High pressure boiler tube
High-pressure boiler tubes are a type of seamless steel pipe used in boiler systems operating at high pressures and temperatures.
Boiler Tubes are metal tubes located inside of boilers that heat water in order to produce steam.
Boiler Tubes are metal tubes located inside of boilers that heat water in order to produce steam. There are two major types of tube boilers: water-tube boilers and fire-tube boilers. In water-tube boilers, water circulates inside the tubes and is heated externally by hot gases generated by the furnace.
Download PDFHigh-pressure boiler tubes belong to the category of seamless steel pipes, such as seamless carbon steel boiler tubes, which have very high requirements on the tightness of the steel pipes.
Boiler tubes refer to steel products that are open at both ends and have a hollow section. The ratio of its length to the surrounding area is large. According to the production method, it can be divided into seamless steel tubes and welded steel tubes. Wall thickness indicates a wide range of sizes, from capillary tubes with very small diameters to large-bore tubes up to several meters in diameter. Seamless steel pipes can be used in pipelines, thermal equipment, machinery industry, petroleum geological exploration, containers, chemical industry and special purposes.

The high-pressure boiler tube is employed in the manufacturing of seamless steel pipes for steam boilers operating at high temperatures and pressures, pipelines, furnace tubes for petrochemical applications, heat exchanger tubes, seamless steel pipes for pressure pipelines, high-pressure fertilizer equipment and pipelines, and seamless steel pipes for other chemical equipment.
The method of production is the same as that of seamless tubes, and the requirements are basically the same. However, the requirements for high-pressure boiler tubes are It is more demanding than ordinary boiler tubes. Because high-pressure boilers often operate in high-temperature and high-pressure environments, ordinary steel pipes cannot meet the operating requirements. This is one of the major reasons why special boiler tubes for high-pressure boiler tubes were born.
High-pressure boiler tubes are pivotal components not just for their ability to withstand elevated temperatures and pressures but also for their crucial role in resisting corrosion and oxidation. The operational environment of high-pressure boilers, frequently in contact with corrosive liquids, demands materials with exceptional resistance. Standard steel, when exposed to corrosive agents in water and steam, undergoes oxidation and corrosion, leading to substantial material wear. To mitigate building material costs, the initial material selection often leans towards anti-corrosion and anti-oxidation properties.
The performance expectations for these tubes are rigorous, emphasizing both rigidity and elasticity. High-pressure boilers, frequently subject to intense vibrations and impacts during operation, necessitate materials that surpass the capabilities of ordinary steel pipes.
The applications of high-pressure boiler tubes are diverse. They are prominently featured in the fabrication of water-cooled wall tubes and steam tubes, crucial components subjected to extremely high temperatures. In the automotive industry, these tubes find essential use in components like engine parts, where exposure to overheated steam and liquids makes ordinary pipes unsuitable due to the risk of corrosion.
Moreover, high-pressure boiler tubes play a key role in constructing ducts and air passages within high-pressure and ultra-high-pressure boilers. Their superior heat and gas conduction properties make them indispensable in ensuring the efficiency of these critical systems. These tubes are characterized by remarkable hardness, making them well-suited for deployment in demanding industrial testing environments.
In essence, the significance of high-pressure boiler tubes extends beyond their structural resilience; they embody a delicate balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and efficiency essential for the optimal functioning of high-pressure boiler systems.
Chinese national standards: GB5310-2017
American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME):ASME SA-106, ASME SA-192M, ASME SA -209M, ASME SA-210M, ASME SA -213M, ASME SA -335M
Deutsches Institut für Normung: DIN17175
Japanese Industrial Standards: JIS G3462
Boiler seamless steel tubes are high-quality carbon steel, alloy steel and stainless heat-resistant seamless steel tubes used to manufacture high-pressure and above-pressure water tube boiler heating surfaces. These boiler tubes often work under high temperature and high pressure, and the tubes will be oxidized and corroded under the action of high temperature flue gas and water vapor. Therefore, steel pipes are required to have high durability, high oxidation resistance and good structural stability.
Industrial boiler tubes are mainly seamless steel tubes, because the various performance indicators of seamless steel tubes can fully meet the requirements of boiler applications. Although the cost is higher, its safety and reliability are higher. Welded steel pipes are generally used as low-pressure fluid delivery pipes within 2Mpa. High-temperature and high-pressure equipment such as industrial boilers must use seamless steel pipes, and the thickness of the pipe walls must be thickened accordingly.
Now, due to the rapid improvement of welding technology, welded steel pipes are also used in medium and low pressure boilers. For example, joints of friction welded steel pipes have the same microstructure. After the pipe joints are remelted by butt joints and fillet joints, it is difficult to observe the butt joint marks with the naked eye. The microstructure and quality of its parts are exactly the same.
Common problems in surface treatment and product processing of seamless steel pipes for high pressure boilers:/p>
Boiler tubes are typically made from various types of steel, and the choice of material depends on factors such as the operating conditions, temperature, and pressure requirements of the boiler. The most commonly used materials for boiler tubes include:
Carbon Steel (ASTM A192, A210, A106, etc.): Carbon steel boiler tubes are widely used for low and medium-pressure boilers. They offer good tensile strength and are cost-effective. However, they are not suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
Alloy Steel (ASTM A213, A335, etc.): Alloy steel boiler tubes contain elements like chromium, molybdenum, and sometimes vanadium to enhance their properties. They are suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure boilers, making them ideal for power generation and industrial applications.
Stainless Steel (ASTM A213, A269, etc.): Stainless steel boiler tubes, especially grades like 304 and 316, are used in applications where corrosion resistance and hygiene are essential, such as in the food and pharmaceutical industries. They are also used in some high-temperature and high-pressure boilers.
Duplex Stainless Steel: Duplex stainless steel combines the properties of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, providing excellent corrosion resistance and high strength. They are used in specific boiler applications where both properties are required.
Inconel and Incoloy Alloys: These high-performance nickel-based alloys are used in extremely high-temperature and corrosive environments, such as in supercritical and ultra-supercritical boilers in power plants.
Copper Alloys: Copper and copper-nickel alloys are used in specialized applications, such as in condenser tubes where excellent heat transfer properties are required.
While choosing boiler tubes, look for the following to pick out the right and good quality tubes:
Specifications and Appearance
(1) GB3087-2008 "Seamless Steel Tubes for Low and Medium Pressure Boilers". There are 43 types of steel pipe specifications for boilers with various structures, with an outer diameter of 10 to 426 mm. A total of 29 kinds of wall thickness 1.5 ~ 26mm. However, the outer diameter and wall thickness of superheated steam pipes, large smoke pipes, small smoke pipes and arch brick pipes used in locomotive boilers are otherwise regulated.
(2) GB5310-2008 "Seamless Steel Tubes for High Pressure Boilers" has an outer diameter of 22-530mm and a wall thickness of 20-70mm. Cold-drawn (cold-rolled) tubes have an outer diameter of 10-108 mm and a wall thickness of 2.0-13.0 mm.
(3) GB3087-2008 "Seamless Steel Tubes for Low and Medium Pressure Boilers" and GB5310-95 "Seamless Steel Tubes for High Pressure Boilers". Appearance quality: cracks, folds, rolling folds, scars, delamination and hairlines are not allowed on the inner and outer surfaces of steel pipes. These defects should be completely removed. The cleaning depth shall not exceed the negative deviation of the nominal wall thickness, and the actual wall thickness of the cleaning place shall not be less than the minimum value allowed by the wall thickness.
(1) GB3087-2008 "Seamless Steel Tubes for Low and Medium Pressure Boilers". The chemical composition test method is in accordance with the relevant parts in GB222-84 and GB223 "Chemical Analysis Methods of Iron, Steel and Alloy".
(2) GB5310-2008 "Seamless Steel Tubes for High Pressure Boilers" regulations. The chemical composition test method is in accordance with relevant parts in GB222-84 and "Chemical Analysis Methods of Iron and Steel and Alloys", and GB223 "Chemical Analysis Methods of Iron, Steel and Alloys".
(3) The chemical composition inspection of imported boiler steel pipes shall be carried out in accordance with the relevant standards stipulated in the contract.
(1) The steel grades of high-quality carbon structural steel are 20G, 20MnG, and 25MnG.
(2) Alloy structural steel Steel grades 15MoG, 20MoG, 12CrMoG, 15CrMoG, 12Cr2MoG, 12CrMoVG, 12Cr3MoVSiTiB, etc.
(3) The 1Cr18Ni9 and 1Cr18Ni11Nb boiler tubes commonly used in rusty and heat-resistant steels must be subjected to hydrostatic tests one by one in addition to ensuring chemical composition and mechanical properties, and flaring and flattening tests. Steel pipes are delivered in a heat-treated state.
In addition, there are certain requirements for the microstructure, grain size and decarburization layer of the finished steel pipe.
