1Cr6Si2Mo Erosion Shield Straight
1Cr6Si2Mo straight erosion shield protector offers exceptional wear and erosion resistance in high-temperature industrial applications.

1Cr6Si2Mo steel plate is a high-quality material widely used in heat-resistant applications. Its excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties make it an ideal choice for industrial components exposed to high temperatures, such as boiler and pressure vessels.



1Cr6Si2Mo is a martensitic heat-resistant steel known for its excellent oxidation resistance at temperatures up to 800°C. Compared to 1Cr5Mo, its higher silicon content (1.5%) increases the risk of temper brittleness during prolonged high-temperature exposure, requiring careful thermal management.
1Cr6Si2Mo is martensitic heat-resistant steel, has better oxidation resistance at 800 ℃. compared with 1CR5Mo steel, containing more than 1.5% Si, so that the tendency of tempering brittle steel increases, parts at high temperatures for a long time will have brittle fracture. 1Cr6Si2Mo Ultrahigh strength steel has excellent corrosion resistance in sulfur-containing oxidizing atmospheres and in hot petroleum media.
After normalizing, tempering heat treatment after a high strength and creep strength. The steel quenching phenomenon, hot processing, such as cooling too fast, cracks will occur, should slow cooling. Weldability is poor, can be used welding, not gas welding, preheated to be preheated to 300 ℃ ~ 400 ℃, 750 ℃ tempering after welding treatment.
