stress gradually develops into loosening. As the looseness increases, the center breaks down forming a "cavity" (also known as the "swing effect"). Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the front end of the plug to the loose position of the tube blank, so as not to form a "cavity". At this time, the perforation force consumption is small, the tool wear is small, and the capillary quality is good. If the "cavity" has been formed, the tube blank is deformed in contact with the plug, and it is easy to form an "inward fold" in the capillary inner hole.
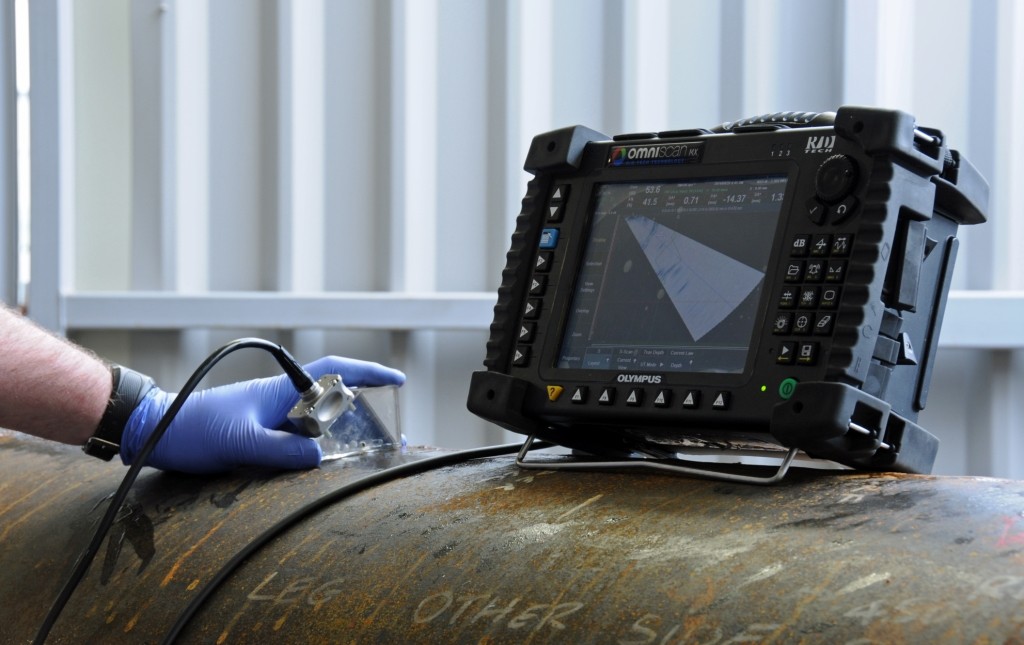

The inspection of Seamless Carbon Steel Pipes is a critical process to ensure the quality, safety, and performance of the pipes according to industry standards and customer requirements.

The Carbon Steel pipes are manufactured in various types, as given below:
– it contains more carbon and iron in its composition. Depending on the grade, trace amounts of silicon, manganese, and copper are permitted in varying quantities. Therefore, the Carbon Steel Seamless Pipe material is stronger and is extremely resistant to stress. In heavy-duty facilities, these features make the pipes applicable.
– The ASTM A335 P11 Seamless Pipe consists of carbon steel with a minimum tensile strength of 415MPa and a minimum yield strength of 205MPa. The material has high durability and high resistance to wear and tear. They are made up of Carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulphur, silicon, chromium, and molybdenum. The composition of the ASME SA335 Grade Crome Pipe gives it the characteristics of strength, strength, stiffness, wear resistance, hardness, hot hardness, and corrosion resistance.
– offer high durability, corrosion resistance, and tensile strength. The Carbon Steel Fabricated Pipes are used in various industries such as Oil & Gas Industry, Chemical Industry, Metallurgical Industry, Energy Industry, Ships Industry, Desalination Industry, Food Industry, and Pulp and Paper Industry.
– are used in high-pressure conditions. In a range of industries, such as the transport of water and waste, the oil and gas industries, high-pressure applications, and chemical manufacturing, carbon steel pipes are commonly used.
– have various features like Lightweight, Corrosion resistance, structured appropriately, Precision engineered, intricate detailing, Economical, and more. These ERW pipes are used in Ship Building, Automobile, Boilers & Pressure Vessels, Railways, Oil & Petro Chemicals, Coal & Mining, Transmission Towers, and General & Heavy Engineering.
– has some fine features such as easy installation, seamless finish, Rustproof, and more. As these LSAW pipes are expensive, they are not widely used in lower value non-energy applications such as water pipelines.

Seamless carbon steel pipes find extensive applications across various industries:
With their excellent properties and versatile applications, seamless carbon steel pipes are indispensable in modern industrial processes and infrastructure development.
The advantages of seamless carbon steel pipes are high pressure resistance, good toughness, long pipe sections and few joints. The disadvantage is that it is expensive, easy to corrode, and thus has a short service life.
Ordinary seamless carbon steel pipes are rolled from ordinary carbon steel, high-quality carbon steel, low alloy steel or alloy structural steel. Various specifications, high strength,
It is the most commonly used pipe for pipelines and is widely used for pipelines with working pressure below 1.6MPa. Such as heat pipes, refrigeration pipes, compressed air pipes, oxygen pipes, acetylene pipes and various chemical pipes except for strong corrosive media.
Stainless steel seamless pipes are made of chromium-nickel stainless steel, and there are two types of hot-rolled and cold-rolled (cold-drawn) pipes. It is characterized by strong acid resistance and corrosion resistance, but it is expensive, and it is mainly used in chemical pipelines with special requirements.
Welded steel pipes for low-pressure fluid transportation are seamed pipes, generally using Q215-A, Q235-A, Q255-A ordinary carbon steel. According to the surface quality, it can be divided into two types: galvanized (white iron pipe) and stainless steel (black iron pipe); according to whether the pipe end is threaded, it can be divided into two types: threaded and non-threaded; according to the thickness of the pipe wall, there are ordinary type and added Two thick types.
Ordinary steel pipes can generally withstand a 2.0MPa hydraulic test, and thickened pipes can withstand a 3.0MPa hydraulic test. Ordinary steel pipes and thickened pipes are generally available for.
The working pressure gauge uses a pipe with a lower medium temperature. For example: Indoor heating pipes, steam pipes, and hot water pipes with a working pressure not exceeding 1.0MPa and a medium temperature not exceeding 200°C can use pipes with a nominal diameter of not greater than 100mm; with a nominal diameter of not greater than 65mm, pipes with a working pressure not exceeding 0.8 MPa compressed air pipelines; those with a nominal diameter not greater than 50mm can be used for coal gas or natural gas and clean water pipelines.
Carbon steel is an alloy with carbon and iron, with carbon content up to 2.1% by weight. The increase in the carbon percentage will raise steel’s hardness and strength, but it will be less ductile. Carbon steel has good properties in hardness and strength, and it is less expensive than other steels.
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casting | API 5CT | Ø114~219 x WT5.2~22.2 | J55, K55, N80, L80, P110 |
| Tubing | API 5CT | Ø48.3~114.3 x WT3.2~16 | J55, K55, N80, L80, P110 |
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line Pipes | API 5L | Ø10.3~1200 x WT1.0~120 | A, B, X42, X46, X52, X60, X70, X80, PSL1 / PSL2 |
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black and Hot-Dipped Zinc-Coated Seamless Steel Pipes | ASTM A53 | Ø10.3~1200 x WT1.0~150 | Gr.A, Gr.B, Gr.C |
| Seamless Carbon Steel Pipes for High Temperature Service | ASTM A106 | Ø10.3~1200 x WT1.0~150 | Gr.B, Gr.C |
| Seamless Cold-Drawn Low-Carbon Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser Tubes | ASTM A179 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | Low Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Carbon Steel Boiler Tubes for High Pressure | ASTM A192 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | Low Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Cold-Drawn Intermediate Alloy Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser Tubes | ASTM A199 | Ø10.3~426 x 1.0~36 | T5, T22 |
| Seamless Medium-Carbon Steel Boiler and Superheater Tubes | ASTM A210 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | A1, C |
| Seamless Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy Steel Boiler, Superheater and Heat-Exchanger Tubes | ASTM A213 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | T5, T9, T11, T12, T22, T91 |
| Seamless Carbon and Alloy Steel for Mechanical Tubing | ASTM A333 | Ø1/4"~42" x WT SCH20~XXS | Gr.1, Gr.3, Gr.6 |
| Seamless and Welded Carbon Steel Pipes and Alloy Steel Pipes for Low Temperature Use | ASTM A334 | Ø1/4"~4" x WT SCH20~SCH80 | Gr.1, Gr.6 |
| Seamless Cold-Drawn Carbon Steel Feedwater Heater Tubes | ASTM A556 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | A2, B2 |
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seamless Steel Tubes for Elevated Temperature | DIN 17175 | Ø10~762 x WT1.0~120 | St35.8, St45.8, 10CrMo910, 15Mo3, 13CrMo44, STPL340, STB410, STB510, WB36 |
| Seamless Steel Tubes | DIN 1629 / DIN 2391 | Ø13.5~762 x WT1.8~120 | St37.0, St44.0, St52.0, St52.3 |
| Seamless Steel Tubes | DIN 2440 | Ø13.5~165.1 x WT1.8~4.85 | St33.2 |
| Seamless Steel Pipes for Structural Purpose | DIN 2393 | Ø16~426 x WT1.0~36 | RSt34-2, RSt37-2, RSt44-2, St52 |
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seamless Steel Tubes for Machine Structure | BS 970 | Ø10~762 x WT1.0~120 | Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Steel Tubes for Boiler and Heat Exchangers | BS 3059 | Ø10~762 x WT1.0~120 | 360, 410, 440, 460, 490 |
1. Structural carbon steel pipe is a carbon steel pipe for general structure and mechanical structure.
2. carbon steel pipe for fluid transportation is a general carbon steel pipe used to transport water, oil, gas and other fluids.