(1) Tube billet control
The tube billet has a great influence on the production of seamless steel pipes, mainly in terms of the stability of the chemical composition of the steel and the purity of the steel. Generally, the high-pressure tube blank usually adopts the production process of "electric furnace + LF + VD". Chemical composition, VD furnace is mainly to purify molten steel to ensure the purity of molten steel. According to the application characteristics of high-pressure boiler tubes, in terms of smelting control technology of boiler steel, in addition to the chemical composition to hit the target, it is also required that the purity of boiler steel should be high, and the control of S and P harmful elements should be low, especially the S element should be strictly controlled. , mainly because S element is the main impurity element that causes the weakening of the original grain boundary, and is the main factor leading to the creep embrittlement of steel. For a long time, boiler tubes have been manufactured by forging and rolling billets. Forging and rolling billets can not only remove shrinkage cavities, slag inclusions and other pouring steel defects on steel ingots, but also eliminate residual defects through large rolling deformation.
In recent years, with the substantial improvement of the level of metallurgical process equipment, the production process of continuous casting and rolling of tube billet has been rapidly promoted due to its advantages of high efficiency, low consumption, high quality and low cost. Magnetic flaw detection, ultrasonic phased array flaw detection or infrared flaw detection and other detection methods, surface peeling and other related supporting means for defects found.
(2) Control points of heat treatment process
In the production process of seamless steel pipes for boilers, heat treatment is a key process. Heat treatment has an important impact on the internal quality and surface quality of seamless steel pipes, especially for the production of alloy seamless steel pipes, and has an impact on the durability of high-pressure boiler tubes for power plant boilers. Larger, stable metallographic structure and good internal and external surface quality represent the manufacturing level of steel pipe enterprises. After the chemical composition of the steel pipe is determined, it is the heat treatment process that finally endows the steel pipe with excellent mechanical properties and internal organization. The ASME standard provides a wide range of process parameters. Manufacturers need to conduct field tests to find out the appropriate heat treatment process. The usual heat treatment process of T22: normalizing at 920°C-940°C, holding for more than 20 minutes; tempering at 720°C-740°C, holding for 2 hours.
(3) Control of non-destructive testing
Generally, boiler companies purchase high-pressure boiler tubes in accordance with GB5310 or enterprise procurement regulations (ordering technical conditions). Non-destructive testing generally uses eddy current and ultrasonic automatic flaw detection. It is required to conduct eddy current flaw detection for steel pipes one by one. The eddy current flaw detection method and acceptance standards are controlled by GB7735 higher level; The steel pipes are subjected to ultrasonic flaw detection one by one, and the flaw detection method is in accordance with GB5777 grade. The acceptance criteria for all specifications of steel pipes should meet the requirements of L2 grade; the non-destructive testing of outlet pipes or steel pipes delivered in accordance with ASME SA-213 standards is controlled in accordance with SA-450.

| Specifications | Steel Grades |
|---|---|
| ASTM A-210 / ASME SA-210 | Gr. A1; C |
| BS 3059-1 | Gr. 320 |
| BS 3059-2 | Gr. 360; 440; 620; 622; |
| EN 17175 | 16Mo3 |
| EN 10216/1 | P235TR1; P235TR2; P265TR1; P265TR2 |
| EN 10216/2 | P235GHTC1; P235GHTC2; P265GHTC1; P265GHTC2 |
| ASTM A-209 ASTM A-213 ASME SA-213 |
Gr. T1; T11; T12; T22; T5; T9; T91; T92 |
| ASTM A-335 / ASME SA-335 | Gr. P1; P11; P12; P22; P5; P9; P91; P92 |
Sunny Steel has an extensive range of boiler and stay tubes available to meet your boiler tube requirements no matter how demanding.
Chinese National standards
American society of mechanical engineers
American Society for Testing and Materials
ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, and services.
Deutsche industrie normen
Deutsche industrie normen
Japanese industrial standards
The SA 213 Tp 304 Material consists of 18% chromium and carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon and nickel in the composition.
SA213 TP304 is a range of minimum wall thickness pipe series. We supply the SA 213 TP 304 Pipes in different types, shapes and sizes. The SA 213 Tp 304 Material consists of 18% chromium and carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon and nickel in the composition. There is also the molybdenum, nitrogen, niobium and titanium addition in trace quantities. The SA 213 Tp 304 Density is lower than the ordinary 304 material. It is 7.8 grams per cubic centimeter. We offer ASTM A213 TP 304 for high temperature services. Our 304 Stainless Steel Tube components are of less absolute roughness which means they could be used in high precision equipment and applications.
Austenitic stainless steels are presented in the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code with two sets of allowable stresses. The reason for this is their relatively low yield strength. The higher allowable stress values were determined at temperatures where the usage would be restricted by the short-time tensile properties.
The higher stresses exceed 62-1/2%, but do not exceed 90% of the yield strength. At these stresses, small amounts of plastic deformation can be expected. These higher stress values are usually used for super-heater and reheater tubing.
The Boiler Code lists maximum allowable stresses for varying temperatures depending on the individual austenitic stainless grade.
Variations of this 18 chromium, 8 nickel grade include 304L, 304LN, 304H and 304N. Each of these offers excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance along with high strength.
High strengths are maintained in the low carbon grades by controlling the nitrogen content.
T304 has higher carbon and a minimum solution annealing temperature to assure good long-time elevated temperature strengths. T304 grades are limited to 1650F under oxidizing conditions. Section I of the ASME Boiler Code lists allowable stresses up to 1500F.
SA213 TP316 Tube is a material standard for heat exchanger tubes that are made from 316 austenitic stainless steel.
The chromium nickel alloy also has molybdenum in its composition which makes it more corrosion resistant and heat resistant than the 304 material. ASME SA213 TP316 is the second most used pipe material in the world next to the 304 material. ASTM A213 TP316 Tube is an austenitic stainless steel but the 213 standard covers both the austenitic and ferritic steels.
Sunny Steel is a supplier of ASTM A213 Grade TP316 products in different standards and sizes. Our 316 Stainless Steel Tube can come with different finishing such as the 316 Stainless Steel Tubing Polished or electropolished. We also provide the pipes in different shapes such the round, rectangular or Stainless Steel 316 Square Tube. The square and 316 Stainless Steel Rectangular Tube is usually used in high pressure applications to withstand the pressure stress at change of directions. The Stainless Steel 316 Seamless Tube is more accurate in dimensions and therefore it is used in high precision applications. Our 316 Stainless Steel Exhaust Tubing is of high quality and can withstand high temperatures; it is used in exhausts, heat exchangers and super heaters. The 316 Stainless Steel Heavy Wall Tubing is used in high pressure applications such as hydraulic systems. Our SS 316 Welded Tube is easy to weld upon. We supply 316 Stainless Steel Welded Tube for affordable prices in different sizes and schedules. Please contact us for further details and pricing.
SA213 TP321 is a specification of heat exchanger tubes that are made from the 321 austenitic stainless steel.
SA213 TP321 is a specification of heat exchanger tubes that are made from the 321 austenitic stainless steel. The SA 213 specifies pipe products for heat exchangers in different material grades, both the ferritic and austenitic steels.
Sunny Steel is a supplier of all kinds of stainless steel pipes. The SA213 Tp321 Material is special in that the composition includes titanium which reduces the density of the ASME SA213 Tp321 and therefore making it lightweight.
T321 and 347 are variations of T304 and have comparable minimum tensile properties. These two grades are stabilized with additions of titanium and columbian respectively, along with proper heat treatment.
To insure good long-time strength at elevated temperatures, T321H and 347H-like 304H-were developed with higher carbon contents and specified minimum solution annealing temperatures.
Of all the stainless steels, T309 (25 chromium, 13 nickel) and T310 (25 chromium, 20 nickel) offer the maximum resistance to oxidation and corrosion. They also offer good high-temperature properties. Since these steels contain ferrite, however, they are more susceptible to sigma phase.
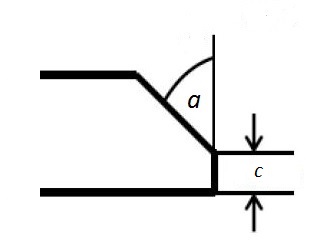
The ends are vertical to the longitudinal axis and are without burrs.

| Tube OD | 26.7 - 114.3 mm |
|---|---|
| Tube WT | 3.2 - 12.5 mm |
| Tube lengths | 4 - 13 meters |
| Deburring angle, a | 30°+ 5 and 37°± 2.5 |
| Dimension, c | 1.6 ± 0.8 mm |
The tubes with deburred ends or ends customized for welding.