The material demonstrates superior corrosion resistance in sulfurous oxidizing atmospheres and hot petroleum mediums. After normalizing and tempering, it achieves high creep strength and tensile strength. Due to air-quenching behavior, slow cooling is essential to prevent cracking after hot processing.
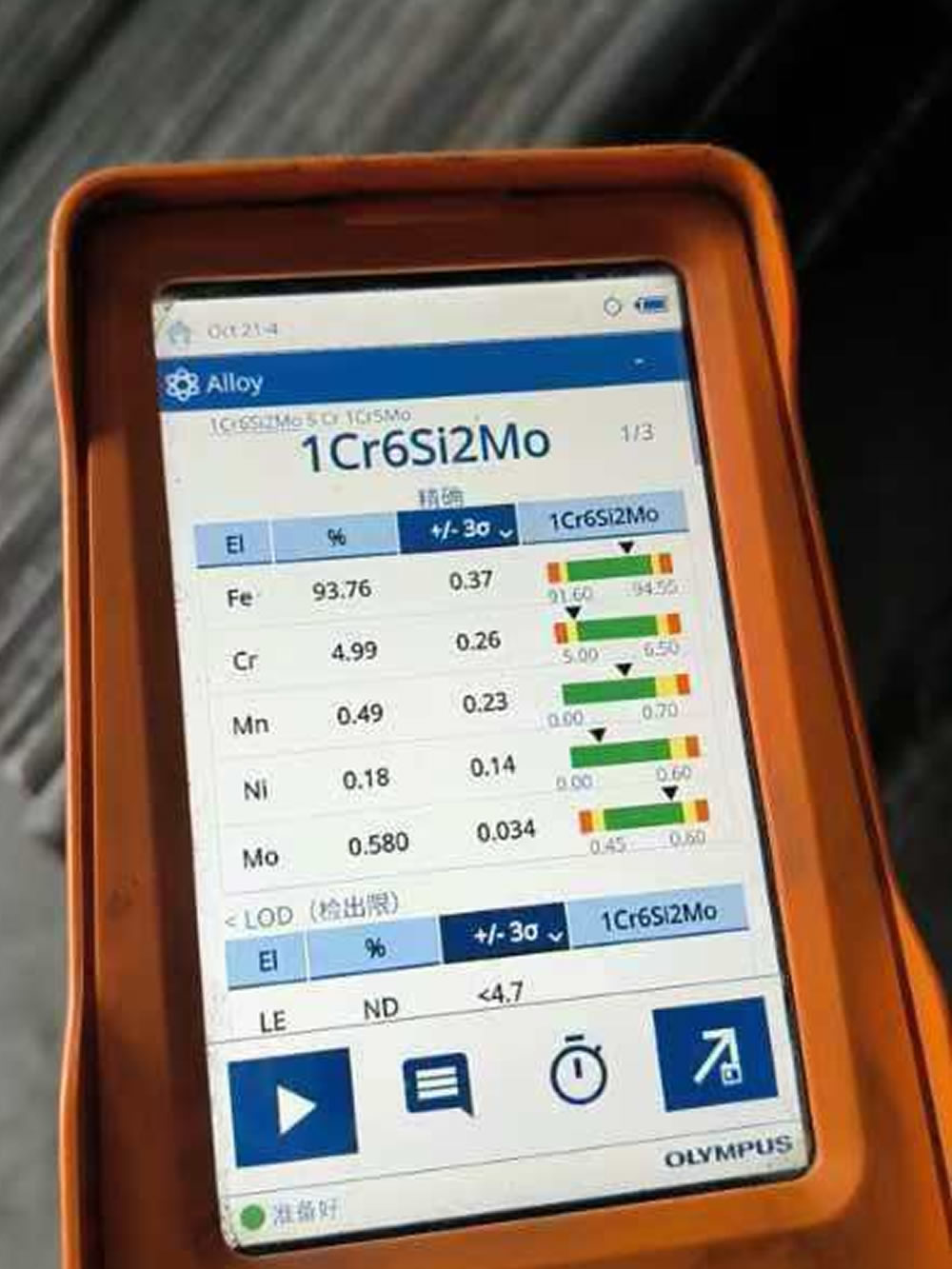
| Element | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.15 |
| Silicon (Si) | 1.5 - 2.0 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 0.7 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.035 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.030 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 5.2 - 6.0 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.45 - 0.6 |
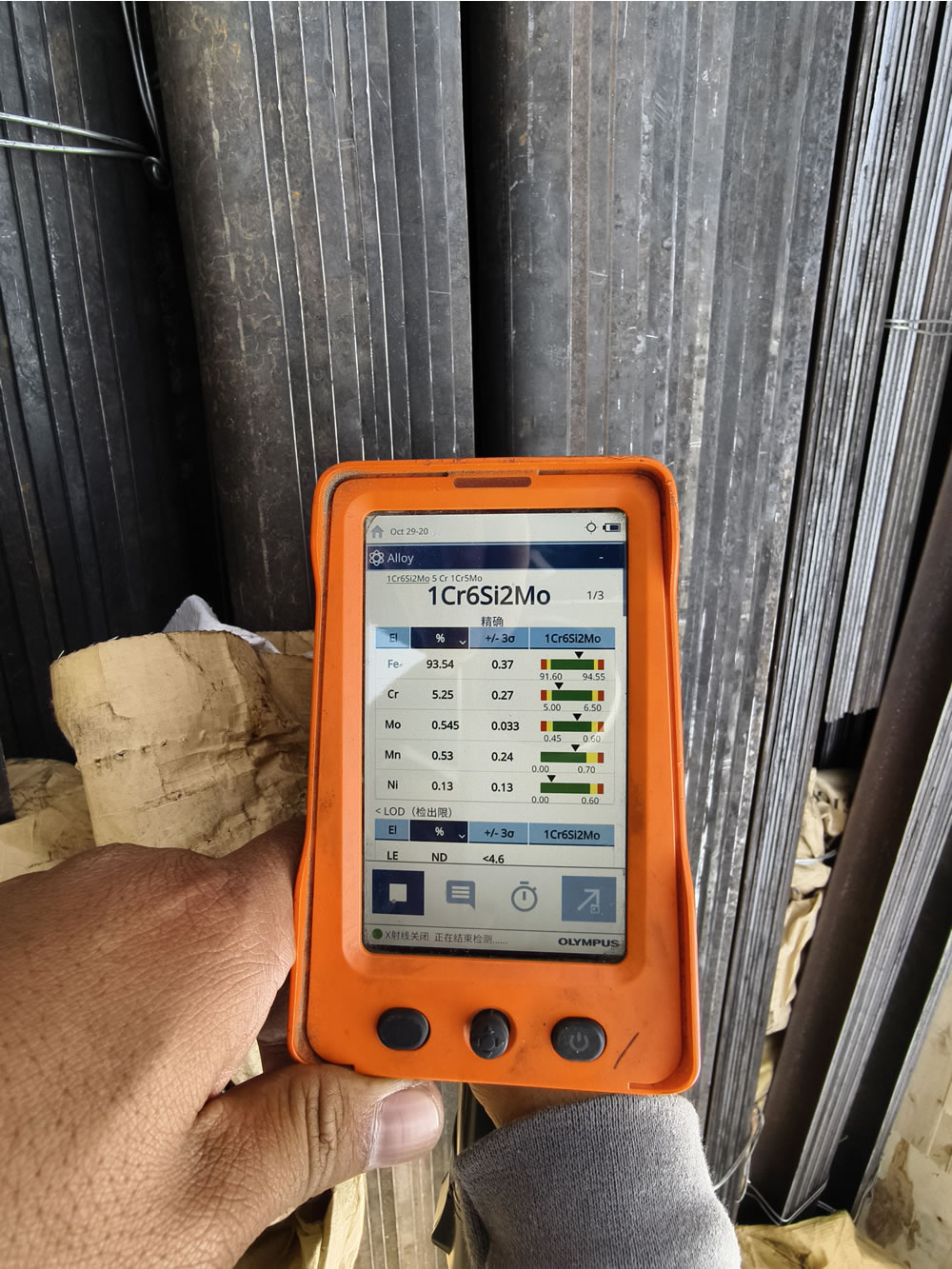


| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 547 MPa |
| Yield Strength | ≥ 401 MPa |
| Elongation | ≥ 31.5% |
1Cr6Si2Mo is a martensitic heat-resistant steel with good oxidation resistance at 800°C. Compared with 1Cr5Mo steel, since it contains 1.5% silicon (Si), the temper brittleness tendency of 1Cr6Si2Mo increases, and brittle fracture may occur when working at high temperatures for a long time. This material shows good corrosion resistance in sulfur-containing oxidizing atmospheres and hot petroleum media.