3. carbon steel pipes for low and medium pressure boilers (GB3087-2008) are used to manufacture superheated steam pipes, boiling water pipes, and superheated steam pipes, large smoke pipes, small smoke pipes and arch bricks for low and medium pressure boilers of various structures. Hot-rolled and cold-drawn (rolled) carbon steel pipes of high-quality carbon structural steel for pipes.
4. Seamless tubes for high pressure boilers (GB5310-2008) are high-quality carbon steel, alloy steel and stainless heat-resistant steel seamless tubes used to manufacture the heating surface of water-tube boilers with high pressure and above.
5. High-pressure carbon steel pipe for fertilizer equipment (GB6479-2000) is a high-quality carbon structural steel and alloy steel carbon steel pipe suitable for chemical equipment and pipelines with a working temperature of -40~400℃ and a working pressure of 10~30Ma.
6. carbon steel pipes for petroleum cracking (GB9948-2006) are carbon steel pipes for furnace tubes, heat exchangers and pipelines in petroleum refineries.
7. The steel pipe for geological drilling (YB235-70) is a steel pipe used by the geological department for core drilling. It can be divided into drill pipe, drill collar, core pipe, casing and sedimentation pipe according to the purpose.
8. carbon steel pipe for diamond core drilling (GB3423-82) is a carbon steel pipe for drill pipe, core pipe and casing for diamond core drilling.
9. Oil drilling pipe (YB528-65) is a carbon steel pipe used for inner or outer thickening at both ends of oil drilling.
10. Carbon steel carbon steel pipe for ships (GB5312-85)
It is a seamless carbon steel pipe used for the manufacture of Class I pressure-resistant piping systems, Class II pressure-resistant piping systems, boilers and superheaters. The working temperature of the carbon steel carbon steel pipe wall does not exceed 450 ℃, and the working temperature of the alloy steel carbon steel pipe wall exceeds 450 ℃.
11. The carbon steel pipe for automobile axle casing (GB3088-82) is a high-quality carbon structural steel and alloy structural steel hot-rolled carbon steel pipe used in the manufacture of automobile axle casing and drive axle axle casing.
12. Diesel high-pressure oil pipe (GB3093-86) is a cold-drawn carbon steel pipe for manufacturing high-pressure pipes for diesel injection systems.
13. Precision inner diameter carbon steel pipes for hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders (GB8713-88) are cold drawn or cold rolled precision carbon steel pipes with precise inner diameters for the manufacture of hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders.
14. Cold-drawn or cold-rolled precision carbon steel pipes (GB3639-83) are cold-drawn or cold-rolled precision carbon steel pipes with high dimensional accuracy and good surface finish for mechanical structures and hydraulic equipment. Use precision carbon steel pipes to manufacture mechanical structures or hydraulic equipment.
15. Structural stainless steel carbon steel pipes (GB/T14975-2002) are hot-rolled ( Extrusion, expansion) and cold drawn (rolled) carbon steel pipes.
16. Stainless steel carbon steel pipes for fluid transportation (GB/T14976-2002) are hot-rolled (extruded, expanded) and cold-drawn (rolled) carbon steel pipes made of stainless steel for fluid transportation.
