2 Piece Ball Valve
Two-piece trunnion mounted ball valve with casting design for various industrial needs.
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways.
Performance. Quality. Long Life. Price Value. That’s why SunnySteel is at the Heart of Valves.
Download PDFA ball valve is a flow control device which uses a hollow, perforated and pivoting ball to control fluid flowing through it.
A ball valve is a shut-off valve that allows, obstructs, and controls the flow of liquids, gases, and vapors in a piping system by rotating the ball having a bore inside the valve. The ball is mounted against two seats and has a shaft that connects it to the operating and control mechanism that rotates the ball.
A butterfly valve is a valve that isolates or regulates the flow of a fluid.
The closing mechanism is a disk that rotates. Butterfly valves are a family of quarter-turn rotational motion valves that are used in pipelines to shut-off flow. It is often said that butterfly valves can be used to regulate the flow.
Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have two openings in the body, one for fluid to enter and the other for fluid to leave.
Check valves are generally installed in pipelines to prevent backflow. A check valve is basically a one-way valve, in which the flow can run freely one way, but if the flow turns, the valve will close to protect the piping, other valves, pumps etc.
A control valve is a valve used to control fluid flow by varying the size of the flow passage as directed by a signal from a controller.
Control valves are used in many processes to control flow, pressure, temperature or other variables. The type of valve used will depend on the size of the pipe, the overall pressure that the system operates, the flowing media, process conditions, and other factors.
Cryogenic valves are kept in a natural closed position to keep cryogenic gasses or other medium secure and safely contained.
In the oil and gas industry, cryogenic valves serve in the control of liquified gasses such as liquid nitrogen, methane, and helium. Because of the ease and safety of non-pressurized storage and transport, these elements cool to cryogenic temperatures, so they remain in the liquid state.
A gate valve, also known as a sluice valve, is a valve that opens by lifting a barrier (gate) out of the path of the fluid.
A gate valve is the most common valve for water supply systems. It represents a linear-motion isolation valve and has a function to stop or allow the flow. Gate valves got their name from the closure element sliding into the flow stream to provide shutoff and, therefore, acting like a gate.
A globe valve, different from ball valve, is a type of valve used for regulating flow in a pipeline, consisting of a movable plug or disc element and a stationary ring seat in a generally spherical body.
Unlike the gate valve, globe valve can be used for regulating flow or pressures as well as complete shutoff of flow. It may also be used sometime as a pressure relief valve or as a check valve. Compared with a gate valve or ball valve, the globe valve has considerably higher pressure loss in the fully open position.
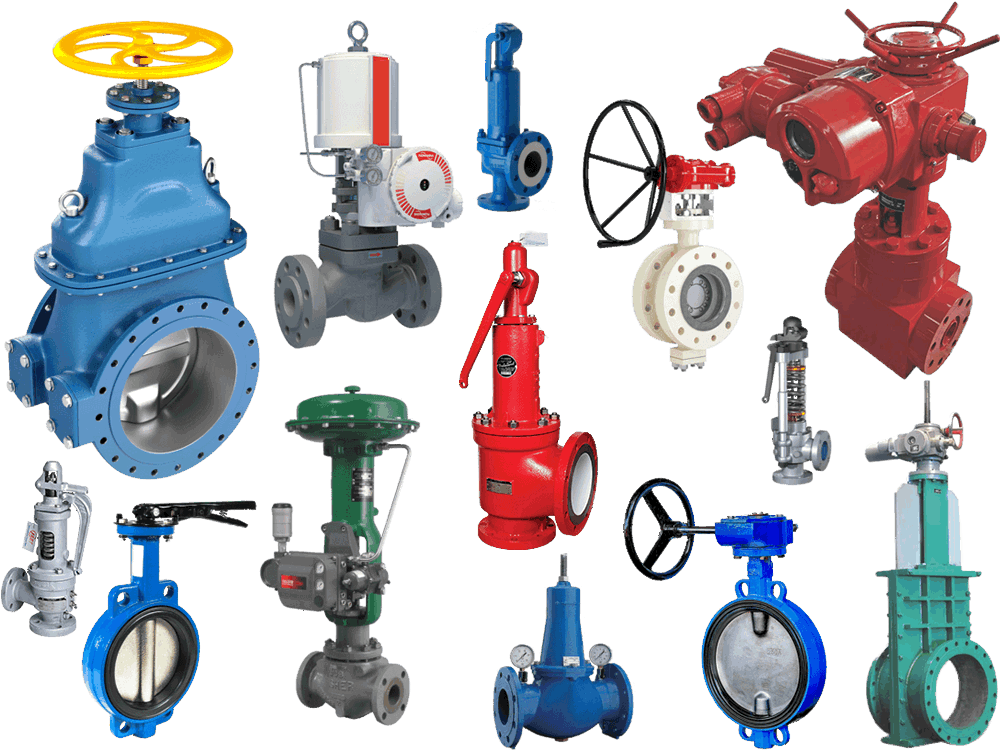
A valve is a device used to control the direction, pressure, and flow of a fluid in a fluid system. It is a device that makes or stops the flow of media (liquid, gas, powder) in piping and equipment and controls its flow.
The valve is a control component in the pipeline fluid conveying system, which is used to change the passage section and the flow direction of the medium, and has the functions of diversion, cut-off, throttling, check, diversion or overflow and pressure relief. Valves used for fluid control range from the simplest shut-off valve to various valves used in extremely complex automatic control systems. Valves for industrial pipelines. It can be used to control the flow of various types of fluids such as water, steam, oil, gas, mud, various corrosive media, liquid metals and radioactive fluids. The working pressure of the valve can be from 0.0013MPa to 1000MPa ultra-high pressure, and the working temperature can be c-270°C ultra-low temperature to 1430°C high temperature.
The control of the valve can adopt a variety of transmission methods, such as manual, electric, hydraulic, pneumatic, turbine, electromagnetic, electromagnetic hydraulic, electrohydraulic, pneumatic hydraulic, spur gear, bevel gear drive, etc.; can be driven by pressure, temperature Under the action of sensing signals in other forms, it acts according to predetermined requirements, or simply opens or closes without relying on sensing signals. The valve relies on drive or automatic mechanism to make the opening and closing parts lift, slide, swing or rotate. Movement, thereby changing the size of its channel area to achieve its control function.