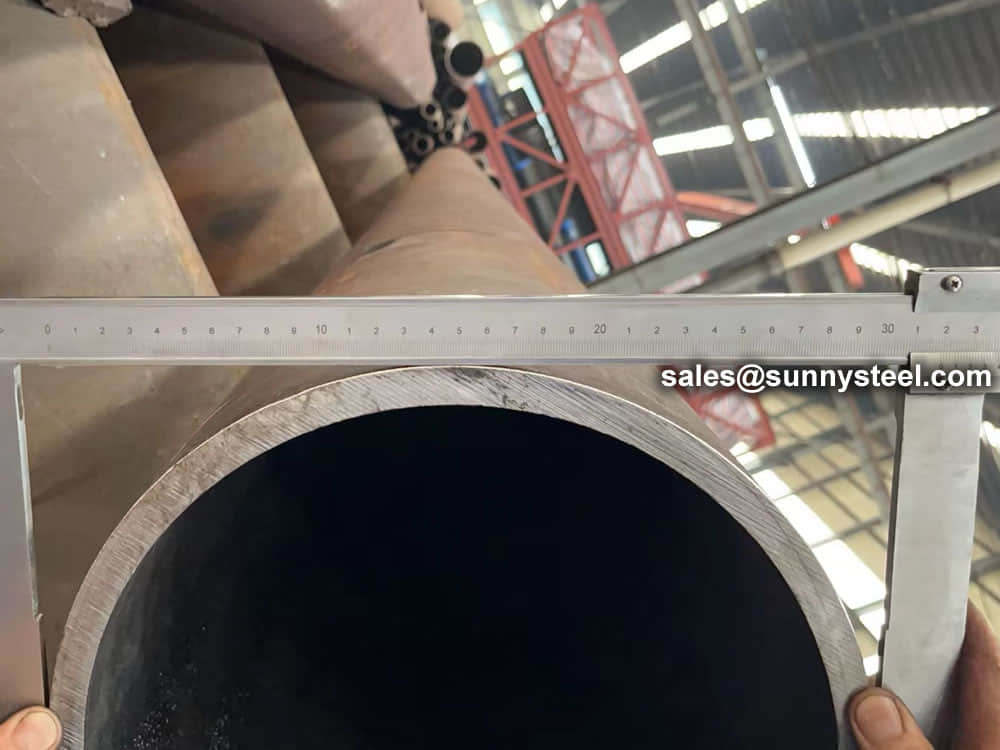
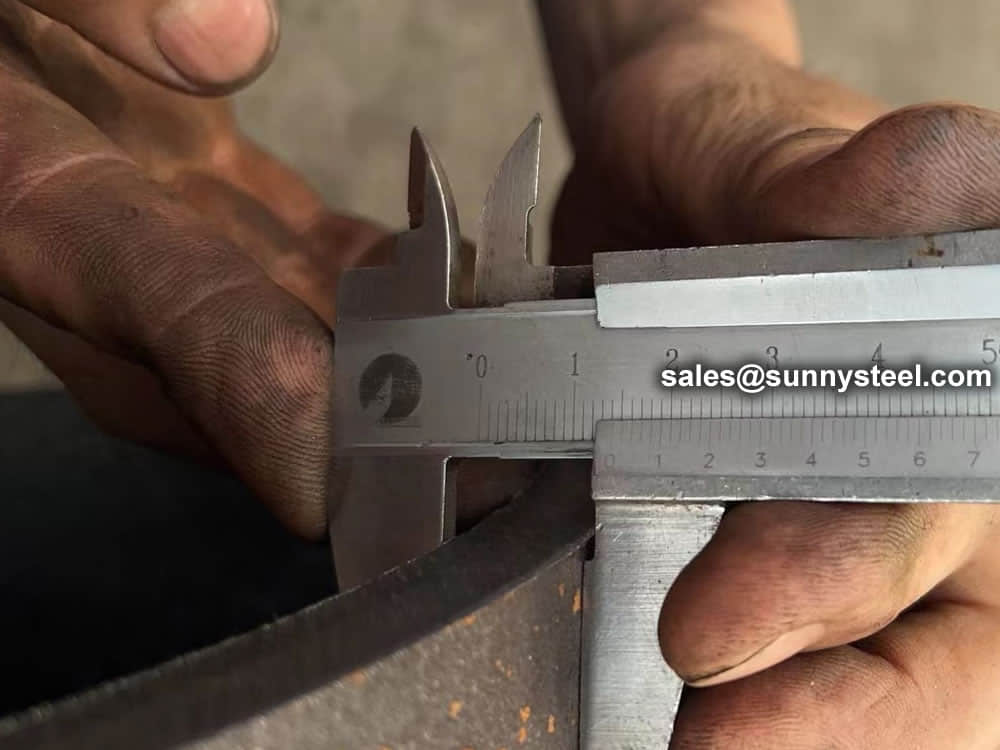
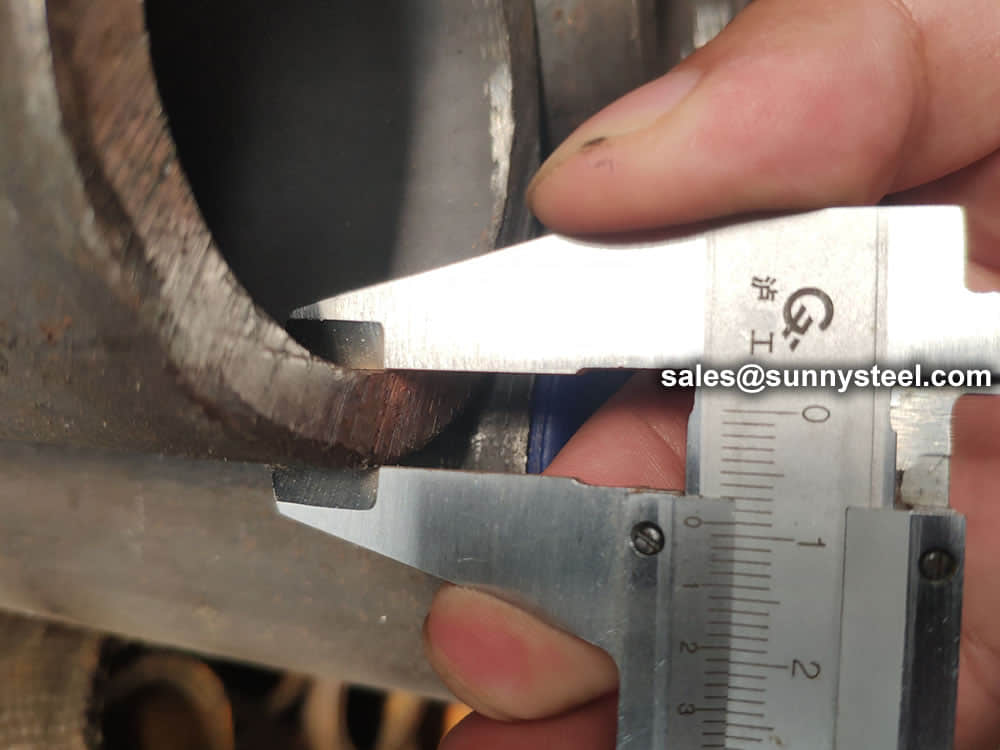
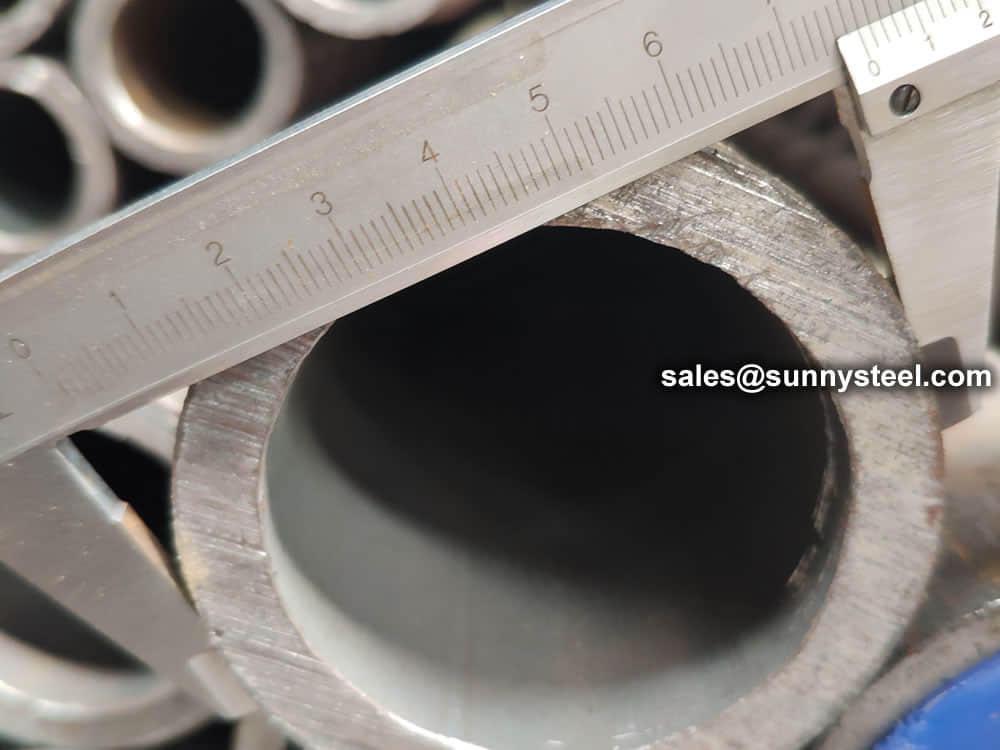
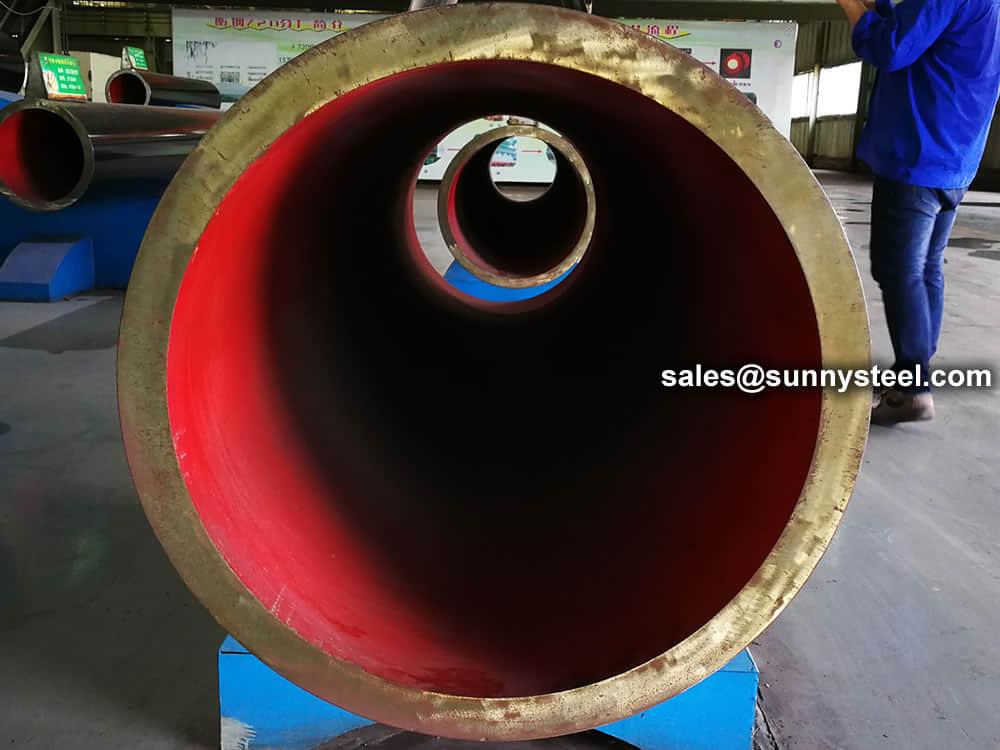
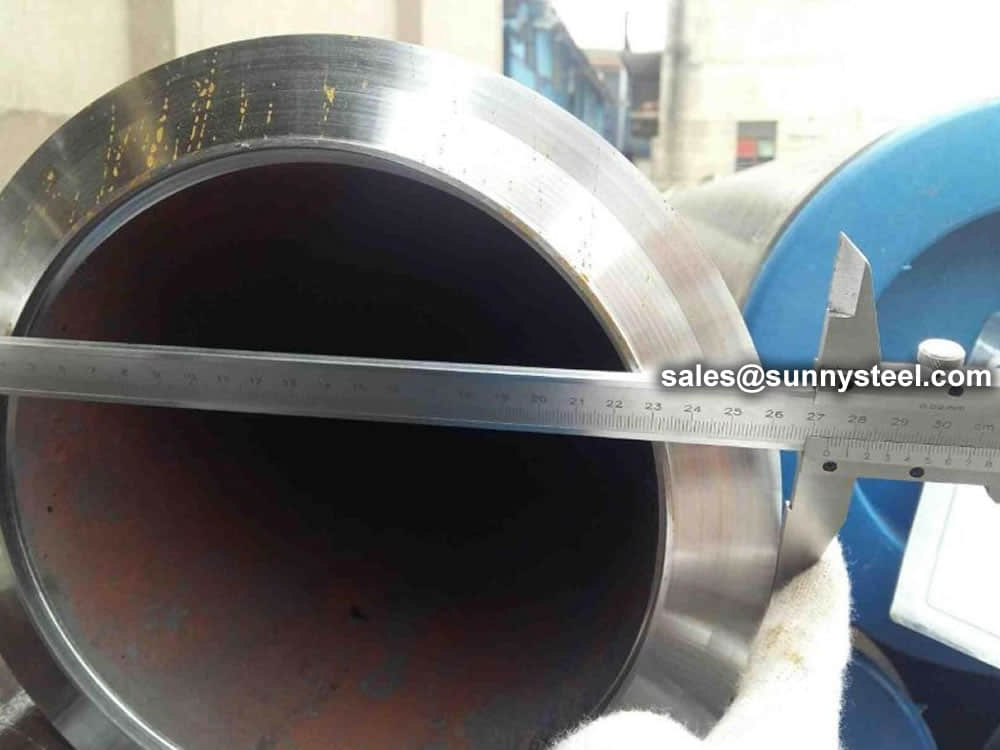
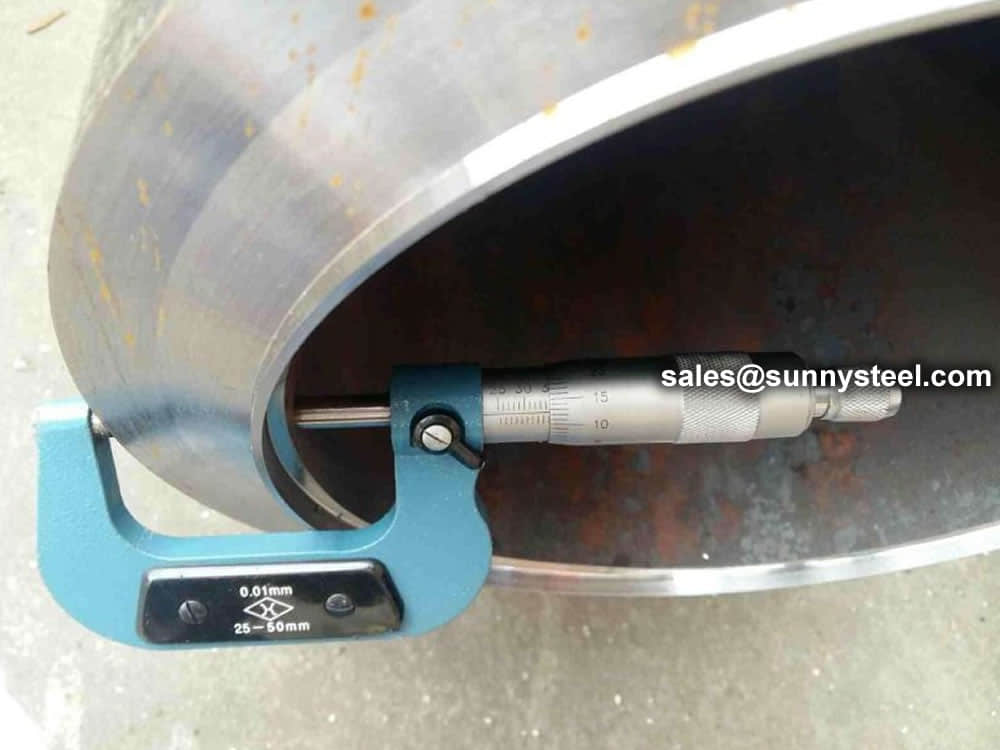
We have capability and capacity to ensure boiler tube in superior condition, with advanced inspection and testing procedures, standard tests include dimensional examination, visual checking, chemical composition, mechanical properties as well as non destructive test 100% eddy current test.
Fire-tube boiler is a type of boiler in which hot gas passes from the fire through one or more pipes that pass through a sealed water container. The heat of the gas is transferred through the wall of the tube through heat conduction, heating the water and eventually generating steam. Fire tube boilers are the third of the four historical types of boilers: low-pressure tank or “haystack” boilers, flue boilers with one or two large flues, fire tube boilers and high-pressure boilers with many small tubes
Water tube boiler is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. The fuel is burned in the furnace to produce hot gas, which heats the water in the steam generation tube. In smaller boilers, the additional power generation tubes are separated in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on water injection tubes that make up the furnace wall to generate steam. High-pressure water tube boiler: The hot water then rises into the steam drum. Here, saturated steam is drawn away from the top of the drum.