17. Special-shaped carbon steel pipe is a general term for carbon steel pipes with other cross-sectional shapes other than round pipes. According to the shape and size of the steel pipe section, it can be divided into equal-wall thickness special-shaped carbon steel pipe (code D), unequal wall thickness special-shaped carbon steel pipe (code BD), variable diameter special-shaped carbon steel pipe (code BJ). Shaped carbon steel pipes are widely used in various structural parts, tools and mechanical parts.
18. Seamless steel pipes for low temperature pipelines (GB/T18984-2003) are seamless steel pipes used for low temperature pressure vessel pipelines and low temperature heat exchanger pipelines at the level of -45℃~-195℃.
Generally, carbon steel pipes are made of 10, 20, 30, 35, 45 and other high-quality carbon steel 16Mn, 5MnV and other low-alloy structural steel or 40Cr, 30CrMnSi, 45Mn2, 40MnB and other combined steel hot-rolled or cold-rolled. carbon steel pipes made of low carbon steel such as 10 and 20 are mainly used for fluid transportation pipelines. 45, 40Cr and other medium carbon steel carbon steel pipes are used to manufacture mechanical parts, such as the stressed parts of automobiles and tractors.
Generally, carbon steel pipes are used to ensure strength and flattening tests. Hot-rolled steel pipes are delivered in a hot-rolled state or heat-treated state; cold-rolled steel pipes are delivered in a heat-treated state. carbon steel pipes for low and medium pressure boilers: used to manufacture various low and medium pressure boilers, superheated steam pipes, boiling water pipes, water wall pipes and superheated steam pipes, large smoke pipes, small smoke pipes and arch brick pipes for locomotive boilers.
Hot-rolled or cold-rolled seamless tubes with high-quality carbon structural steel. Mainly made of No. 10 and No. 20 steel, in addition to ensuring chemical composition and mechanical properties, water pressure test, hemming, flaring, flattening and other tests are required. Hot-rolled delivery is in hot-rolled state, and cold-rolled is delivered in heat-treated state.
With years of expertise, we provide a diverse array of steel tube processing options. From sawing and machining tube blanks to intricate bending and upsetting operations, we actively assist you throughout your projects.
Our capabilities extend to eccentricity reduction and concentricity enhancement through turning and grinding. We excel in creating complex geometries using processes like rotary swaging and axial forming. Additionally, we offer property modifications via partial heat treatment, ensuring tailored solutions for your specific needs.












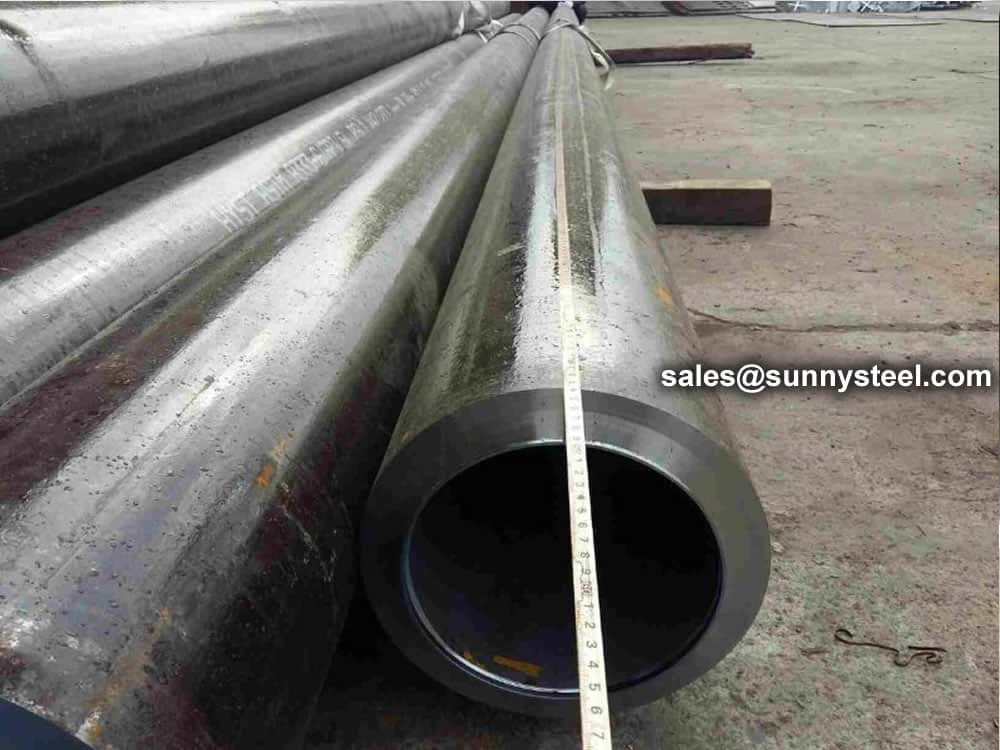
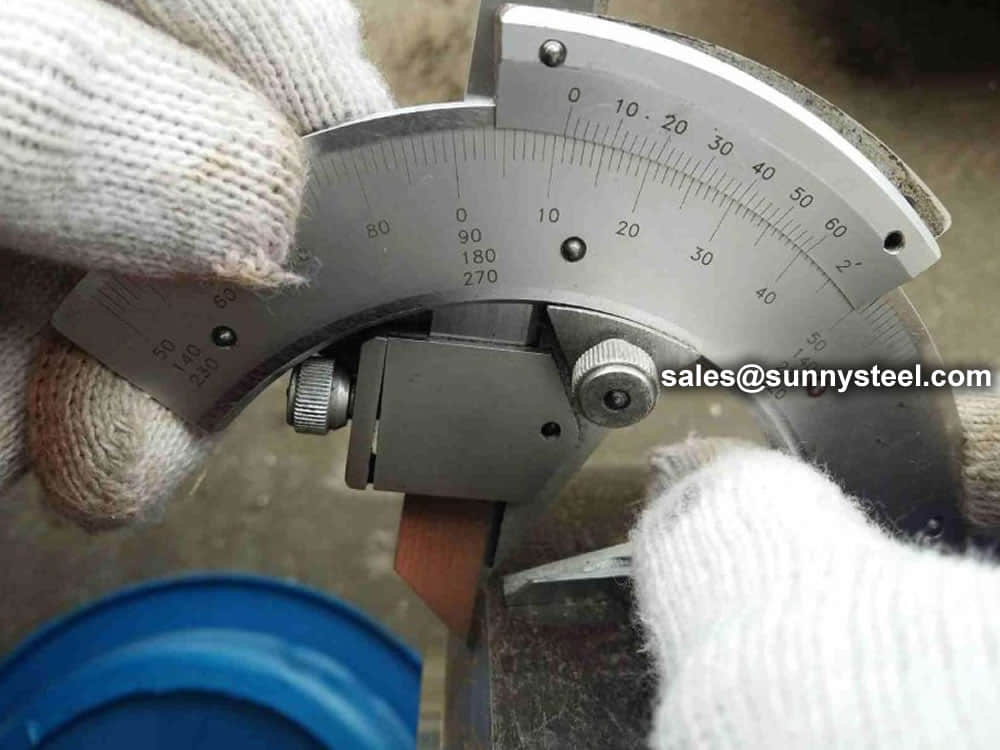
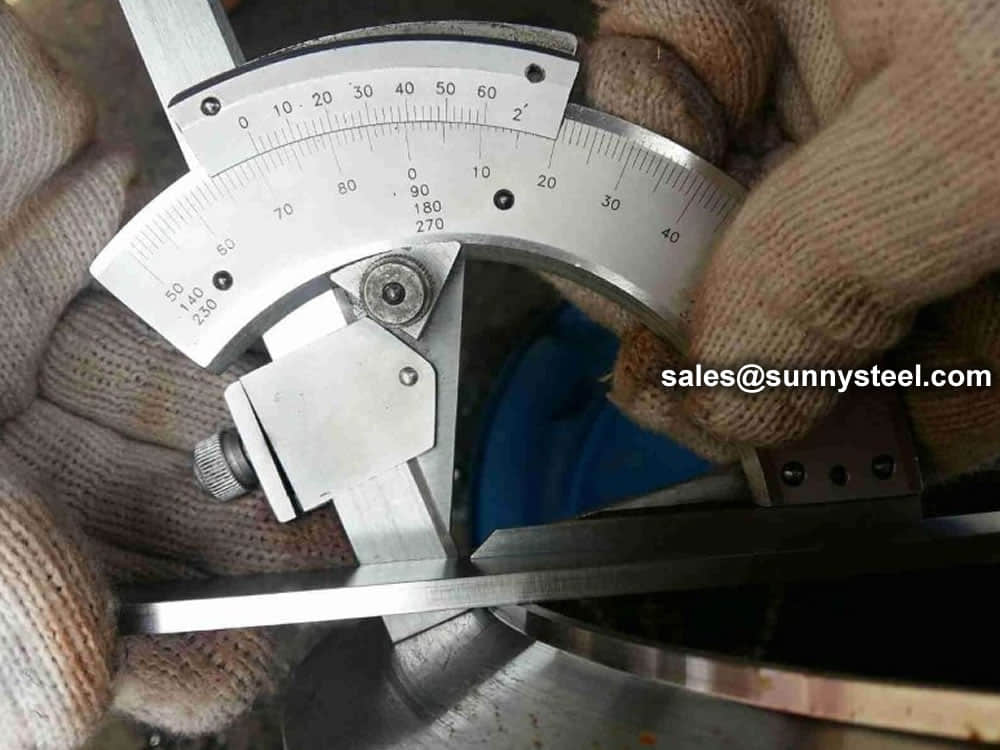
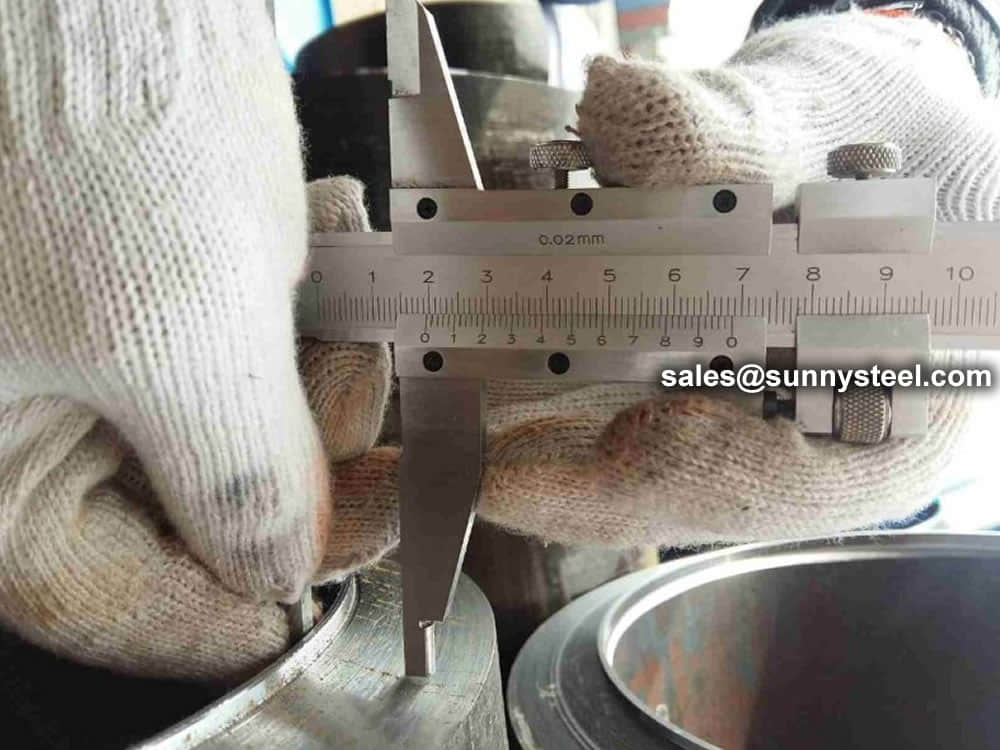
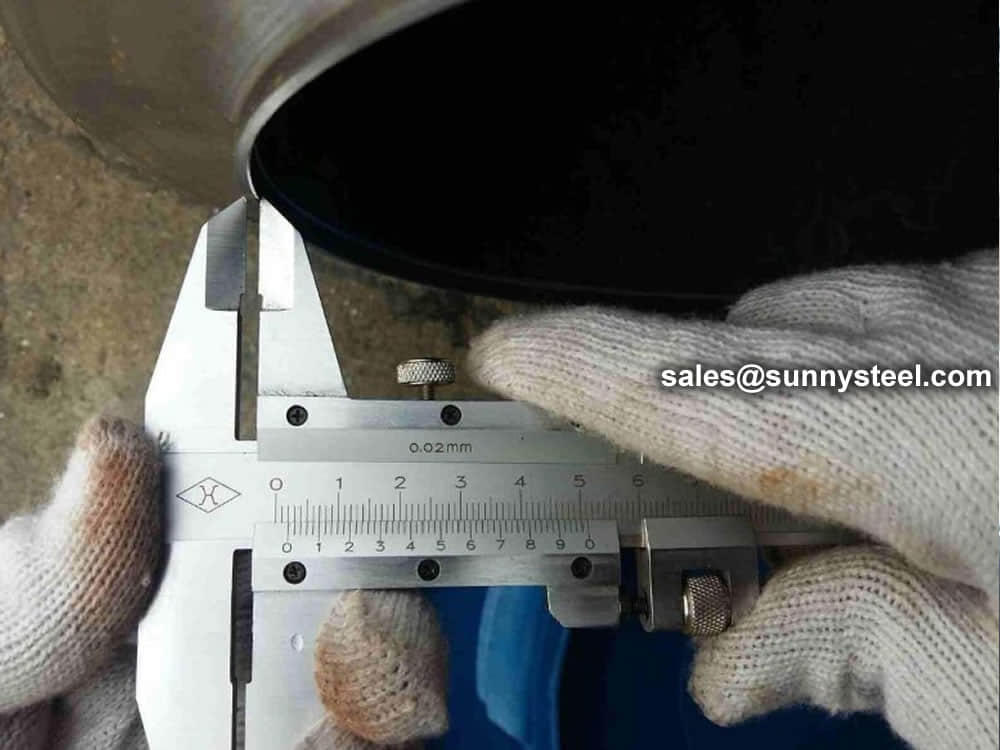
Chemical composition inspection, mechanical properties test(tensile strength,yield strength, elongation, flaring, flattening, bending, hardness, impact test), surface and dimension test,no-destructive test, hydrostatic test.
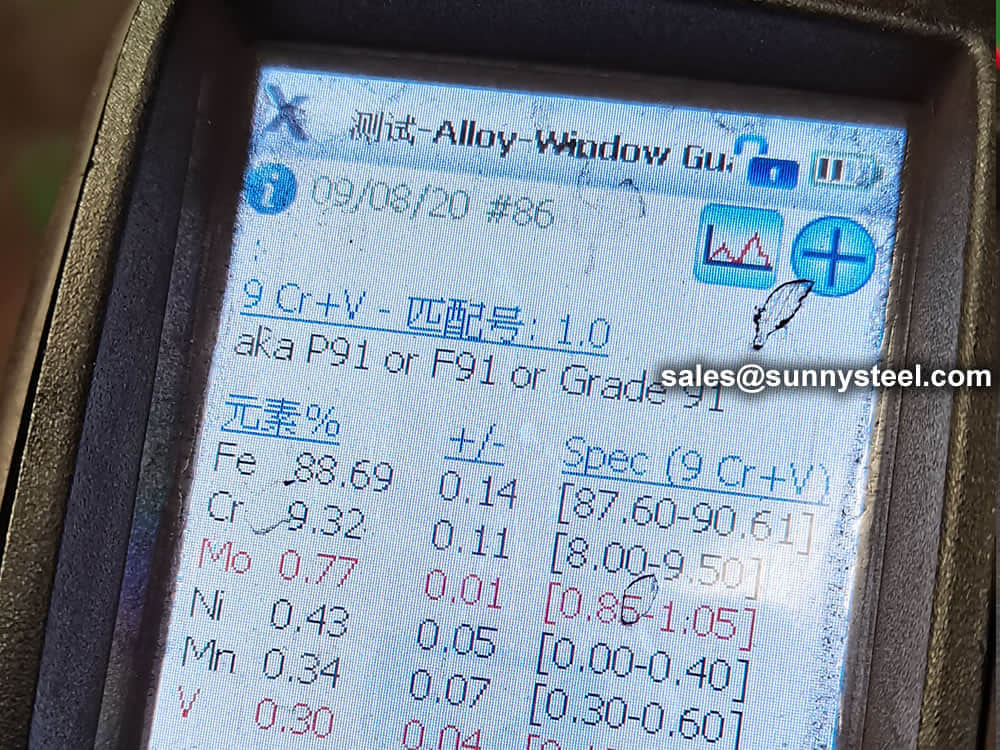
identification of the chemical composition of the metal used to manufacture the fitting. Uses PMI sensors, including X-ray fluorescence or optical emission spectrometry.