This type of valve is used for opening and closing. It is permanently installed on the inlet and outlet of cold and heat sources, the inlet and outlet of equipment, and branch lines of pipelines (including standpipes). It can also be used as a water discharge valve and air release valve. Common shut-off valves include gate valves, globe valves, ball valves and butterfly valves.
Gate valves can be divided into bright rods and dark rods, single gates and double gates, wedge gates and parallel gates, etc. The closing tightness of the gate valve is not good, and it is difficult to open the large-diameter gate valve; the size of the valve body is small in the direction of water flow, the flow resistance is small, and the nominal diameter span of the gate valve is large.
Globe valves are divided into three types: straight-through type, right-angle type and straight-through type according to the flow direction of the medium, and there are bright rods and dark rods. The closing tightness of the globe valve is better than that of the gate valve, the valve body is long, the flow resistance is large, and the maximum nominal diameter is DN200.
The spool of the ball valve is a ball with a hole. When the plate moves the valve stem so that the opening of the ball is facing the axis of the pipeline, it is fully open, and when it is turned 90°, it is fully closed. The ball valve has a certain adjustment performance and is more tightly closed.
The valve core of the butterfly valve is a circular valve plate, which can rotate along the vertical shaft perpendicular to the pipeline axis. When the plane of the valve plate is consistent with the axis of the pipe, it is fully open; when the plane of the gate plate is perpendicular to the axis of the pipe, it is fully closed. Butterfly valve body length is small, flow resistance is small, and the price is higher than gate valve and globe valve.
This type of valve is used to prevent the medium from flowing backwards. It uses the kinetic energy of the fluid itself to open itself and closes automatically when it flows in the reverse direction. It is always installed at the outlet of the water pump, the outlet of the steam trap and other places where the reverse flow of fluid is not allowed. There are three types of check valves: swing type, lift type and wafer type. For the swing check valve, when fluid can only flow from left to right, it will automatically close when it flows in the opposite direction. For the lift check valve, when the fluid flows from left to right, the valve core is lifted to form a passage, and when the fluid flows in the reverse direction, the valve core is pressed against the valve seat to be closed. For the wafer check valve, when the fluid flows from left to right, the valve core is opened to form a passage, and when the fluid flows in the opposite direction, the valve core is pressed to the valve seat to be closed. Installation, small size, light weight, compact structure.
The pressure difference between the front and back of the valve is constant. When the opening of the ordinary valve changes in a wide range, the flow rate changes little, but when it reaches a certain opening degree, the flow rate changes sharply, that is, the regulation performance is not good. The regulating valve can change the stroke of the spool to change the resistance of the valve according to the direction and magnitude of the signal, so as to achieve the purpose of regulating the flow of the valve. Regulating valves are divided into manual regulating valves and automatic regulating valves, and manual or automatic regulating valves are divided into many types, and their regulating performance is also different. Automatic regulating valves include self-operated flow regulating valves and self-operated differential pressure regulating valves.
Vacuum categories include vacuum ball valves, vacuum flapper valves, vacuum inflation valves, pneumatic vacuum valves, etc. Its function is that in the vacuum system, the components of the vacuum system used to change the direction of the air flow, adjust the size of the air flow, and cut off or connect the pipeline are called vacuum valves.
Special purpose categories include pigging valves, vent valves, drain valves, exhaust valves, filters, etc.
The exhaust valve is an indispensable auxiliary component in the pipeline system, and is widely used in boilers, air conditioners, oil and gas, water supply and drainage pipelines. It is often installed at commanding heights or elbows to remove excess gas in the pipeline, improve the efficiency of pipeline use and reduce energy consumption.
According to nominal pressure:
(1) Vacuum valve: refers to a valve whose working pressure is lower than the standard atmospheric pressure.
(2) Low-pressure valve: refers to the valve with nominal pressure PN ≤ 1.6Mpa.
(3) Medium pressure valve: refers to the valve with nominal pressure PN of 2.5Mpa, 4.0Mpa, 6.4Mpa.
(4) High pressure valve: refers to the valve whose nominal pressure PN is 10.0Mpa~80.0Mpa.
(5) Ultra-high pressure valve: refers to the valve with nominal pressure PN ≥ 100.0Mpa.
By working temperature:
(1) Ultra-low temperature valve: used for valves with medium working temperature t<-101°C.
(2) Normal temperature valve: used for valves with medium working temperature -29°C (3) Medium temperature valve: used for valves with medium working temperature of 120°C (4) High temperature valve: used for valves with medium working temperature t>425°C.
According to the driving mode, it can be divided into automatic valves, power driven valves and manual valves.
(1) Small diameter valve: a valve with a nominal diameter DN≤40mm.
(2) Medium diameter valve: a valve with a nominal diameter DN of 50-300mm.
(3) Large diameter valve: a valve with a nominal diameter DN of 350-1200mm.
(4) Extra-large diameter valve: a valve with a nominal diameter DN≥1400mm
The structural characteristics of the valve can be divided into:
(1) Cut-off shape: the closing member moves along the center of the valve seat; such as a globe valve
(2) Plug and spherical: the closing member is a plunger or a ball, which rotates around its own center line; such as plug valves, ball valves
(3) Gate shape: the closing member moves along the center of the vertical seat; such as gate valve, gate, etc.
(4) Swing shape: the closing member rotates around the axis outside the valve seat; such as swing check valve, etc.
(5) Butterfly: the disc of the closing member rotates around the axis in the valve seat; such as butterfly valve, butterfly check valve, etc.
(6) Slide valve shape: the closing member slides in a direction perpendicular to the channel. slippery
(1) Threaded connection valve: the valve body has internal or external threads, and is connected to the pipe thread..
(2) Flange connection valve: The valve body has a flange and is connected to the pipe flange.
(3) Welding connection valve: The valve body has a welding groove and is welded with the pipeline.
(4) Clamp connection valve: the valve body has a clamp, which is connected with the pipe clamp.
(5) Ferrule connection valve: it is connected with the pipe by ferrule.
(6) Wafer connection valve: a connection form in which the valve and the pipes at both ends are directly clamped together by bolts.
(1) Metal material valve: its valve body and other parts are made of metal material. Such as cast iron valves, cast steel valves, alloy steel valves, copper alloy valves, aluminum alloy valves, lead alloy valves, titanium alloy valves, Monel alloy valves, etc.
(2) Non-metallic material valves: The valve body and other parts are made of non-metallic materials. Such as plastic valves, enamel valves, ceramic valves, FRP valves, etc.