Boiler Tubes are metal tubes located inside of boilers that heat water in order to produce steam.
There are two major types of tube boilers: water-tube boilers and fire-tube boilers. In water-tube boilers, water circulates inside the tubes and is heated externally by hot gases generated by the furnace. Boiler tube is installed inside boiler to heat water in order to generate steam, boiler is a closed pressure vessel designed in varieties of types, water tube boiler and fire tube boiler are main types.
| Steel Grade | Standard | Application | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB(China) | ASME(USA) | DIN/EN(Euro) | ||
| Carbon steel | 10 20 20G 20MnG 25MnG |
SA-106B SA-192 SA-210A1 SA106C SA-210C |
PH265GH P195GH P235GH St35.8 St45.8 |
Economizer tube Water wall tube |
| Mo steel | 15MoG 20MoG |
SA-209 T1 SA-209 T1a SA-209 T1b |
15Mo3 16Mo3 |
Water wall tube Superheater tube Reheater tube |
| Cr-Mo Steel | 12CrMoG 12Cr2MoG 12Cr1MoVG 15CrMoG 10Cr9MoVNb |
SA-213 T11 SA-213 T22 SA-213 T24 SA-213 T91 A335 P1 A335 P2 A335 P5 A335P9 A335 P11 |
12Cr1MoV 14MoV63 10CrMo910 X10CrMoVNb91 10CrMo5-5, 13CrMo4-5 |
Superheater tube Reheater tube |
| Cr-Mo-W steel | 12Cr2MoWVTiB | SA-213 T23 SA-214 T911 SA-213 T92 SA-213 T122 A335 P23 A335 P911 A335 P92 A335 P122 |
--- | Superheater tube Reheater tube |
| Austentic Stainless steel | --- | AP304 TP304H TP321 TP321H TP347 TP347H TP316 TP316H S30432 TP310HCbN |
--- | Superheater tube Reheater tube |
Boiler tubes are used in fire-tube boiler, a type of boiler in which hot gases from a fire pass through one or more tubes running through a sealed container of water.