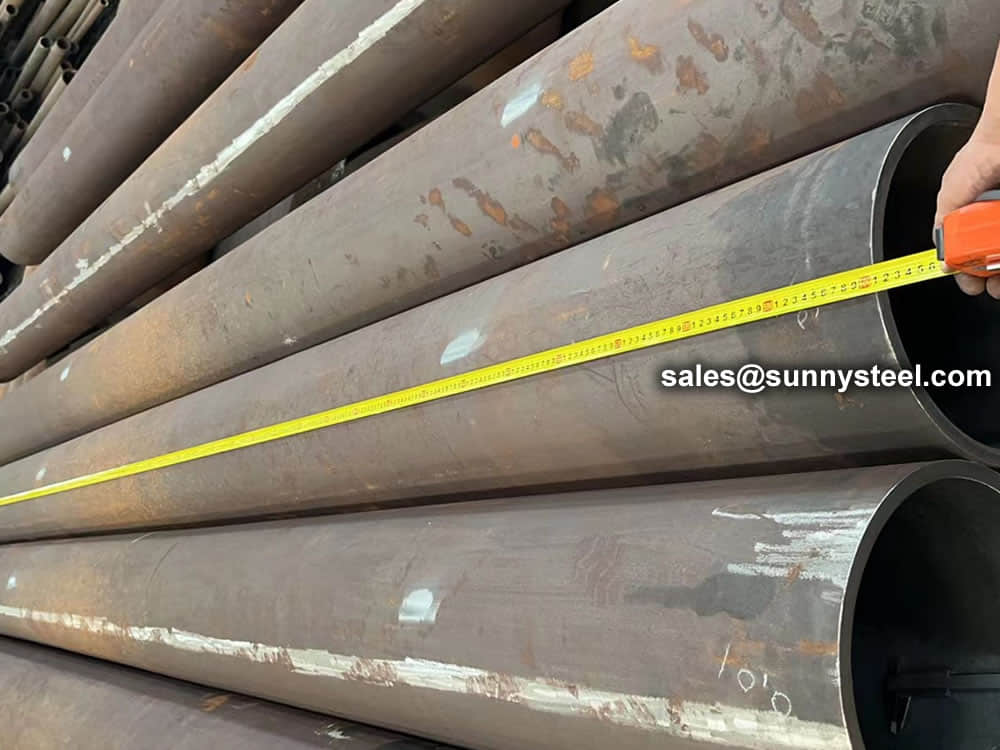
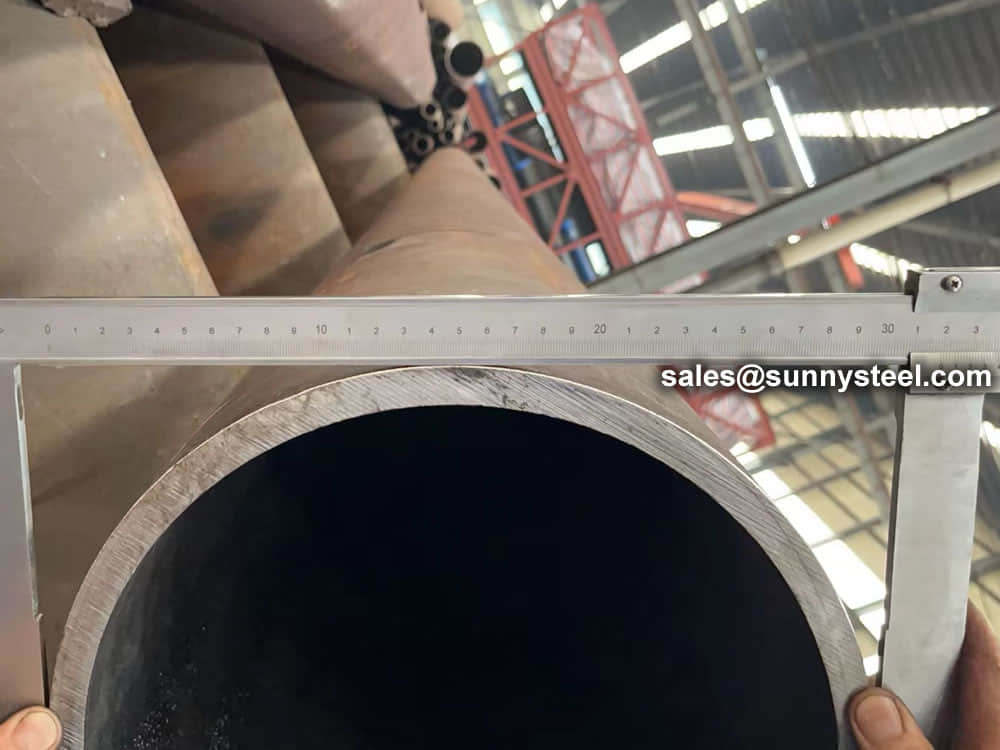
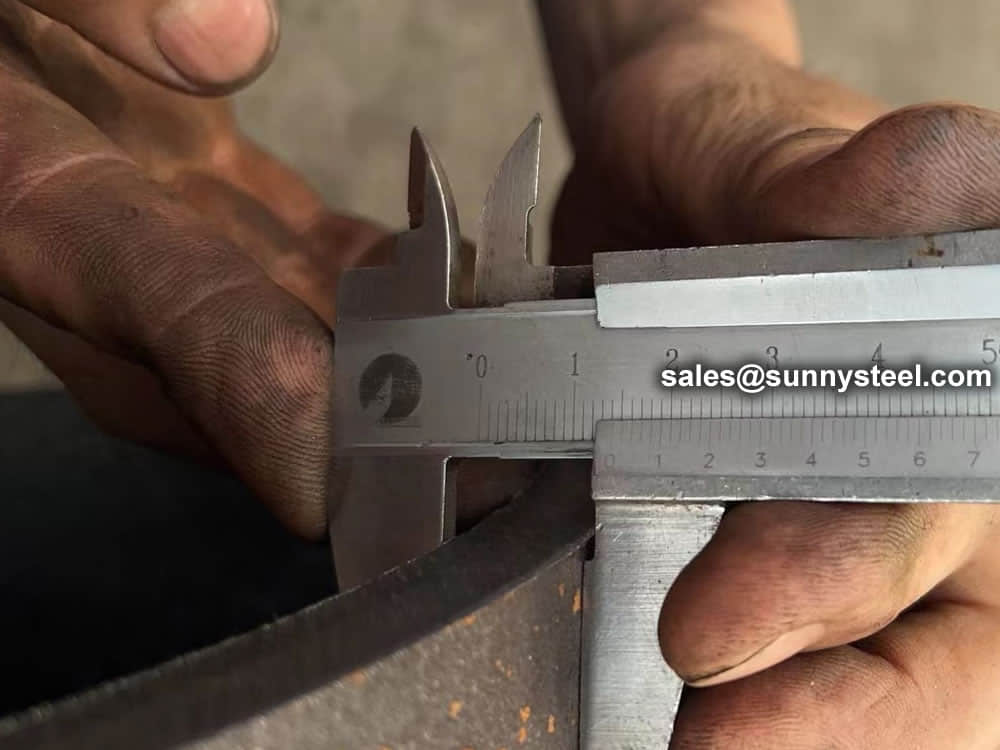
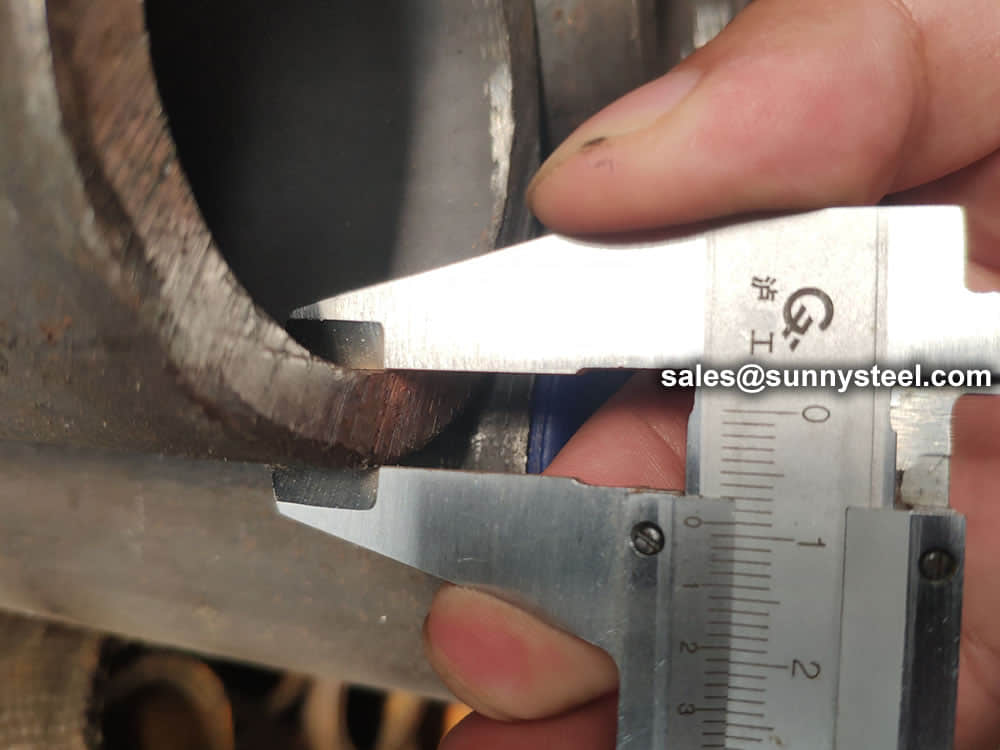
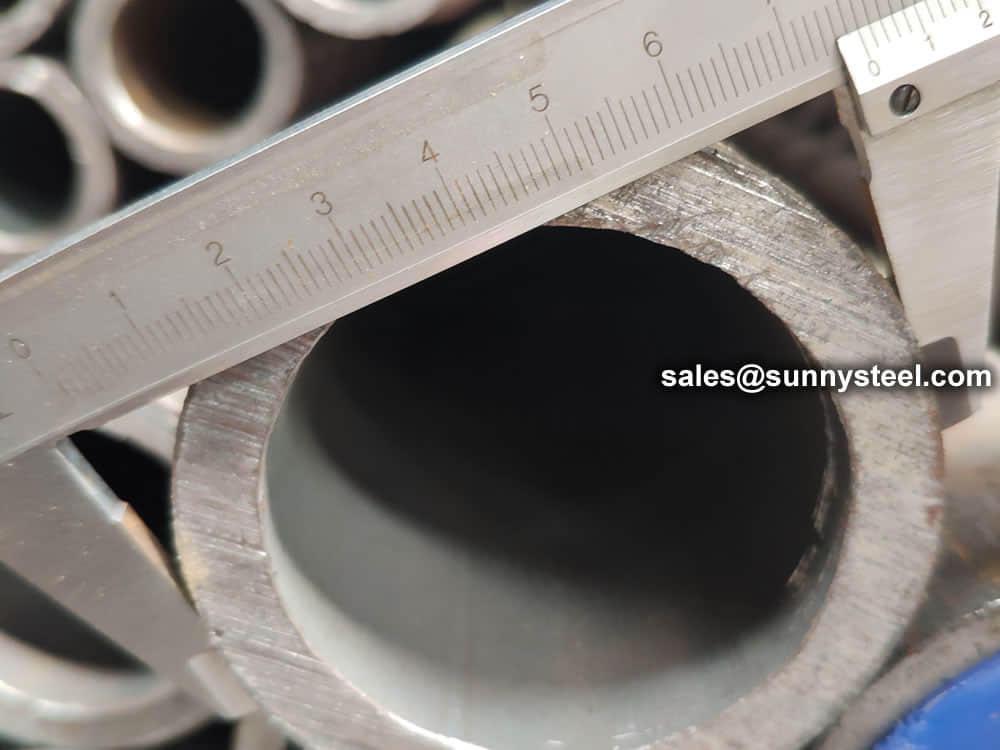