We offer valves of various materials which can meet your needs on diverse occasions. Come get your valves right now!
Our Valves materials can be the following grade, another grade is also available on request.
TITANIUM ALLOY:
Titanium Gr.2, Gr.3, Gr.5, Gr.6, Gr.7, Gr.12
NICKEL ALLOY:
Inconel 600, 625; Hastelloy B, B-2, B3, C276, C-22, C-4, G; Incoloy 800, 800H, 825; Monel 400, K500; Nickel 200, 201
ZIRCONIUM ALLOY:
Zirconium 702, 705
BRONZE:
C95800, C95500, C95400, C63200
SUPER STAINLESS STEEL:
904L, 254SMO, AL-6XN, ALLOY20
DUPLEX&SUPER DUPLEX:
S31803, S32750, S32760
STAINLESS STEEL:
SS304, SS304L, SS316, 316L, 316Ti, SS317, 317L, 347SS, SS310
Many kinds of valves are used in the industrial process, and to ensure proper functionality, compatibility, and safety for end-users, EPC, or engineering, every country has particular organizations to make standards.
The major standard organizations include the American National Standards Institute(ANSI), American Petroleum Institute(API), The American Society of Mechanical Engineers(ASME), British(BS), China valve standards(GB, JB, HG), and so on. THINKTANK provides standard resources for all interesting valves friends study.
American National Standards Institute
| ANSI Standard Code | ANSI Standard Name |
|---|---|
| ANSI A126 | Grey iron castings for valves flanges and pipe fittings |
| ANSI A181 | Standard specifications for forged or rolled steel pipe flanged forged fittings and valves and parts for general service |
| ANSI B16.10 | Face to face and end to end dimension of ferrous valves |
| ANSI B16.34 | Steel valves |
| ANSI B127.1 | Constant-level oil valves |
The American Petroleum Institute
| API Standard Code | API Standard Name |
|---|---|
| API SPEC6D | Supplement 1 to API spec 6D (sixteenth edition ) specification for pipeline valves |
| API STD6D | Steel gate plug ball and check valves for pipeline service |
| API STD6D | API Specification for flanged steel gate and plug valves for drilling and production service |
| API SPE14D | API Specification for wellhead surface safety valves for offshore service |
| API 526 | Flanged steel safety relief valves |
| API 527 | Commercial seat tightness of safety relief valves with metal – to metal seats |
| API 528 | API standard for safety relief valve nameplate nomenclature |
| API 529 | Cast – forged Steel plug valves flanged ends |
| API 594 | Wafer-type check valves |
| API 595 | Cast iron gate valves flanged ends |
| API 597 | Steel venturi gate valves flanged or butt welding ends |
| API 598 | Valve inspection and test |
| API 599 | Steel plug valves flanged or butt welding ends |
| API 600 | Flanged and butt – welding – end steel gate and plug valves for refinery use |
| API 602 | Compact design carbon steel gate valves for refinery use |
| API 603 | 150 – pound light – wall corrosion – resistant gate valves for refinery use |
| API 604 | Ductile iron gate valves flanged ends |
| API 607 | Fire-resistant testing of ball valves with soft contact faces |
| API 609 | Butterfly valves to 150 PSIG and 150 F |
| API SPEC 6FA | Specification for fire test for valves |
| API SPEC 6FC | Specification for fire test for valves with automatic backseats |
| API BULL 6RS | Bulletin on referenced standards for committee 6, standardization of valves and wellhead equipment |
| API RP 11V6 | Recommended practice for the design of continuous flow gas lift installations using injection pressure operated valves first edition |
| API RP 11V7 | Recommended practice for repair, testing, and setting gas lift valves |
| API RP 520 PT 1 | Sizing, selection, and installation of pressure-relieving devices in refineries part 1- sizing and selection |
| API RP 574 | Inspection of piping, tubing, valves, and fittings first edition, replaces guide for inspection of refinery equipment Chapter XI |
| API RP 576 | Inspection of pressure-relieving devices first edition |
| API STD 608 | Metal ball valves-flanged, threaded, and welding end |
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers
| ASME Valve Standard Code | ASME Standard Name |
|---|---|
| ASME A105/105M | Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Forgings for piping applications |
| ASME A181/181M | Standard Specification for Carbon Steel Forgings for General purpose piping |
| ASME A182/182M | Standard Specification for forged or rolled alloy-steel pipe flanges, forged fittings and valves and parts for high-temperature service |
| ASME A727/727M | Standard specification for carbon steel forgings for piping components with inherent notch toughness. |
| ASME A961 | Standard Specification for Common Requirements for Steel Flanges, Forged Fittings, Valves, and Parts for Piping Applications |
| ASME B462 | Standard Specification for Forged or Rolled UNS N08020, UNS N08024, UNS N08026, UNS N08367, and UNS R20033 Alloy Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, and Valves and Parts for Corrosive High-Temperature Service |
| ASME B834 | Standard Specification for Pressure Consolidated Powder Metallurgy Iron-Nickel- Chromium-Molybdenum (UNS N08367) and Nickel- Chromium Molybdenum Columbium (Nb) (UNS N06625) Alloy Pipe Flanges, Fittings, Valves, and Parts |
| ASME D5500 | Standard Test Method for Vehicle Evaluation of Unleaded Automotive Spark-ignition Engine Fuel for Intake Valve Deposit Formation |
| ASME F885 | Standard Specification for Envelope Dimensions for Bronze Globe Valves NPS 1/4 to 2 El-1996 R(1996) |
| ASME F992 | Standard Specification for Valve Label Plates El-1997 R(1997) |
| ASME F993 | Standard Specification for Valve Locking Devices El-1997 R(1997) |
| ASME F1020 | Standard Specification for Line-Blind Valves for marine Applications El-1996 RI’1996) |
| ASME F1098 | Standard Specification for Envelope Dimensions for Butterfly Valves – NPS 2 to 24 EI-1993 R(1993) |
| ASME F1271 | Standard Specification for Spill Valves for Use in Marine Tank Liquid Overpressure Protection Applications EI-1995 R (1995) |
| ASME F1370 | Standard Specification for Pressure Reducing valves for Water Systems, Shipboard |
| ASME F1508 | Standard Specification for Angle Style, Pressure Relief Valves for Steam, Gas, and Liquid Services |
| ASME F1565 | Standard Specification for Pressure-Reducing Valves for Steam Service |
| ASME F1792 | Standard Specification for Special Requirements for Valves Used in Gaseous Oxygen Service |