How to get rid of surface stains of cracking tube follow the steps below:
The first step is to clean, we must first petroleum cracking tube surface oil, dirt, grease, and some other substances removed. The second step is naturally acid, generally speaking, there are two pickling treatment, a chemical treatment, another treatment method is electrolysis, which can be handled in two ways petroleum cracking tube surface cleaning clean, but chemical pickling is a pipeline anti-corrosion measures.
The third step is necessary to use the tool to the surface of the oil cracking pipe polished, although the effect may not be very good polish, but this procedure is also indispensable. The final step is to make the surface of petroleum cracking tube jet, one can remove some of the dirt, the second is to make the roughness of petroleum cracking tube more evenly.
For petroleum cracking tube defects formed on the surface there are many, but certainly there are a lot of different reasons, the specific form of the crack is different, often found defective for its appearance on petroleum cracking tube we can see, the main reason for its main form by the following points. In fact, for the production process, the emergence of various drying phenomena of its raw materials for steelmaking summer rainy season or when it will produce up to steel gas content's sake.
In the process, the ingot when heated due to heating of the air bubbles are burned through, it will have more cracks after the rolling, which will meet the petroleum cracking tube relatively thin, dense and sizes, its length ranging from cracks, these things collectively referred to as hairline, this is a defect. So the cause of the surface oil cracking tube defects are many, so we have to remedy. After oil cracking pipe handling, appearance becomes smoother, more beautiful. Although after the rust will not affect the use again, but if we do the work in advance, so do not bother it. We buy petroleum cracking tube among the first to note that it is not a strong corrosion resistance, have a longer life does not have to select a high-quality petroleum cracking pipe products that can reduce our future work a lot of trouble.
Small diameter high-pressure boiler tube surface defects that affect the quality, mainly due to waste generation.
Boiler pipes often in high temperature and high pressure work, pipe smoke and water at high temperature steam oxidation and corrosion effects will occur, thus requiring durable steel with high strength, high oxidation resistance, and good organizational stability, high pressure boiler tube in addition to chemical composition and mechanical properties, hydrostatic testing done by the root, to be flaring, flattening test. Steel to heat treatment delivery. In addition, the finished steel microstructure, grain size, there are certain requirements decarburization.
High-pressure boiler tubes are seamless steel pipe categories. Seamless same manufacturing method, but used in the manufacture of steel pipe, there are strict requirements. Often in high-pressure boiler tubes at high temperature and pressure conditions of use, the tube under the effect of high temperature gas and water vapor, oxidation and corrosion will occur. Require durable steel with high strength, high resistance to oxidation corrosion, and have good organizational stability.
High-pressure boiler tube is mainly used to manufacture high-pressure and high pressure boiler superheater tubes, reheater tubes, windpipe, the main steam pipe. High-pressure boiler tubes for low and medium pressure boiler (working pressure is generally not more than 5.88Mpa, working temperature below 450 ℃) of heating surface tubes; used for high-pressure boilers (above 9.8Mpa working pressure in general, the working temperature of 450 ℃ ~ 650 ℃ between) the heating surface tubes, economizer, superheater, reheater, petrochemical industrial pipe.
High pressure boiler tube hardness testing should take into account its mechanical properties, which is related to stainless steel as raw material for the deformation, such as punching, cutting processing performance and quality.
Therefore, all of the high-pressure boiler tubes need to conduct mechanical tests. Mechanical performance testing method is mainly divided into two kinds, one kind is tensile test, the other kind is usually hardness test.
Tensile test is the high pressure boiler tube sample, high pressure boiler tube tend to sample to the fracture on tensile testing machine, mechanical properties and determination of one or more, usually only determination of tensile strength, yield strength, break elongation, and reduction of area. Tensile test is the most basic mechanical properties of metallic materials testing methods, almost all of the metal material, as long as the requirements of the mechanical properties of the high pressure boiler tube, the provisions of the tensile test. Especially those appearance and high pressure boiler tube is not good for the material of hardness test, tensile test became the only means of mechanical properties testing.
A steam boiler is a device used to create steam by applying heat energy to water.
A continuous helical fin is attached to the base tube by high frequency electric resistance welding in order to give an efficient and thermally reliable bond. Fins can be either solid or serrated (segmented). The weld produced in this process is a true forge, blacksmith weld. This type of weld is comprised of a fusion between two portions of parent metal without the introduction of a filler material. The weld is simply produced by heating the interfaces to be joined to a plastic state and applying pressure.
Used in boilers, furnaces and fired heaters for efficient heat recovery.
High-pressure boiler tubes are frequently occurs fault because of high temperatures, affecting the entire heating system, mainly due to an internal boiler for heat treatment is not perfect, a lot of heat can not be effectively converted and timely treatment.
High pressure boiler tube hardness testing should take into account its mechanical properties, which is related to stainless steel as raw material for the deformation, such as punching, cutting processing performance and quality.
Therefore, all of the high-pressure boiler tubes need to conduct mechanical tests. Mechanical performance testing method is mainly divided into two kinds, one kind is tensile test, the other kind is usually hardness test.
Finned tubes are used in applications involving the transfer of heat from a hot fluid to a colder fluid through a tube wall.
The rate at which such heat transfer can occur depends on three factors:
a. Cleaning
Using the solvent and emulsion to clean the surface of high pressure boiler pipe, so as to achieve the purpose of removing oil, grease, dust, lubricant and similar organic matter. But it cannot remove the dust, oxide skin, welding medicine and so on. So it is only as a supplementary method in the anti-corrosion production.
b. Tool
Tool rust removal mainly use wire brush and other tools to grind the surface of high pressure boiler pipe. It can remove loose or warping of the oxide skin, rust, welding slag and so on. Manual tool can reach SA2 level, power tool can reach SA3 level. If the iron oxide scale attached to the surface, it cannot reach the anchorage depth required by the anti-corrosion construction.
c. Acid cleaning
High pressure boiler pipe generally adopt chemical and electrolytic methods to do pickling treatment.
d. Spray rust removal
Spray rust removal cannot only remove rust, oxide and dirt completely, but also high pressure boiler pipe can achieve the required uniform roughness under the action of abrasive impact and friction force.
Spay rust removal cannot only expand the physical adsorption on the surface of high pressure boiler pipe, but also enhance the mechanical adhesion between the anti corrosion layer and the pipe surface. So spray rust removal is ideal method of rust removing for pipeline corrosion.
Boiler pipe forming include fin tube, serpentine tube and reaming welding.
Boiler tubes need take for a variety of molding in the boiler manufacture and installation process
Heat treatment is a method of changing the physical properties of high pressure boiler pipe by heating and cooling. Heat treatment can improve the microstructure of high pressure boiler pipe, so as to meet the required physical requirements. Toughness, hardness and wear resistance are obtained by heat treatment. In order to obtain these characteristics, it is necessary to adopt quenching, annealing, tempering and surface hardening.
a. Quenching
Hardening, also called quenching, is that high pressure boiler pipe is heated evenly to the appropriate temperature, then quickly immerse in water or oil for rapid cooling, and cooling in the air or in the freezing zone. So that the high pressure boiler pipe can obtain the required hardness.
b. Tempering
High pressure boiler pipe will become brittle after hardening. And the stress caused by quenching can make the high pressure boiler pipe tapped and broken. The tempering method can be used to eliminate brittleness. Although the hardness of high pressure boiler pipe is lighter reduced, its the toughness can be increased to reduce the brittleness.
c. Annealing
Annealing is the method to eliminate the internal stress of high pressure boiler pipe. The annealing method is that the steel parts need to be heated to the critical temperature, then put in dry ash, lime, asbestos or closed in the furnace, then let it cooling slowly.
Chemical composition inspection, mechanical properties test(tensile strength,yield strength, elongation, flaring, flattening, bending, hardness, impact test), surface and dimension test,no-destructive test, hydrostatic test.
identification of the chemical composition of the metal used to manufacture the fitting. Uses PMI sensors, including X-ray fluorescence or optical emission spectrometry.