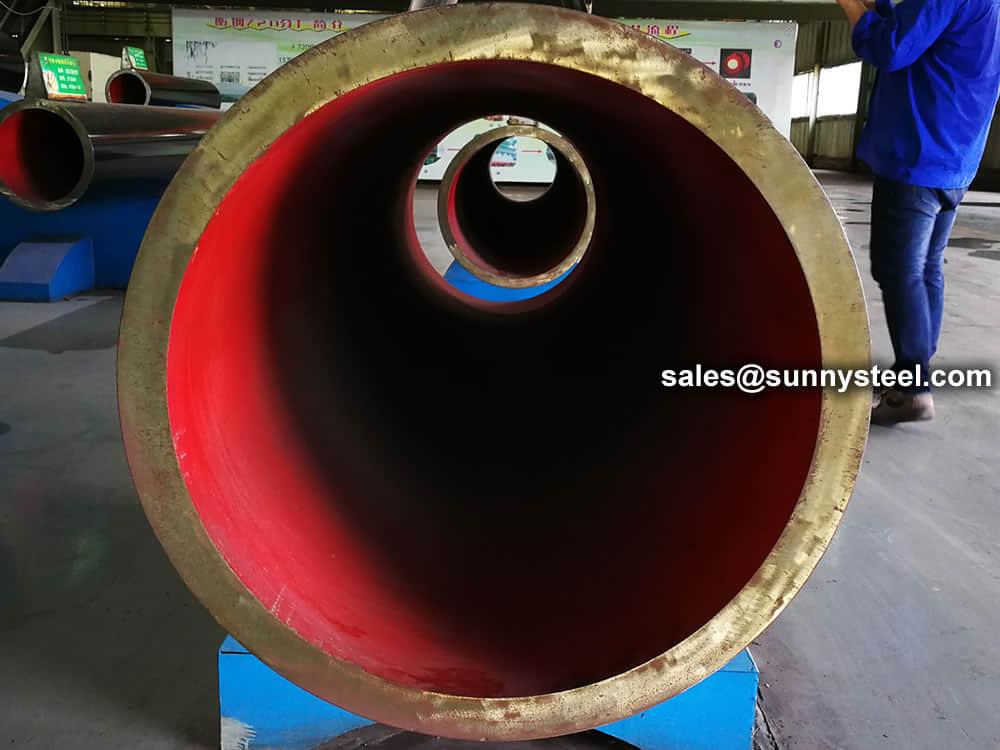
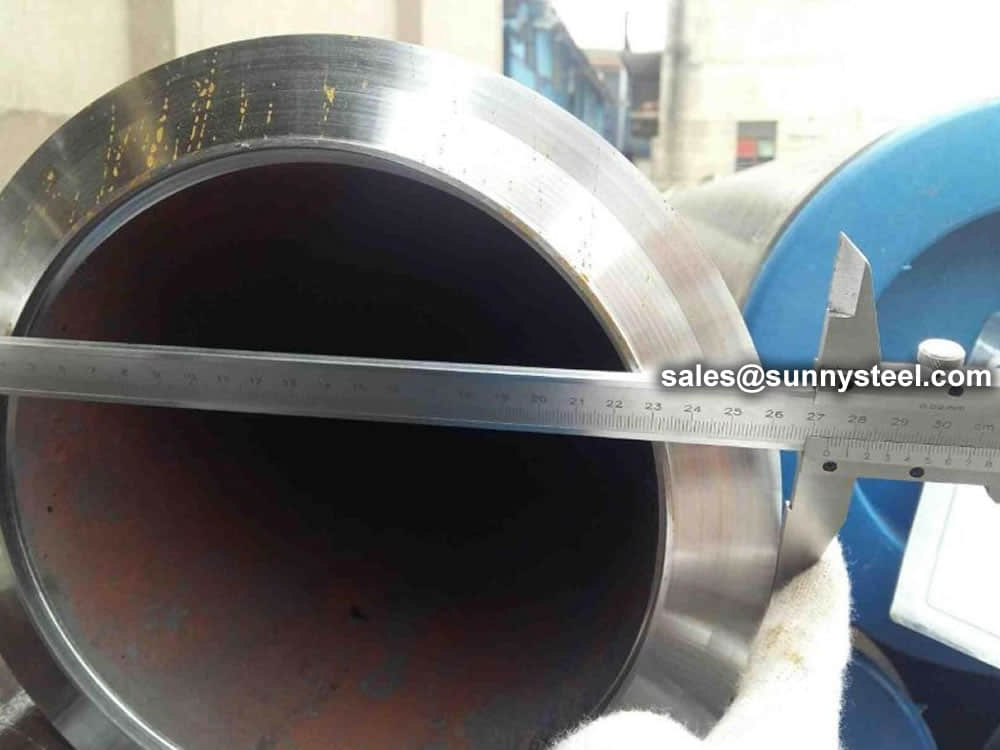
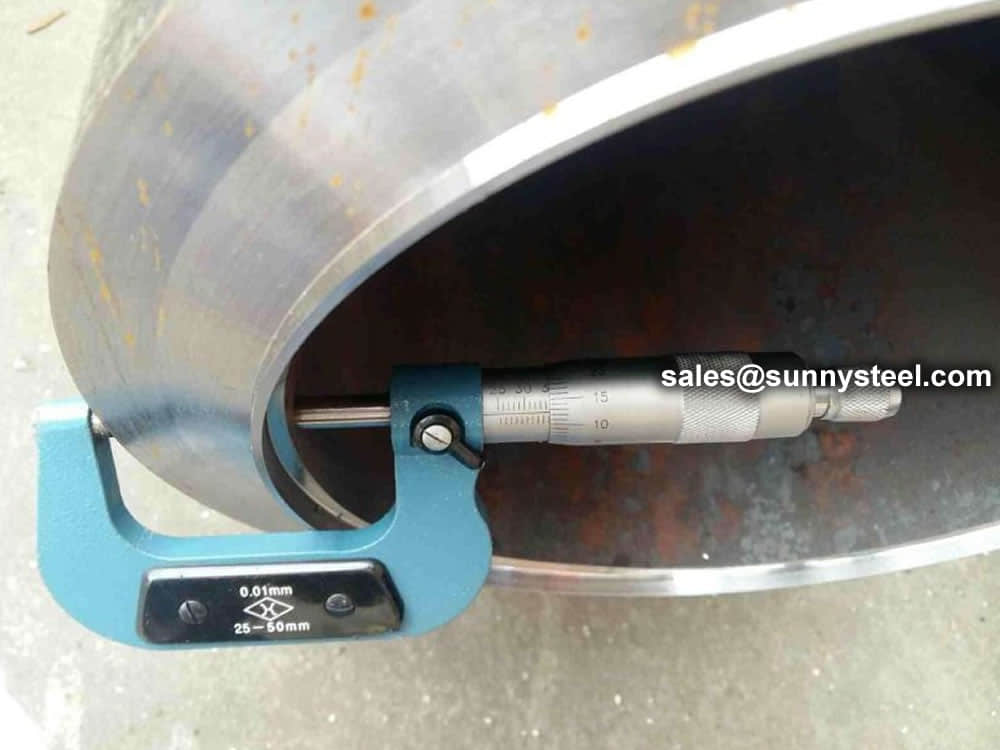
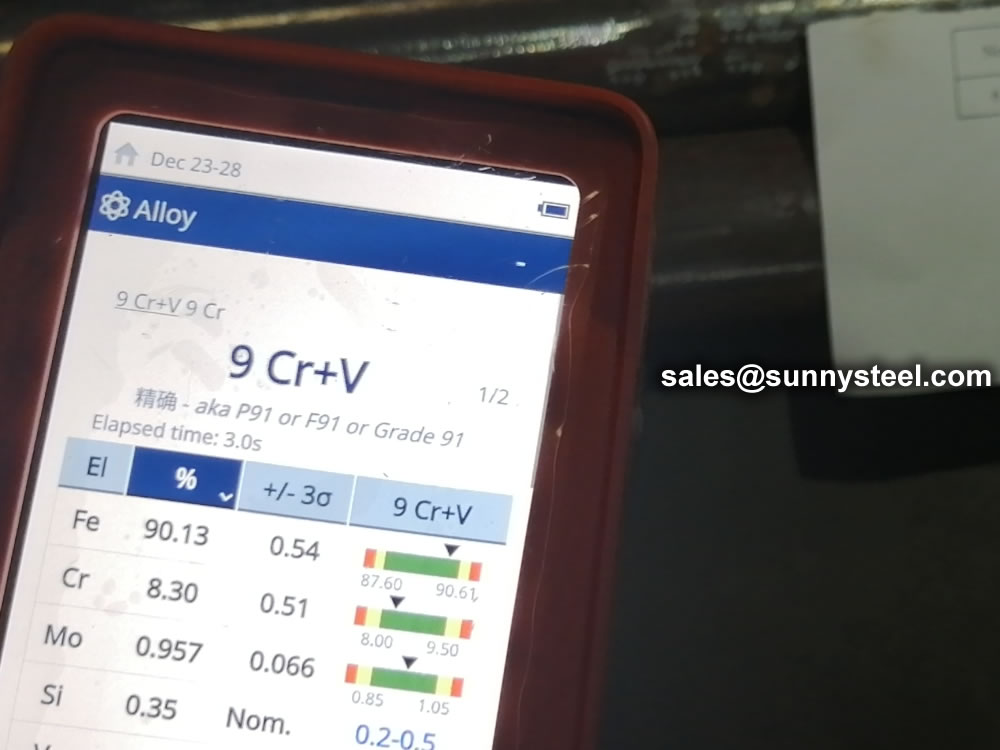
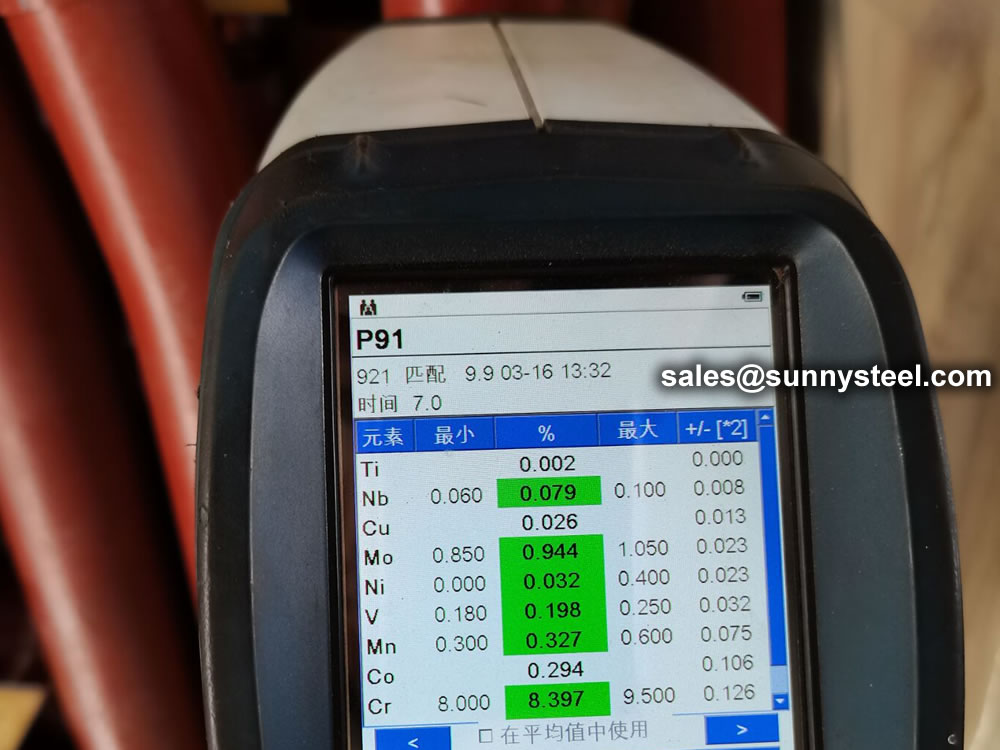
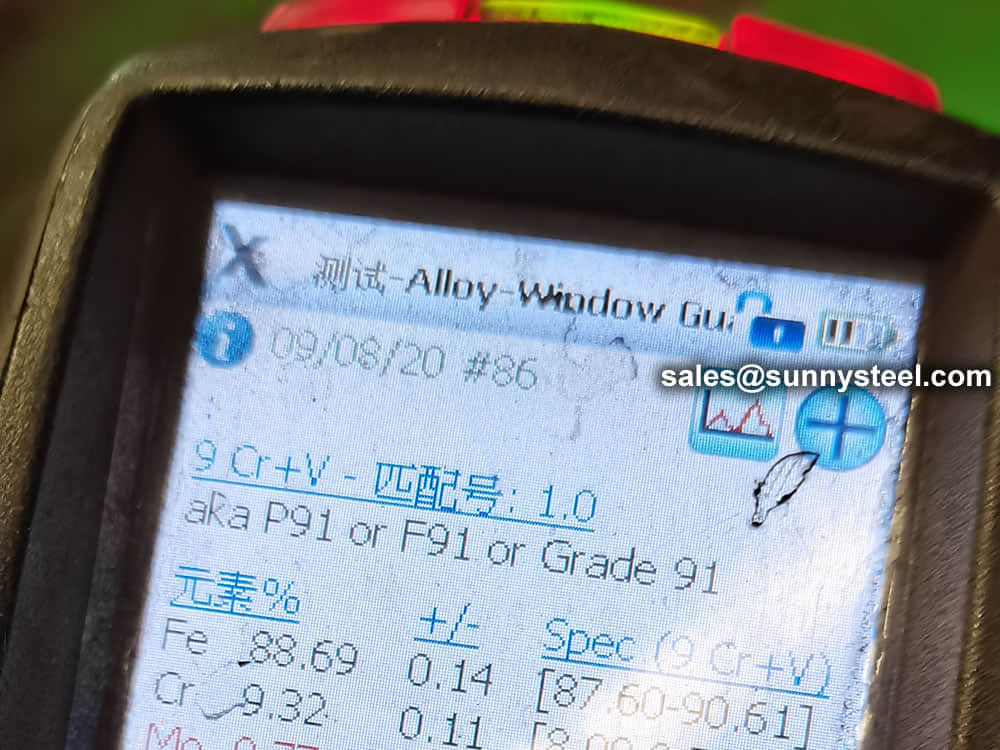