| ASME F1793 | Standard Specification for Automatic Shut-Off Valves (Also Known as Excess Flow Valves, EFV) for Air or Nitrogen Service |
| ASME F1794 | Standard Specification for Hand operated, Globe-Style Valves for Gas (Except Oxygen Gas), and Hydraulic Systems |
| ASME F1795 | standard Specification for pressure-reducing Valves for Air or Nitrogen Systems |
| ASME A230 | Standard specification for steel wire oil – tempered carbon valve spring quality |
| ASME A232 | Standard specification for chromium-vanadium alloy steel valve spring quality |
| ASME A350 | Standard specification for forged or rolled carbon and alloy steel flanges forged fittings and valves and parts for low – temperature service |
| ASME A338 | Standard specification for ultrasonic examination of heavy steel forgings |
| ASME A694 | Standard specification for forgings carbon and alloy steel for pipe flanges fittings valves and parts for high-pressure transmission service |
| ASME A404 | Standards specification for forged or rolled alloy – steel pipe flanged forged fittings and valves and parts specially heat-treated for high-temperature service |
| ASME A522 | Forged or rolled 8% and 9% nickel alloy steel flanges fittings valves and parts for low – temperature service |
British – BS – valve standards
| British Standard Code | British Standard Name |
|---|---|
| BS 1212 | Ball valves (Portsmouth type ) excluding floats |
| BS 1123 | Specification for safety valves, gauges, and other safety fittings for air receivers and compressed air installations |
| BS 1414 | Specification for steel wedge gate valves ( flanged and butt-welding ends ) for the petroleum, petrochemical, and allied industries |
| BS 1552 | Control plug cocks for low-pressure gases |
| BS 1570 | Specification for Flanged and Butt – welding ends steel plug valves for the petroleum industry (excluding well – Head and flow – line valves) |
| BS 1735 | Specification for Flanged cast iron outside – screw – and – yoke edge gate valves class 125, size 1.5 into 24 in for the petroleum industry |
| BS 1868 | Specification for steel check valves (flanged and butt-welding ends ) for the petroleum, petrochemical, and allied industries |
| BS 1873 | Specification for Steel globe and globe stop and check valves (flanged and butt-welding ends ) for the petroleum, petrochemical, and allied industries |
| BS 1952 | Specification for copper alloy gate valves for general purposes |
| BS 1953 | Copper alloy check valves for general purposes |
| BS 1968 | Floats for Ball valves ( copper ) |
| BS 2060 | Copper alloy screw-down stop valves for general purposes |
| BS 2080 | Specification for Face to face, center to face end – to -end and center – to – end dimensions of flanged and butt-welding end steel valves for the petroleum, petrochemical, and allied industries |
| BS 2591 PT.1 | British standard glossary for valves and valve parts (for fluids ) part 1. screw-down stop, check, and gate valves |
| BS 2591 PT.2 | British standard glossary for valves and valves parts ( for fluids) part,2 safety valves and relief valves |
| BS 2591PT.3 | British standard glossary for valves and valve parts (for fluids ) part 3, Plug valves and cocks |
| BS 2591PT.4 | British standard glossary for valves and valves (for fluids ) part4, butterfly valves |
| BS 2591PT.5 | British standard glossary for valves and valve parts ( for fluids ) part5, Ball valves |
| BS 2995 | Specification for cast and forged steel wedge gate, globe, check and plug valves screwed and socket – Welding sizes 2 in and smaller for the petroleum industry |
| BS 3464 | Specification for cast iron gate valves for general purposes |
| BS 3808 | Specification for cast and forged steel flanged, screwed and socket – welding Wedge gate valves (compact design ) sizes 2 in and smaller for the petroleum industry |
| BS 3948 | Specification for cast iron parallel slide valves for general purposes |
| BS 3952 | Specification for cast iron butterfly valves for general purposes |
| BS 3961 | Specification for cast iron screw-down stop valves and stop and check valves for general purposes |
| BS 4090 | Cast Iron check valves for general purposes |
| BS 4133 | Flanged steel parallel slide valves for general purposes |
| BS 4312 | Flanged steel screw-down stop valves and stop and check valves for general purposes |
| BS 4460 | Steel Ball valves for the petroleum industry |
| BS 5146 | Specification for inspection and test of steel valves for the petroleum petrochemical and allied industries |
| BS 5150 | Cast iron wedge and double disk gate valves for general purposes |
| BS 5151 | Cast iron gate (parallel slide ) valves for general purposes |
| BS 5152 | Cast iron globe and globe stop and check valves for general purposes |
| BS 5153 | Cast Iron check valves for general purposes |
| BS 5154 | Copper alloy globe stop and check, check and gate valves for general purposes |
| BS 5155 | Cast iron and carbon steel butterfly valves for general purposes |
| BS 5156 | Screw down diaphragm valves for general purposes |
| BS 5157 | Steel gate (parallel slide ) valves for general purposes |
| BS 5159 | Specification for cast iron and carbon steel ball valves for general purposes |
| BS 5160 | Specification for Flanged steel globe valves, globe stop, check valves and lift type check valves for general purposes |
| BS 5351 | Steel ball valves for the petroleum petrochemicals and allied industries |
| BS 5417 | Test of general-purpose industrial valves |
| BS 5418 | Marking of general-purpose industrial valves |
| China Standard Code | China Standard Name | Adopting Standard |
|---|---|---|
| GB12220 | General valve – marking | ISO 5209 |
| GB12221 | Flanged ends metal valve – face-to-face dimensions | ISO 5752 |
| GB12222 | Multi-turn valve – the connection of the driving device | ISO 5210/1 – 3 |
| GB12223 | Part-turn valve – the connection of the driving device | ISO 5211/1 – 3 |
| GB12224 | Steel valve – general requirements | ANSI B16.34 |
| GB12225 | General valve – copper alloy casting ware technology requirements | ASTM B584 |
| GB12226 | General valve – gray casting iron technology requirements | ISO 185,BS 1452 |
| GB12228 | General valve – carbon forging steel technology requirements | ASTM A 105,A181 |
| GB12229 | General valve – carbon casting steel technology requirements | ASTM A703 |