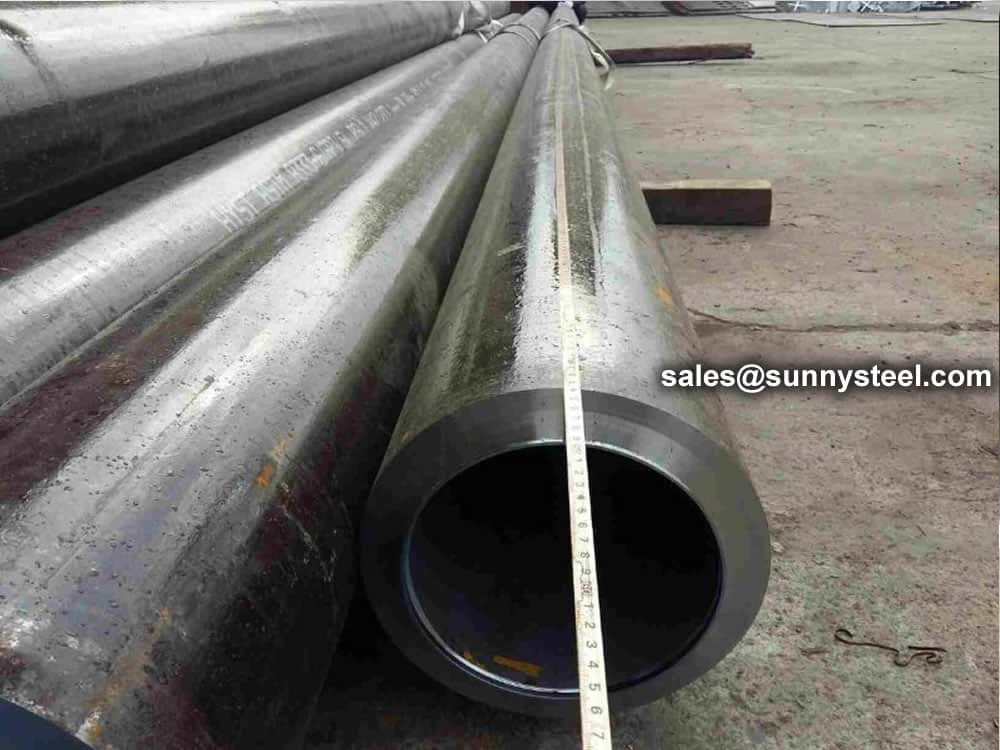
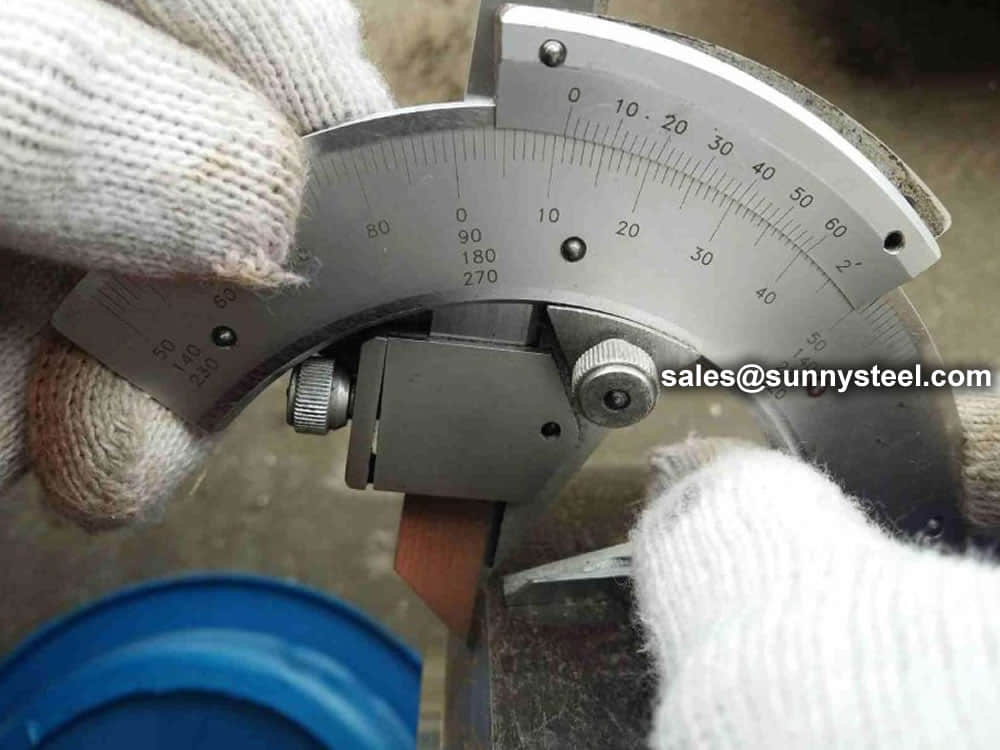
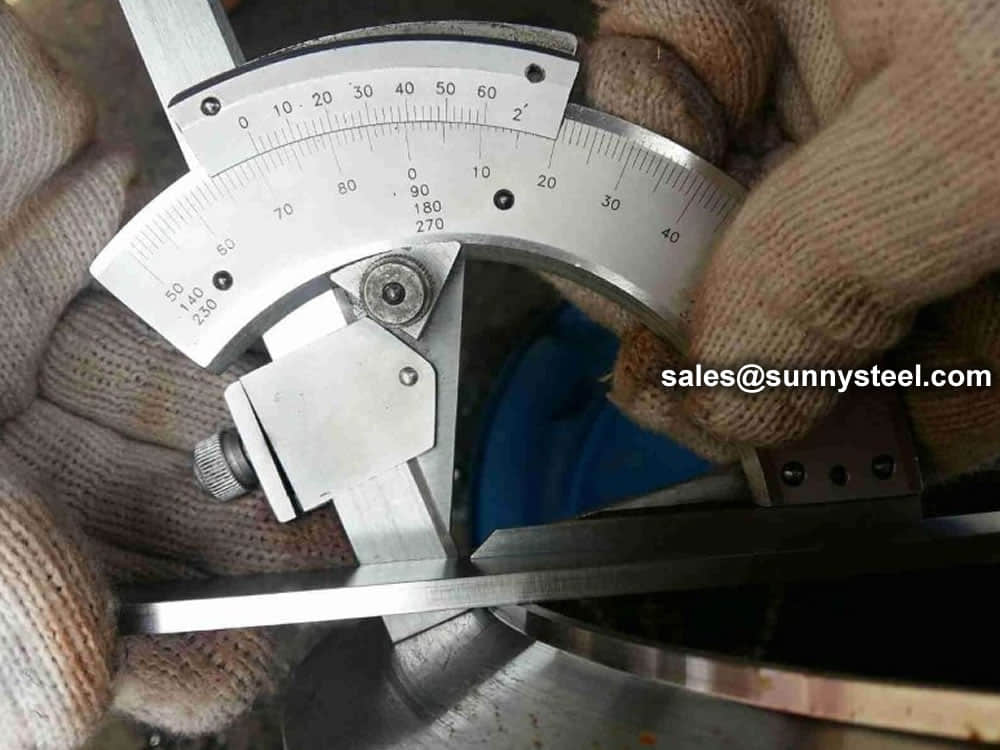
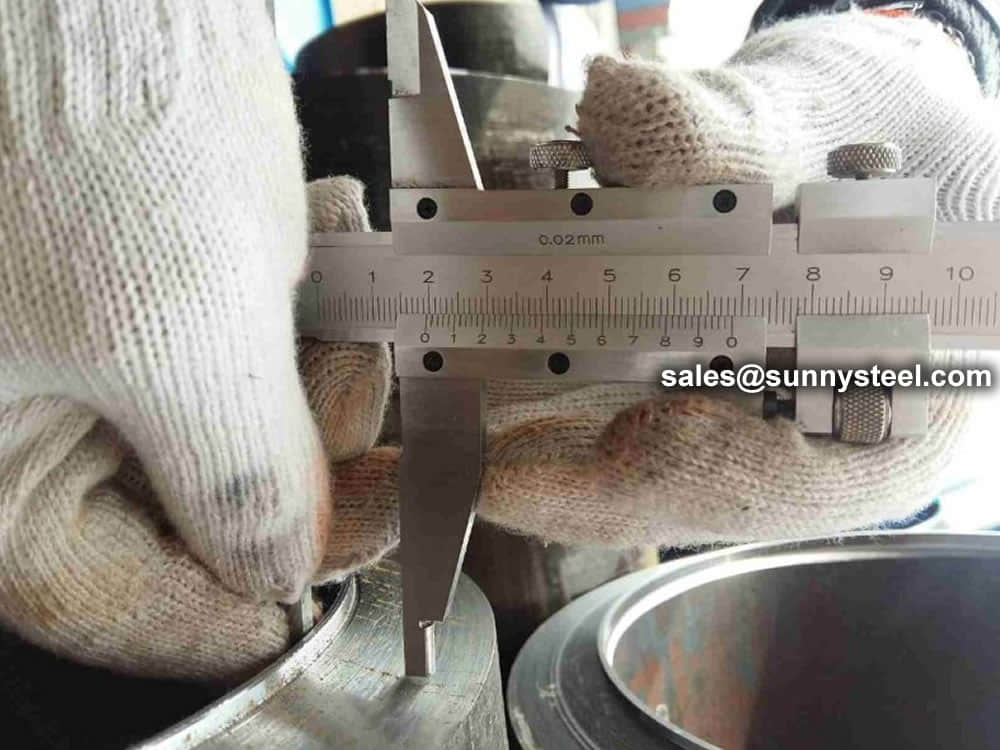
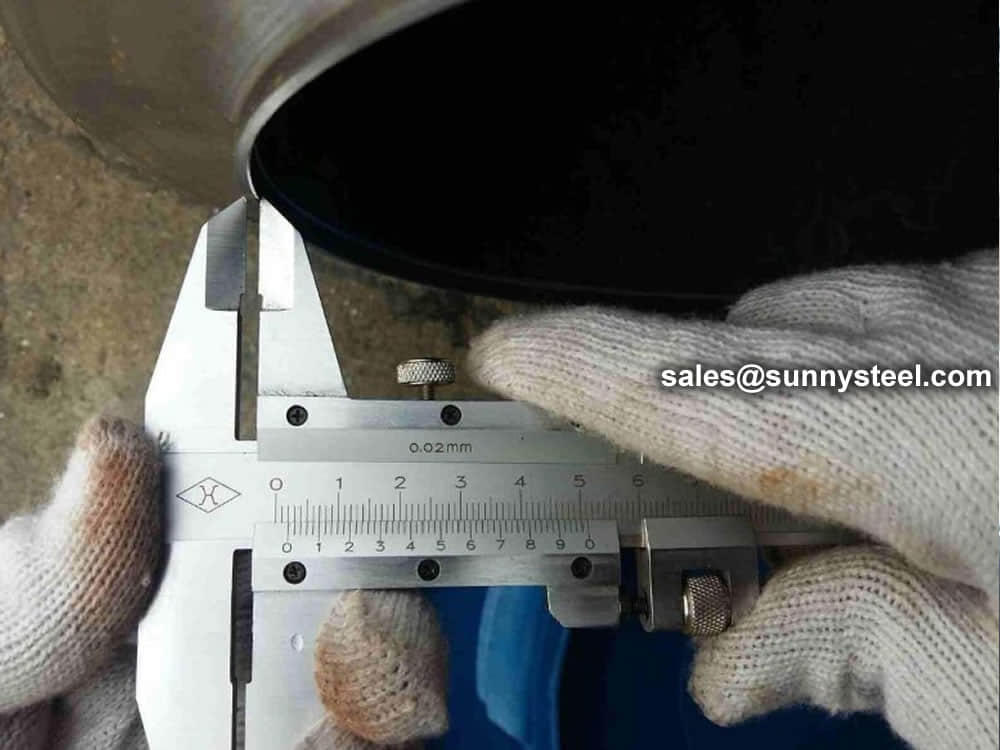
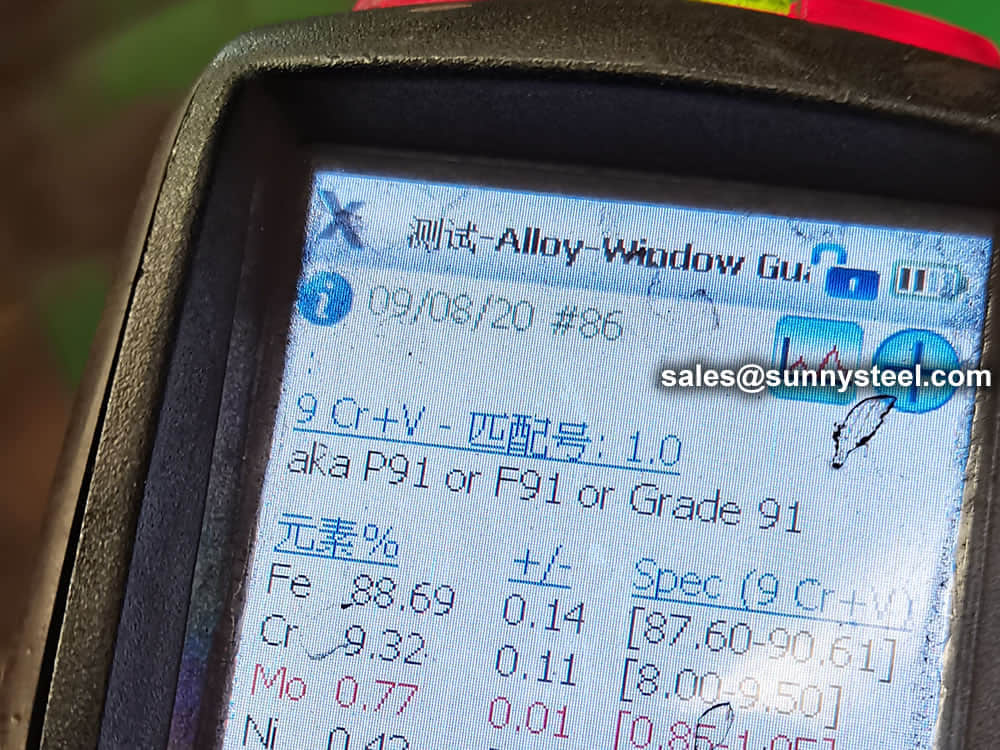
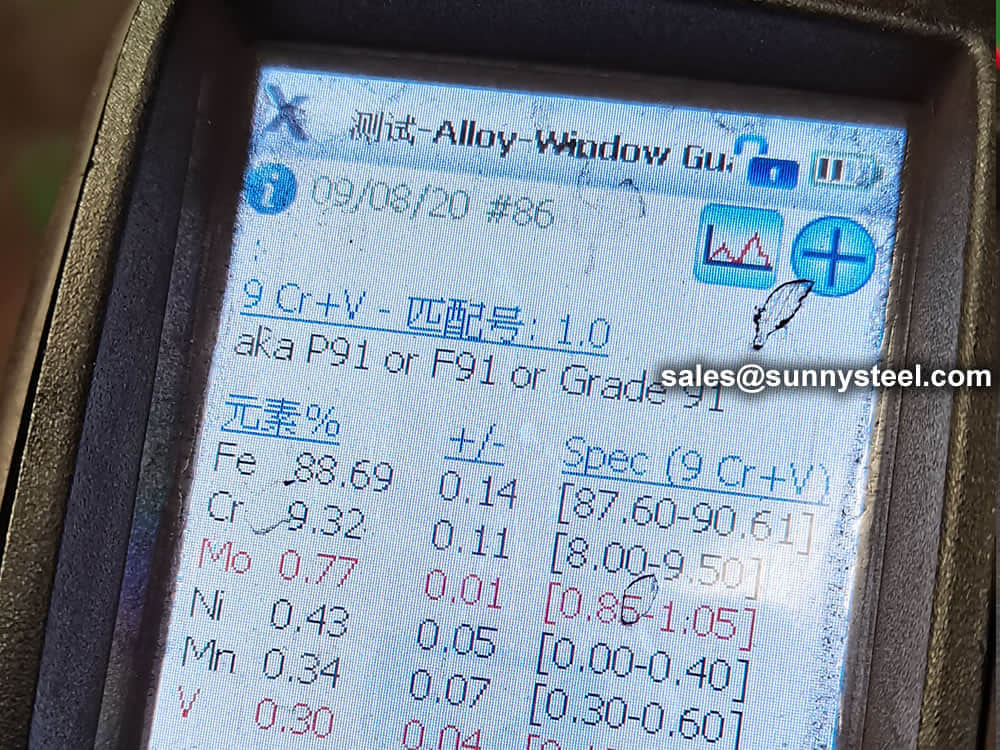















Steel pipe delivery status(condition): cold / hard (BK), cold / soft (BKW), after cold stress relief annealing (BKS), annealing (GBK), normalized (NBK).
| Term | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-finished/hard (cold-finished as-drawn) | BK | No heat treatment after the last cold-forming process. The tubes therefore have only low deformability. |
| Cold-finished/soft (lightly cold-worked) | BKW | After the last heat treatment there is a light finishing pass (cold drawing) With proper subsequent processing, the tube can be cold-formed (e.g. bent, expanded) within certain limits. |
| Annealed | GBK | After the final cold-forming process the tubes are annealed in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
| Normalized | NBK | The tubes are annealed above the upper transformation point in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
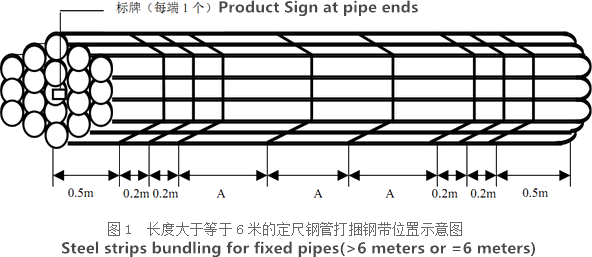
The general cold strip mills, volume should go through continuous annealing (CAPL unit) to eliminate cold hardening and rolling stress, or batch annealing reach the mechanical properties of the corresponding standard specifies. Cold rolled steel surface quality, appearance, dimensional accuracy better than hot-rolled plate, and right-rolled thin product thickness is about 0.18mm, so the majority of users favor.
Cold rolled steel coil substrate products deep processing of high value-added products. Such as electro-galvanized, hot dip galvanized, electro-galvanized fingerprint resistant, painted steel roll damping composite steel, PVC laminating steel plates, etc., so that the excellent quality of these products has a beautiful, high resistance to corrosion, has been widely used.
Cold rolled steel coil finishing after annealing, cut the head, tail, trimming, flattening, smooth, heavy volume, or longitudinal clipboard. Cold-rolled products are widely used in automobile manufacturing, household electrical appliances, instruments, switches, buildings, office furniture and other industries. Steel plate strapping package weight of 3 to 5 tons. Flat sub-volume typically 3 to 10 tons / volume. Coil diameter 6m.