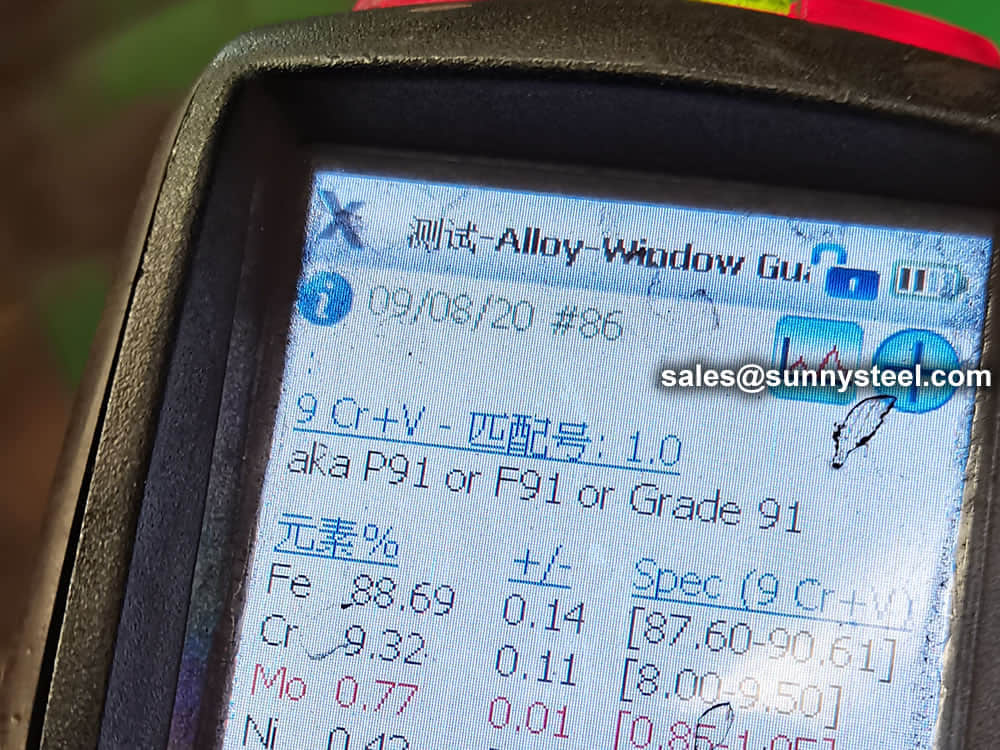















Steel pipe delivery status(condition): cold / hard (BK), cold / soft (BKW), after cold stress relief annealing (BKS), annealing (GBK), normalized (NBK).