| GB12230 | General valve – Ao casting steel technology requirements | ASTM A351 |
| GB12232 | General valve – flanged ends iron gate valve | ISO5996-1982, API 595 |
| GB12233 | General valve – iron gate valve and lift check valve | BS5152,5153 |
| GB12234 | General valve – flanged and butt-welding ends copper gate valve | API 600 |
| GB12237 | General valve – flanged and butt-welding ends steel ball valve | ISO7121, API 607 |
| GB12238 | General valve – flanged and wafer ends butterfly valve | BS5155 |
| GB12239 | General valve – diaphragm valve | BS5156,NFE29 |
| GB12240 | General valve – iron plug valve | API 593 |
| GB12241 | Safety valve – general requirements | ISO 4126 |
| GB12242 | Safety valve – characteristic testing solution | ANSI/ASME PTC25.3 |
| GB12243 | Direct spring-loaded safety valve | JIS B 8210 |
| GB12244 | Pressure reducing valve – general requirements | JIS B 8372, B8410 |
| GB12245 | Pressure reducing valve – characteristic testing solution | JIS B 8372, B8410 |
| GB12246 | Pilot operated pressure reducing valve | JIS B 8372, DSS405 |
| GB12247 | Steam trap valve – classification | ISO 6704 |
| GB12248 | Steam trap valve – technology terms | ISO 6552 |
| GB12249 | Steam trap valve – marking | ISO 6553 |
| GB12250 | Steam trap valve – face-to-face dimensions | ISO 6554 |
| GB12251 | Steam trap valve – testing solution | ISO 6948,7841,7842 |
| GB/T13927 | General valve – pressure testing | ISO 5208 |
| JB/T6899-93 | Valve fire-proof test | ISO10497 |
| JB/T7927-95 | Valve casting steelware out-form quality requirements | MSS SP55 |
| ZBJ16006-90 | Inspection and testing of valve | API 598 |
| China Standard Code | China Standard Name |
|---|---|
| GB12220 | General valve – marking |
| GB12221 | Flanged ends metal valve – face-to-face dimensions |
| GB12222 | Multi-turn valve – connection of the driving device |
| GB12223 | Part-turn valve – connection of the driving device |
| GB12224 | Steel valve – general requirements |
| GB12225 | General valve – copper alloy casting ware technology requirements |
| GB12226 | General valve – gray casting iron technology requirements |
| GB12227 | General valve – ductile casting iron technology requirements |
| GB12228 | General valve – carbon forging steel technology requirements |
| GB12229 | General valve – carbon casting steel technology requirements |
| GB12230 | General valve – a casting steel technology requirements |
| GB12232 | General valve – flanged ends iron gate valve |
| GB12233 | General valve – iron gate valve and lift check valve |
| GB12234 | General valve – flanged and butt-welding ends copper gate valve |
| GB12235 | General valve – flanged steel stop and lift check valve |
| GB12236 | General valve – steel swing check valve |
| GB12237 | General valve – flanged and butt-welding ends steel ball valve |
| GB12238 | General valve – flanged and wafer ends butterfly valve |
| GB12239 | General valve – diaphragm valve |
| GB12240 | General valve – iron plug valve |
| GB12241 | Safety valve – general requirements |
| GB12242 | Safety valve – characteristic testing solution |
| GB12243 | Direct spring-loaded safety valve |
| GB12244 | Pressure reducing valve – general requirements |
| GB12245 | Pressure reducing valve – characteristic testing solution |
| GB12246 | Pilot operated pressure reducing valve |
| GB12247 | Steam trap valve – classification |
| GB12248 | Steam trap valve – technology terms |
| GB12249 | Steam trap valve – marking |
| GB12250 | Steam trap valve – face-to-face dimensions |
| GB12251 | Steam trap valve – testing solution |
| GB/T13927 | General valve – pressure testing |
| GB/T13932 | General valve – iron swing check valve |
| GB/T15185 | Iron and copper ball valve |
| GB/T15188.1 | Valve face-to-face dimensions – butt-welding ends valve |
| GB/T15188.2 | Valve face-to-face dimensions – wafer ends valve |
| GB/T15188.3 | Valve face-to-face dimensions – female screw-down valve |
| GB/T15188.4 | Valve face-to-face dimensions – male screw-down valve |
| JB93 | Handle |
| JB94 | Spanner |
| JB106 | Valve – marking and identifying paint |
| JB308 | Valve – type establishing a way |
| JB/T450 | PN16.032.0Mpa forging angle type high-pressure valve, fastener, and technology requirements |
| JB451 | Lever-type safety valve technology requirements |
| JB1308 | Pg(2500kgf/cm2)valve type and base specification |
| JB1309 | Pg(2500kgf/cm2)valve pipe and fastener technology requirements |
| JB/T1691 | Valve key construction element dimension of the stemhead |
| JB1692 | Umbrella type handwheel |
| JB1693 | Plane handwheel |
| JB1694 | Valve stem nut (1) |
| JB1695 | Valve stem nut (2) |
| JB1696 | Valve stem nut (3) |
| JB1698 | Valve stem nut (5) |
| JB1699 | Valve stem nut (4) |
| JB1700.1 | Locking nut (1) |
| JB1700.2 | Locking nut (2) |
| JB1701 | Valve stem nut (6) |
| JB1702.1 | Bearing gland (1) |
| JB1702.2 | Bearing gland (2) |
| JB1703 | Sleeve liner |
| JB1706 | Pressing sleeve nut |
| JB1708 | Gland |
| JB1709 | T type bolt |
| JB1712 | Asbestos packing |
| JB1713 | Packing seat(1) |
| JB1716 | Packing seat(2) |
| JB/T1717 | Valve construction key element back seat ring dimensions |
| JB1718 | Spacer (1) |
| JB1719 | Spacer (2) |
| JB1720 | Spacer (3) |
| JB1721 | Spacer (4) |
| JB1726 | Valve disc seat |
| JB1727 | Folio circle |
| JB1728 | Stop collar |
| JB/T1732 | Valve construction key element taper sealing face dimensions |
| JB/T1733 | Valve construction key element valve body copper sealing face dimensions |
| JB/T1734 | Valve construction key element wedge disc and valve disc copper sealing face dimensions |
| JB1735 | Foot valve disc sealing ring |
| JB1736 | Swing check valve disc sealing ring |
| JB1737 | Swing check valve disc sealing ring pressing board |
| JB/T1738 | Valve construction key element dimensions of wedge gate valve body slideway and slideway groove |
| JB/T1739 | Valve construction key element dimensions of wedge gate valve body sealing plane clearance and wedge angle |
| JB/T1740 | Valve construction key element dimensions of wedge disc sealing plane |
| JB1741 | Thimble |
| JB1742 | Adjusting ring |
| JB1747 | Packing ring |
| JB1749 | Ammonia valve disc |
| JB/T1750 | Valve construction key element ammonia valve body sealing plane dimensions |
| JB/T1751-92 | Valve construction key element socket welding and fitting pipe head dimension |