After normalizing and tempering heat treatment, 1Cr6Si2Mo has high creep strength and durability. In addition, 1Cr6Si2Mo has an air quenching phenomenon. If it cools too quickly after hot processing, cracks may occur, so slow cooling is required.
Its weldability is poor. Electric welding is recommended instead of gas welding. It needs to be preheated to 300°C - 400°C before welding and tempered at 750°C after welding.
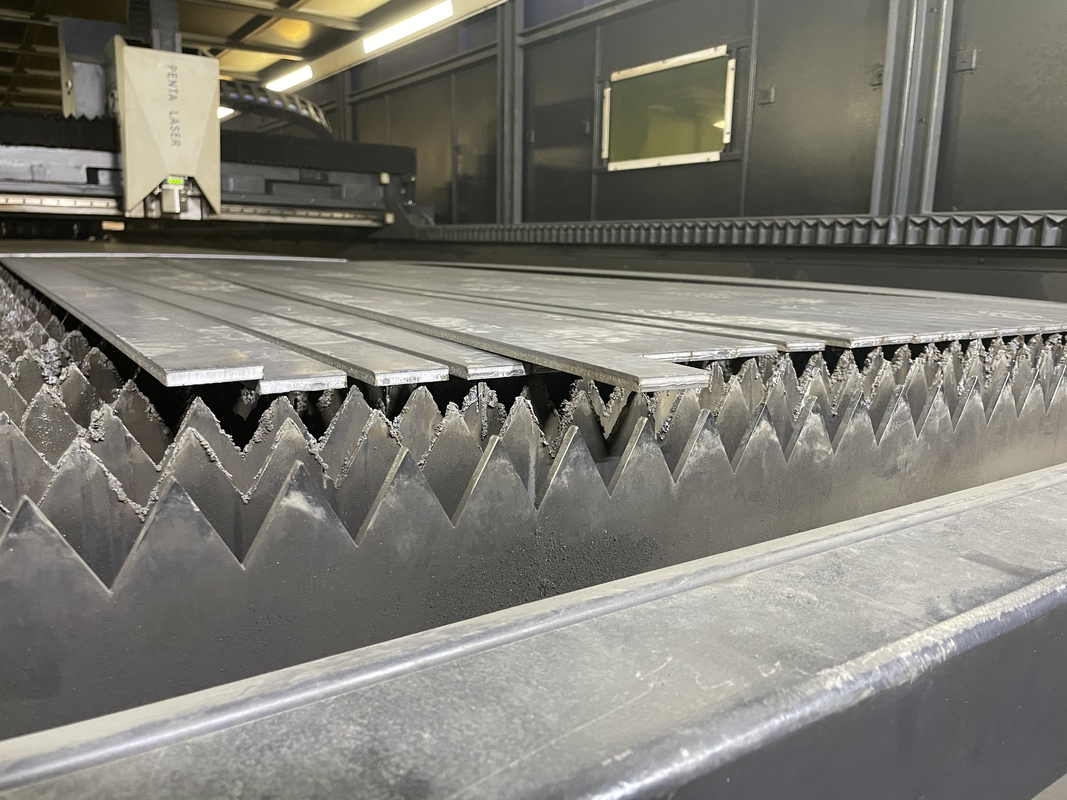

1Cr6Si2Mo is a heat-resistant alloy steel commonly used in high-temperature applications, such as boiler components. When cutting 1Cr6Si2Mo flat bars, it's essential to consider the material's properties to ensure precision and maintain its structural integrity.
The hot working process of 1Cr6Si2Mo steel plate is a key step in its manufacturing process. Hot working includes forging, rolling, and drawing, etc. These processes can reduce the hardness of the material at high temperatures, increase plasticity, and make it easier to form the required shape. During the hot working process, the initial forging temperature and final forging temperature need to be strictly controlled to avoid material performance degradation or crack generation due to improper temperature. Since 1Cr6Si2Mo has an air quenching phenomenon, slow cooling treatment should be carried out after hot working to prevent crack generation. The specific temperature range and cooling rate of hot working need to be determined according to the specific chemical composition and microstructure of the material.