| Term | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-finished/hard (cold-finished as-drawn) | BK | No heat treatment after the last cold-forming process. The tubes therefore have only low deformability. |
| Cold-finished/soft (lightly cold-worked) | BKW | After the last heat treatment there is a light finishing pass (cold drawing) With proper subsequent processing, the tube can be cold-formed (e.g. bent, expanded) within certain limits. |
| Annealed | GBK | After the final cold-forming process the tubes are annealed in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
| Normalized | NBK | The tubes are annealed above the upper transformation point in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
The general cold strip mills, volume should go through continuous annealing (CAPL unit) to eliminate cold hardening and rolling stress, or batch annealing reach the mechanical properties of the corresponding standard specifies. Cold rolled steel surface quality, appearance, dimensional accuracy better than hot-rolled plate, and right-rolled thin product thickness is about 0.18mm, so the majority of users favor.
Cold rolled steel coil substrate products deep processing of high value-added products. Such as electro-galvanized, hot dip galvanized, electro-galvanized fingerprint resistant, painted steel roll damping composite steel, PVC laminating steel plates, etc., so that the excellent quality of these products has a beautiful, high resistance to corrosion, has been widely used.
Cold rolled steel coil finishing after annealing, cut the head, tail, trimming, flattening, smooth, heavy volume, or longitudinal clipboard. Cold-rolled products are widely used in automobile manufacturing, household electrical appliances, instruments, switches, buildings, office furniture and other industries. Steel plate strapping package weight of 3 to 5 tons. Flat sub-volume typically 3 to 10 tons / volume. Coil diameter 6m.
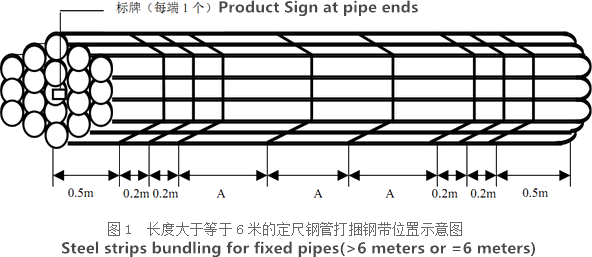