| JB/T1752-92 | Valve construction key element male screw ends head dimensions |
| JB1753-91 | Joint ring |
| JB1754-91 | Joint |
| JB1755-91 | Joint nut |
| JB/T1756-92 | Valve construction key element dimensions of bayonet joint ends |
| JB1757-91 | Bayonet |
| JB1758-91 | Bayonet nut |
| JB1759-91 | Bearing ring |
| JB1760- 91 | Six-angle bolt |
| JB1761-91 | Bolt ring |
| JB/T1762-92 | Valve construction key element spanner dimensions |
| JB2202-77 | Direct spring-loaded safety valve specification |
| JB2203-77 | Direct spring-loaded safety valve face-to-face dimensions |
| JB2205-77 | Reducing valve face-to-face dimensions |
| JB2206-77 | Reducing valve technology requirements |
| JB2311-78 | Ball valve technology requirements |
| JB2765-81 | Valve technology terms |
| JB2766-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa dimensions of forging high-pressure valve |
| JB/T2768-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa Pipe, piping fitting, valve head dimensions |
| JB/T2769-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa screw flange |
| JB/T2770-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa joint nut |
| JB/T2771-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa joint |
| JB/T2772-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa Blind plate |
| JB/T2773-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa double head bolt |
| JB/T2774-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa double-bolt ends and thread hole dimensions |
| JB/T2775-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa nut |
| JB/T2776-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa lens ring |
| JB/T2777-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa Non-hole lens ring |
| JB/T2778-92 | PN16.0- 32.0Mpa temperature marking of pipe and fastener |
| JB3328-83 | Air jar valve and pipe-line valve |
| JB3339-83 | Little type medical air jar frame type valve connection dimensions |
| JB5206.1-91 | Packing gland (1) |
| JB5206.2-91 | Packing gland (2) |
| JB5206.3-91 | Packing gland (3) |
| JB5207-91 | Packing pressing plate |
| JB5208-91 | Separating circle |
| JB5209-91 | Plastics packing |
| JB5210-91 | Back sealing ring |
| JB5211-91 | Gate valve seat ring |
| JB/T5296-91 | General valve testing way of flow rate coefficient and flow resistant coefficient |
| JB/T5298-91 | Steel plate gate valve for pipeline using |
| JB/T5299-91 | General valve Hydraulic actuator butterfly type check valve |
| JB/T5300-91 | General valve material |
| JB/T6438-92 | Valve sealing face plasma arc welding – technology requirements |
| JB/T6439-92 | Valve pressing casting steelware – magnetism powder flaw detector inspection |
| JB/T6440-92 | Valve pressing casting steelware – rax irradiating inspection |
| JB/T6441-92 | The safety valve for compressor purpose |
| JB/T6495-92 | Valve construction key element Gate valve (or disc) T type groove dimensions |
| JB/T6496-92 | Valve construction key element packing dimensions |
| JB/T6497-92 | Valve construction key element stem head dimensions |
| JB/T6498-92 | Valve construction key element disc and stem connection groove dimensions |
| JB/T6899-93 | Valve fire-proof test |
| JB/T6900-93 | Draught valve |
| JB/T6901-93 | Seal type glasses valve |
| JB/T6902-93 | Valve casting steelware hydraulic penetrating inspection way |
| JB/T6903-93 | Valve forging steelware superwave inspection way |
| JB/T6904-93 | Inspection and testing of air jar valve |
| JB/T7248-94 | Technology terms of low temperature casting steel for valve purpose |
| JB/T7744-95 | Valve sealing face alloy powder for plasma arc welding |
| JB/T7745-95 | Pipeline ball valve |
| JB/T7746-95 | Diameter-shrinking forging steel valve |
| JB/T7747-95 | Needle type stop valve |
| JB/T7748-95 | Valve clearance degree and inspection way |
| JB/T7749-95 | Technology terms of sub-zero valve |
| JB/T7927-95 | Valve casting steelware out-form quality requirements |
| JB/T7928-95 | General valve offer requirements |
| JB/Z243-85 | Gate valve static pressure length of life test rules |
| JB/Z244-85 | Stop valve static pressure length of life test rules |
| JB/Z245-85 | Plug valve static pressure length of life test rules |
| JB/Z246-85 | Ball valve static pressure length of life test rules |
| JB/Z247-85 | Valve – electrically device length of life test rules |
| JB/Z248-85 | Butterfly valve static pressure length of life test rules |
| ZBJ16002-87 | Valve electrically driving apparatus technology terms |
| ZBJ16004-88 | Reducing valve type and basing coefficient |
| ZBJ16006-90 | Inspection and testing of valve |
| ZBJ16007-90 | Steam trap valve technology terms |
| ZBJ16008-90 | Hydraulic petroleum gas device urgent shutdown valve – technology terms |
| ZBJ16009-90 | Valve pneumatic actuator technology terms |
| JB/T8473-96 | Instrument valve series |
| JB/T8528-97 | General valve electric actuator – technology terms |
| JB/T8527-97 | Metal sealing butterfly valve |
| JB/T8529-97 | Explosion-proof type valve electric actuator – technology terms |
| JB/T8530-97 | Valve electric actuator – type establishing a way |
| JB/T8531-97 | Valve manual actuator – technology terms |
| JB/T8670-97 | YBDF2 series explosion-proof three-phase asynchronous generator for valve electric actuator purpose – technology terms |
The Fluid Control Institute (FCI) provides standards and other materials to assist purchasers and users in understanding and using fluid control and conditioning equipment such as control valves, solenoid valves, and regulators.
| FCI 68-2 | Procedure in rating flow and pressure characteristic of solenoid valve for liquid service. |
|---|---|
| FCI 70-1 | Standard terminology and definition for filled thermal systems for remote sensing temperature regulators |
| FCI 75-1 | Test conditions and procedures for measuring electrical characteristics of solenoid valves |
| FCI 82-1 | Recommended methods for testing and classifying the water hammer characteristics of electrically operated valves. |
| FCI 84-1 | Metric definition of the valve flow coefficient CV |
| FCI 91-1 | The standard for qualification of control valve stem seals |
Valves are found in virtually every industrial process, including water and sewage processing, mining, power generation, processing of oil, gas and petroleum, food manufacturing, chemical and plastic manufacturing and many other fields.