The cold working process of 1Cr6Si2Mo steel plate includes cold rolling, cold drawing, and cold forging, etc. Cold working can increase the hardness and strength of the material, and at the same time obtain better surface quality and dimensional accuracy. For thin plates, operations such as bending and crimping can be performed at room temperature. If more complex forming is required, it can be preheated to 200°C to improve plasticity and thereby reduce the risk of cracks during processing. During the cold working process, it is necessary to select the appropriate processing speed and lubrication conditions to ensure processing efficiency and product quality.
1Cr6Si2Mo steel plate can be processed into various shaped parts through cutting processes, including turning, milling, and drilling. During the cutting process, it is necessary to select the appropriate cutting tools and cutting parameters to ensure processing efficiency and processing quality. Due to the high hardness of 1Cr6Si2Mo, it is recommended to use carbide or ceramic tools for processing and adopt appropriate coolant to extend tool life. Parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and cutting depth need to be optimized according to specific processing conditions and requirements.
The weldability of 1Cr6Si2Mo steel plate is poor, but it can be welded by electric welding and is not suitable for gas welding. It needs to be preheated to 300°C - 400°C before welding to reduce the risk of welding stress and cracks. After welding, tempering treatment at 750°C should be carried out to restore the material's performance and reduce residual stress. During the welding process, the appropriate welding materials and process parameters should be selected, such as the chemical composition and diameter of the electrode and welding wire, as well as the welding current, voltage, and welding speed, to ensure the quality of the welded joint meets the design requirements.
The heat treatment process of 1Cr6Si2Mo steel plate includes normalizing and tempering. These processes can significantly improve the creep strength and durability of the material. Normalizing is usually carried out at high temperatures to obtain a uniform microstructure, while tempering is carried out at a lower temperature to reduce brittleness and improve toughness. The specific temperature, time, and cooling rate of heat treatment need to be determined according to the specific application and performance requirements of the material. The correct heat treatment process is crucial to ensure the stability and reliability of 1Cr6Si2Mo steel plate in high-temperature environments.
Hot processing requires slow cooling to prevent cracks due to air quenching. Preheating (300°C-400°C) is recommended for welding, followed by post-weld tempering at 750°C to ensure stability and minimize residual stress.
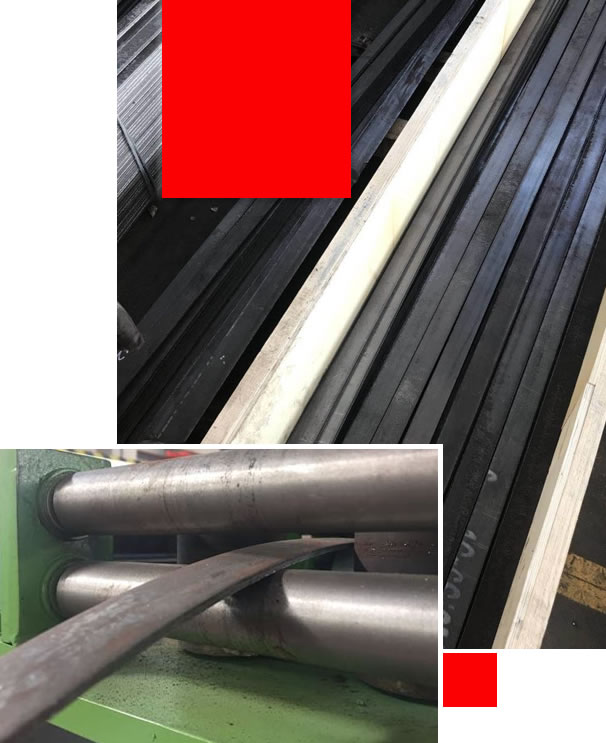

Alloy steel, 1Cr6Si2Mo, is a martensitic-type heat-resistant steel known for its excellent oxidation resistance and high strength.
1Cr6Si2Mo has superior oxidation resistance at temperatures up to 800°C. Compared to 1Cr5Mo steel, it contains over 1.5% silicon, which increases the tendency for tempering brittleness. As a result, components exposed to high temperatures for prolonged periods may experience brittle fractures.
This ultrahigh-strength steel exhibits remarkable corrosion resistance in sulfur-containing oxidizing atmospheres and hot petroleum media. After normalizing and tempering, it achieves high strength and creep resistance.
Special care is required during processing. Rapid cooling during hot working can cause cracks, so slow cooling is recommended. While its weldability is poor, welding is possible with proper precautions, including preheating to 300°C–400°C and tempering at 750°C post-welding for optimal results.
High temperature resistance structure parts of the boiler of thermoelectric power plant, supporting parts, structure parts of auxiliary boiler etc.

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