Bare packing/bundle packing/crate packing/wooden protection at the both sides of tubes and suitably protected for sea-worthly delivery or as requested.
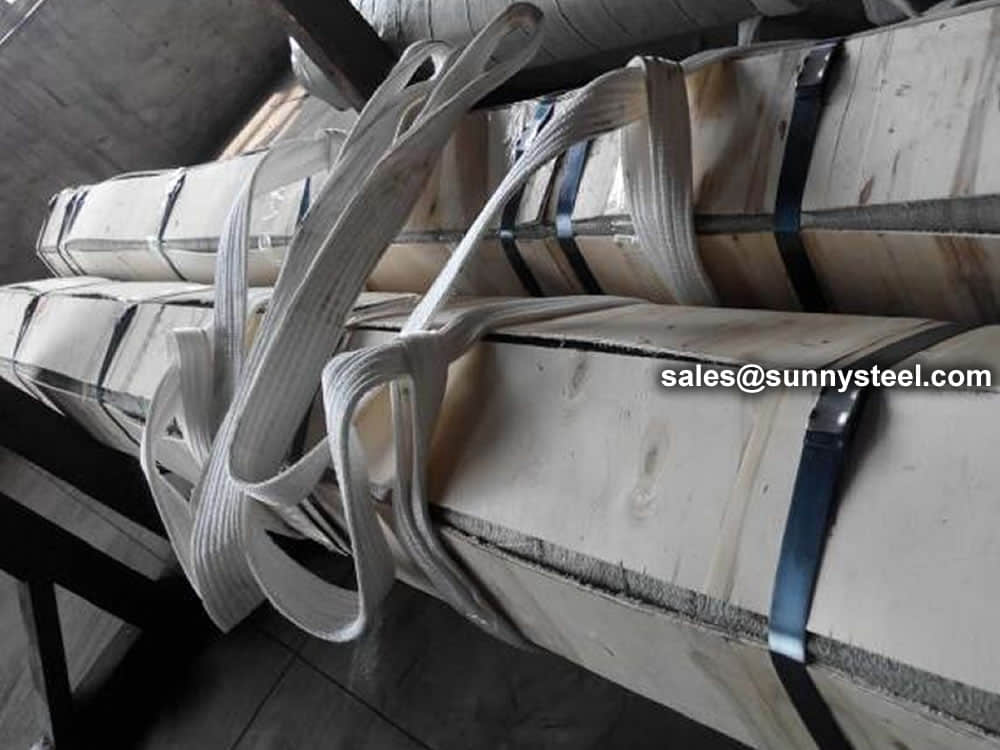
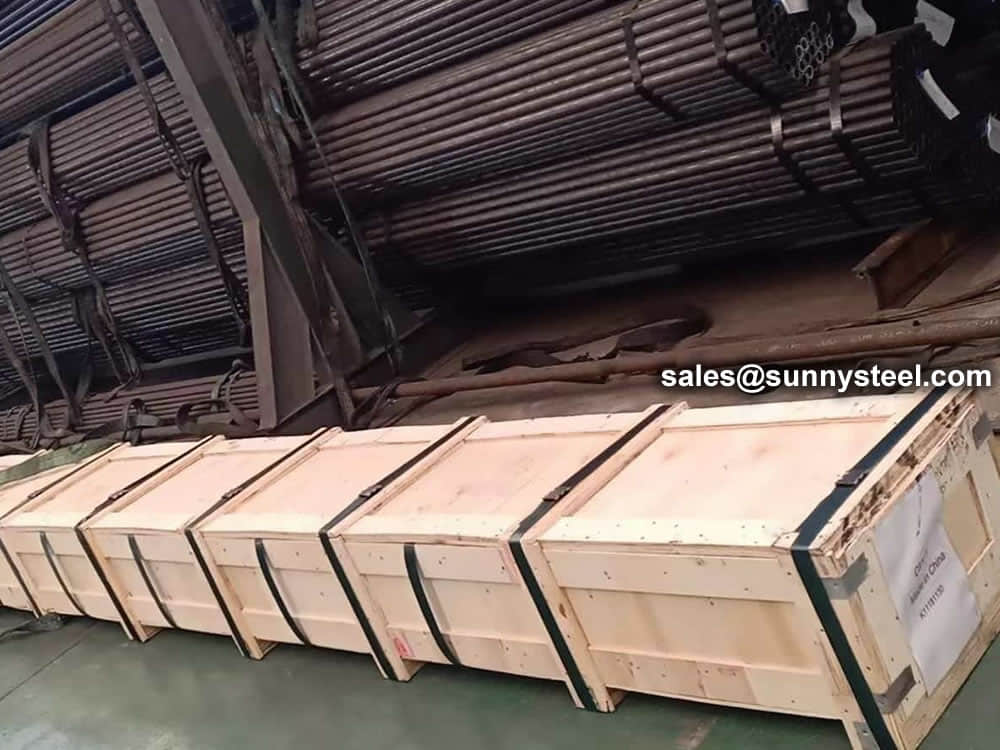
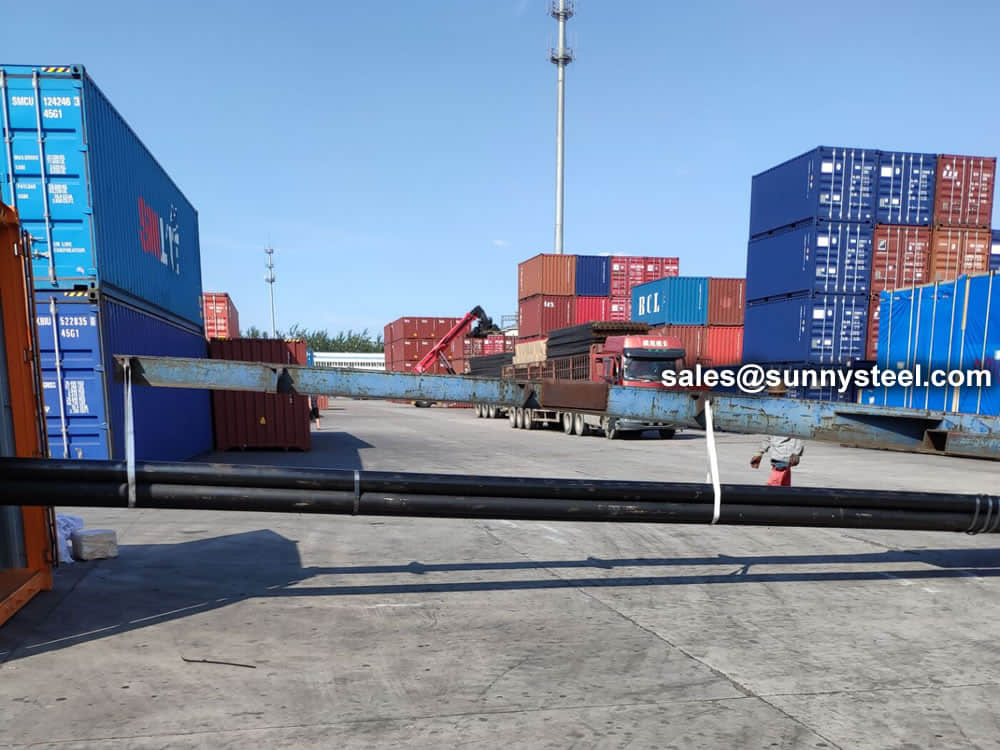
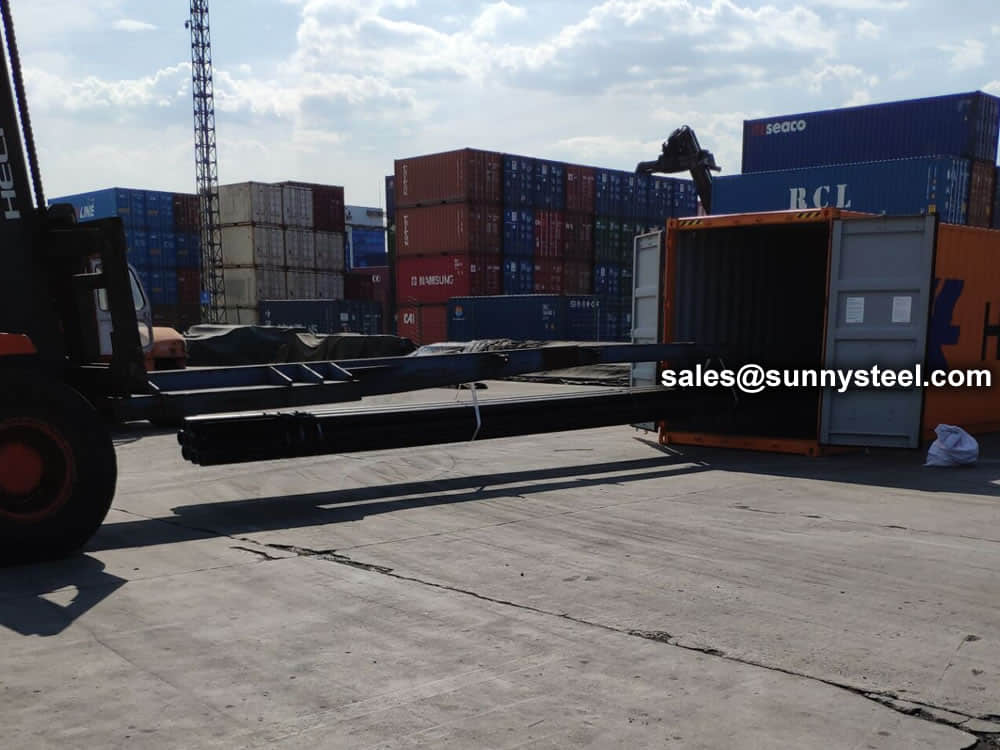
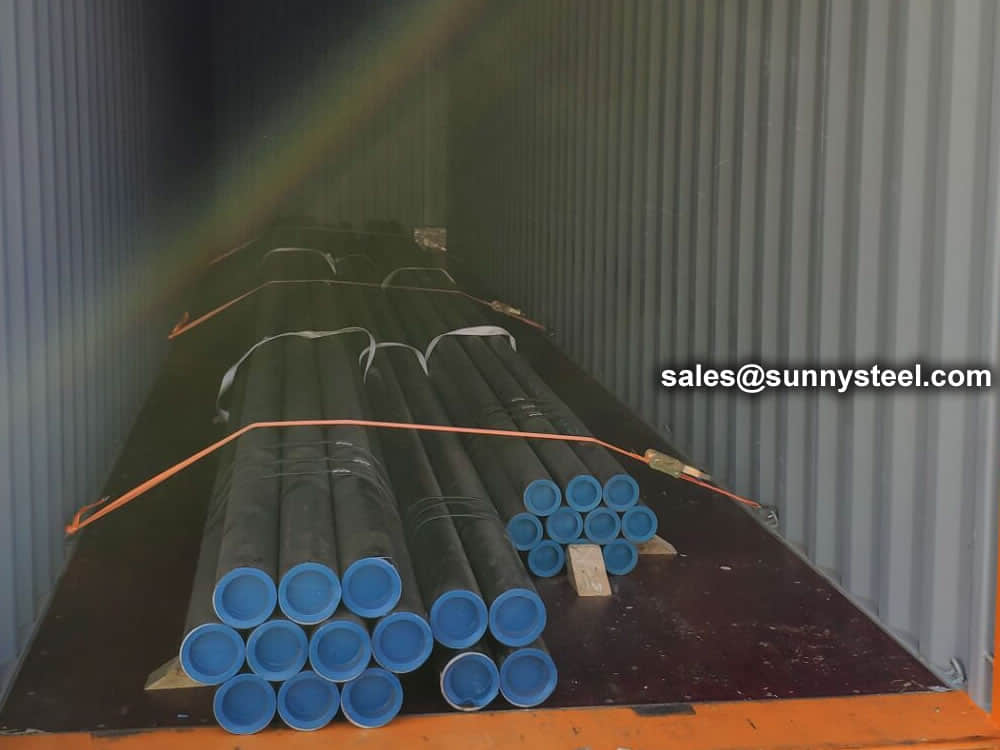
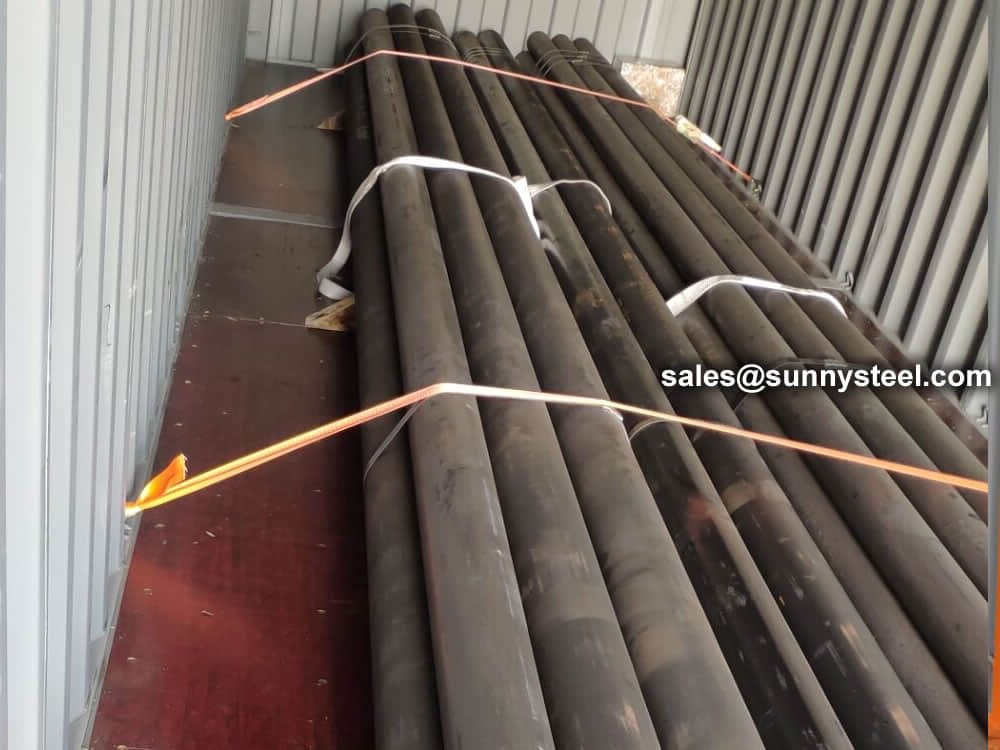












There are probably hundreds of different methods for packing a pipe, and most of them have merit, but there are two principles that are vital for any method to work prevent rusting and Sea transportation security.
Our packing can meet any needs of the customers.
Commonly used alloying elements and their effects are listed in the table given below.
| Alloying Elements | Effect on the Properties |
|---|---|
| Chromium | Increases Resistance to corrosion and oxidation. Increases hardenability and wear resistance. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Nickel | Increases hardenability. Improves toughness. Increases impact strength at low temperatures. |
| Molybdenum | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Enhances the effects of other alloying elements. Eliminate temper brittleness in steels. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Manganese | Increases hardenability. Combines with sulfur to reduce its adverse effects. |
| Vanadium | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Improves fatigue resistance. |
| Titanium | Strongest carbide former. Added to stainless steel to prevent precipitation of chromium carbide. |
| Silicon | Removes oxygen in steel making. Improves toughness. Increases hardness ability |
| Boron | Increases hardenability. Produces fine grain size. |
| Aluminum | Forms nitride in nitriding steels. Produces fine grain size in casting. Removes oxygen in steel melting. |
| Cobalt | Increases heat and wear resistance. |
| Tungsten | Increases hardness at elevated temperatures. Refines grain size. |

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