A valve can be described as a mechanism that controls the passage of liquids through a pipe. Research states that valves being manufactured in China are amongst the top valve competitors in the valve industry.
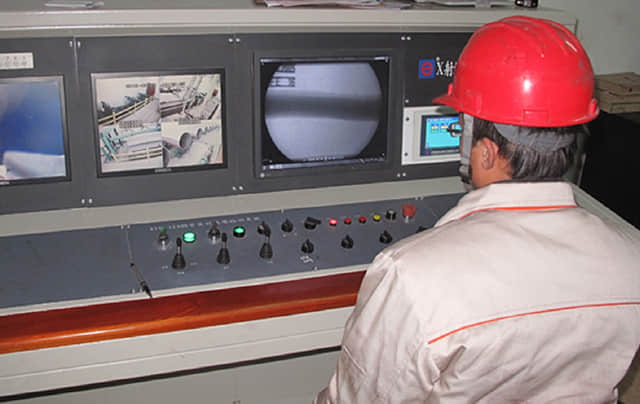
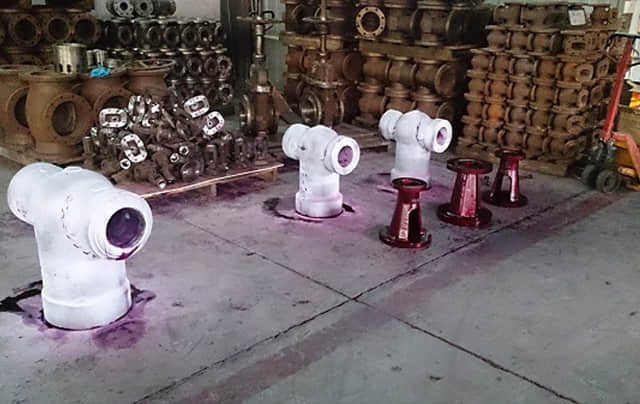



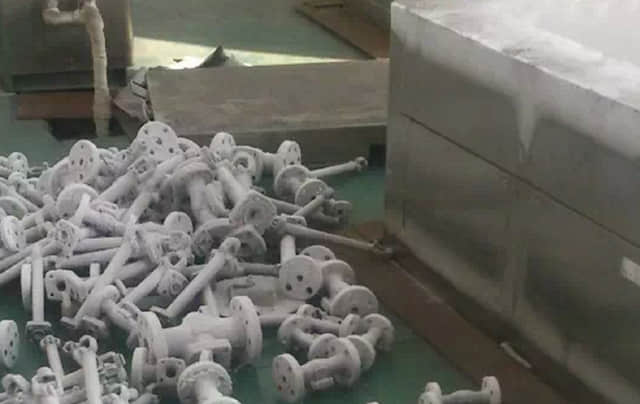
Radiography Inspection guarantees no failures inside of the castings or forgings. Ultrasonic inspection acts an alternative of inspection. Dye penetrant testing and magnetic particle testing can examine surface failures on castings and forgings.
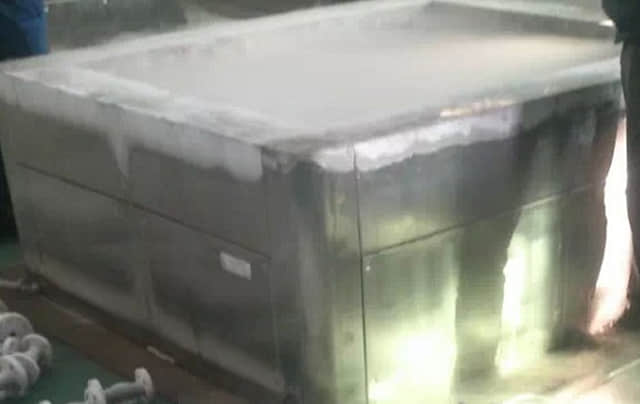
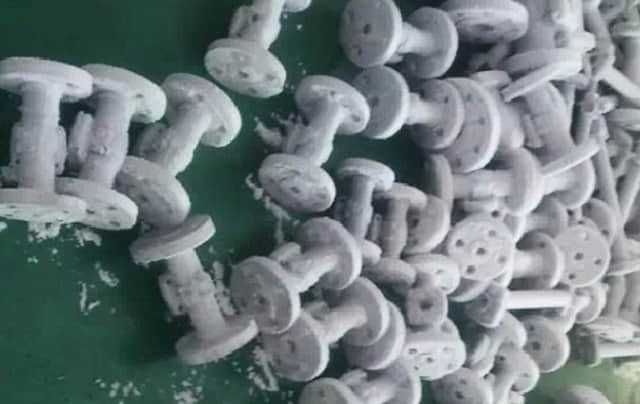



-196 ℃ Cryogenic Treatment System is a basic treatment for LNG usage valves or similiar applications.
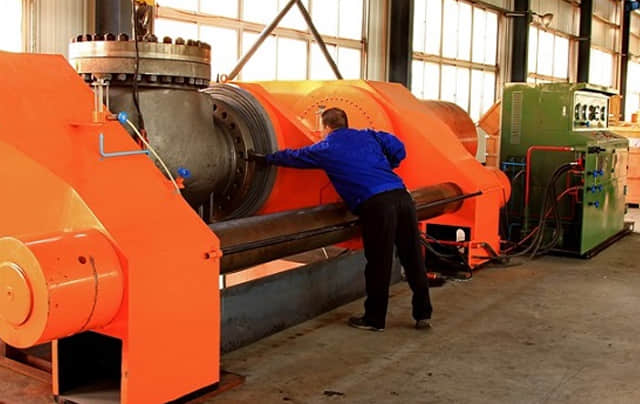
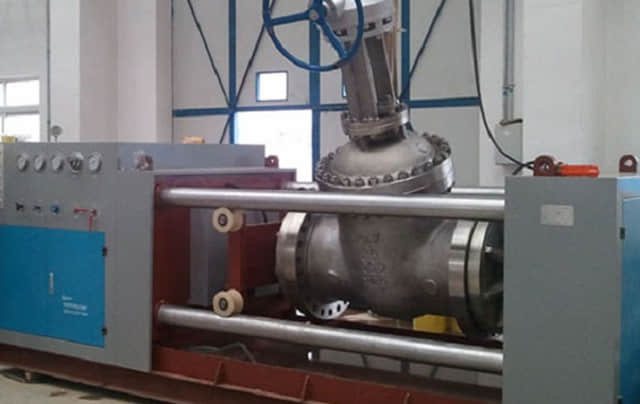


Leak testing is a procedure that inspectors use to determine whether an object or system is functioning within a specific leak limit.
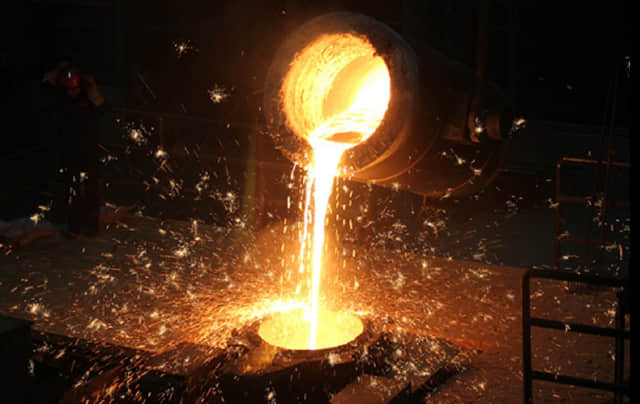
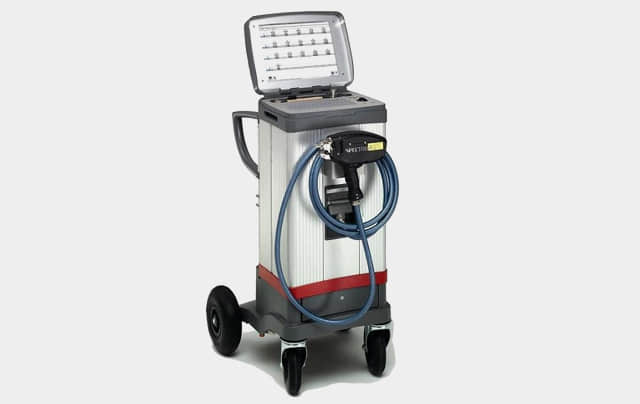


All our materials are strictly made under supervision of ladle analysis instrument in the foundries and inspected by high precision spectroanalysis instrument when they arrive in our plant.
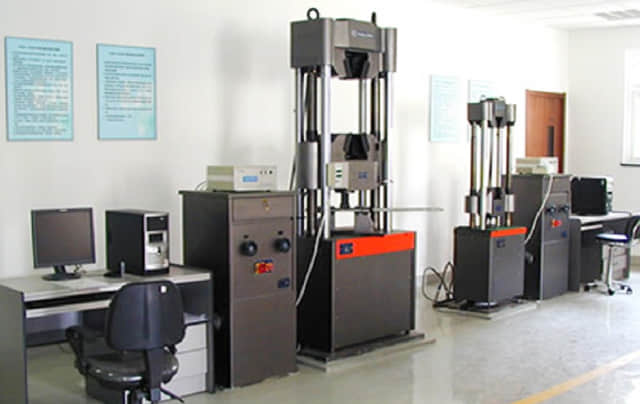
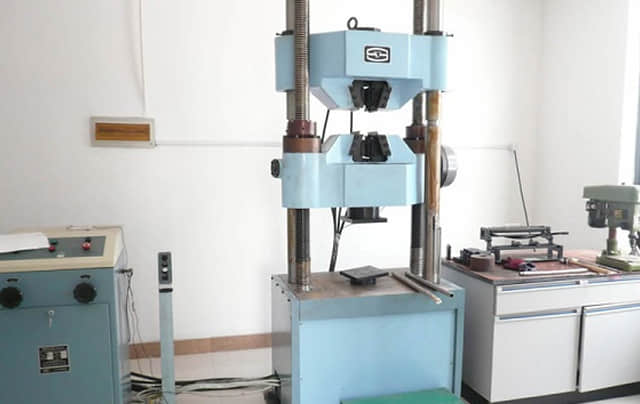


All mechanical properties test will act before we use the materials to secure the performance and safety.
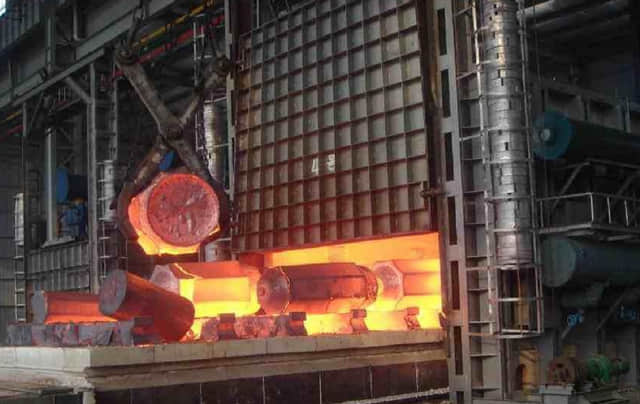
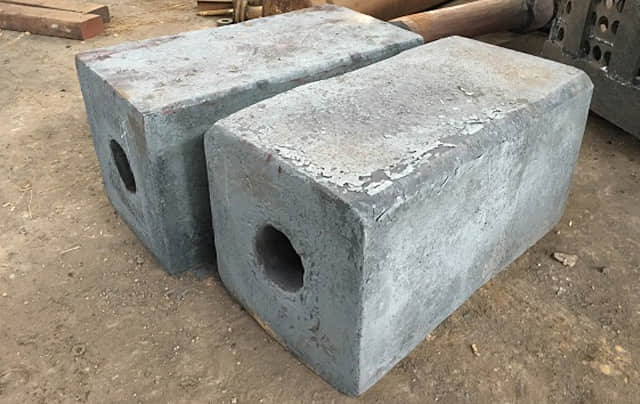


Up to 1200 ℃ electric furnance provide an availability of various heat treatment cycles.

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