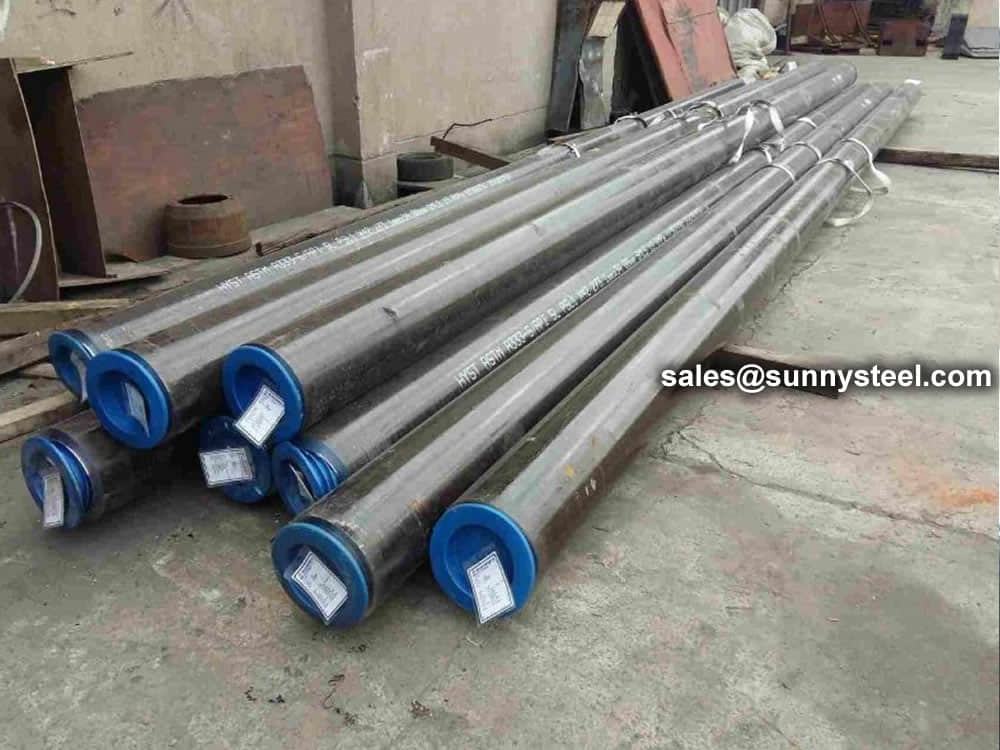
Bare packing/bundle packing/crate packing/wooden protection at the both sides of tubes and suitably protected for sea-worthly delivery or as requested.
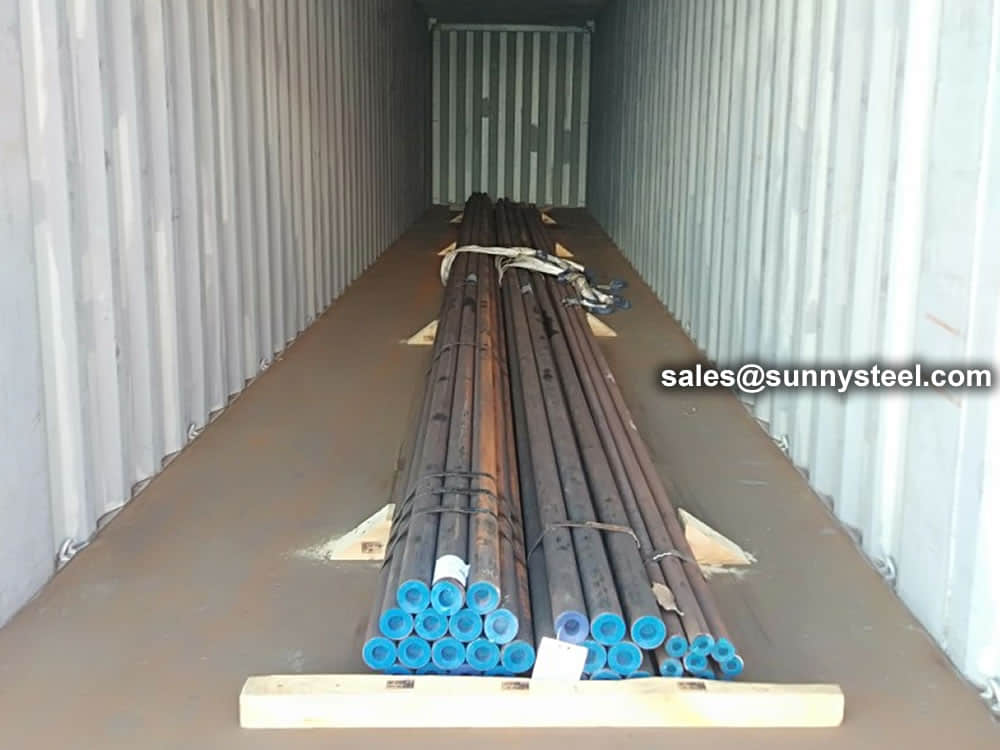
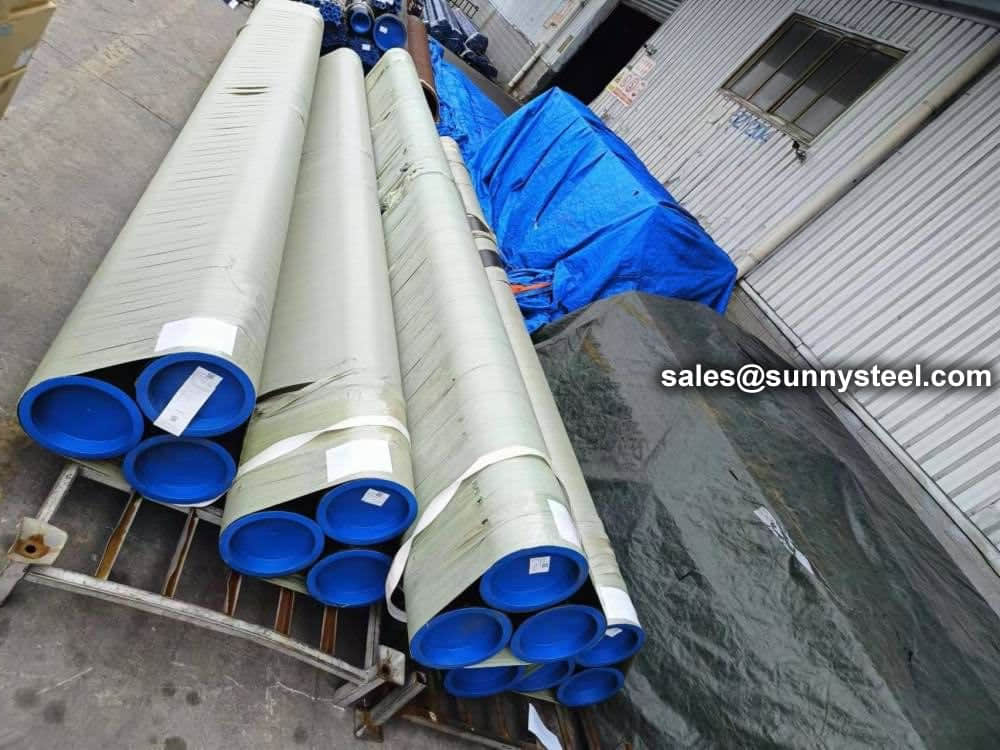
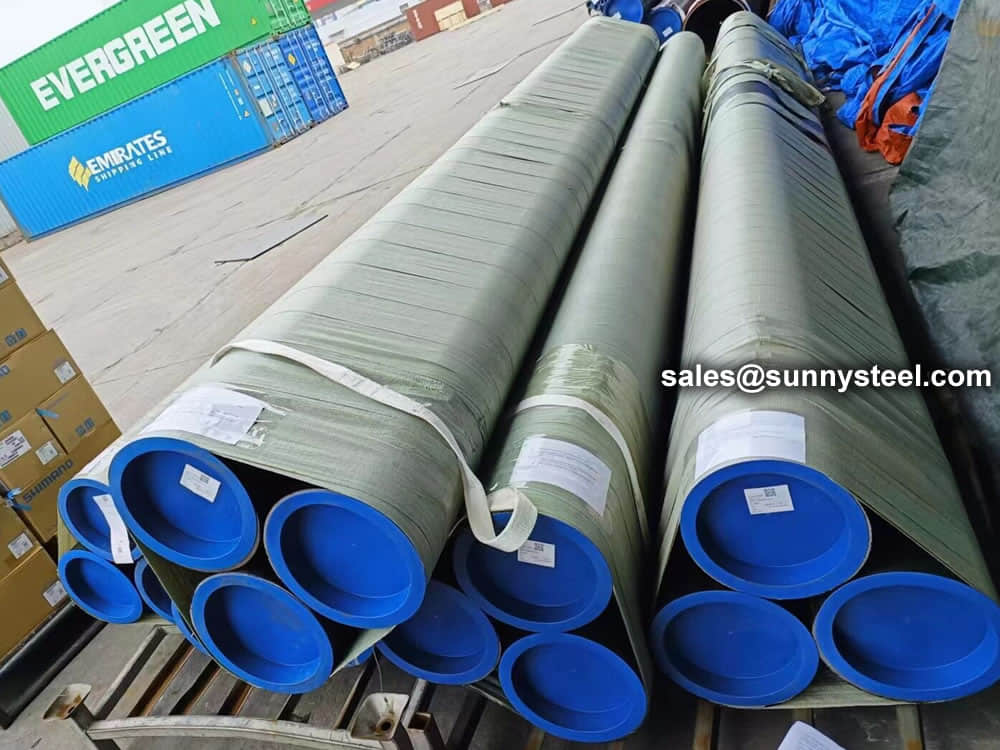
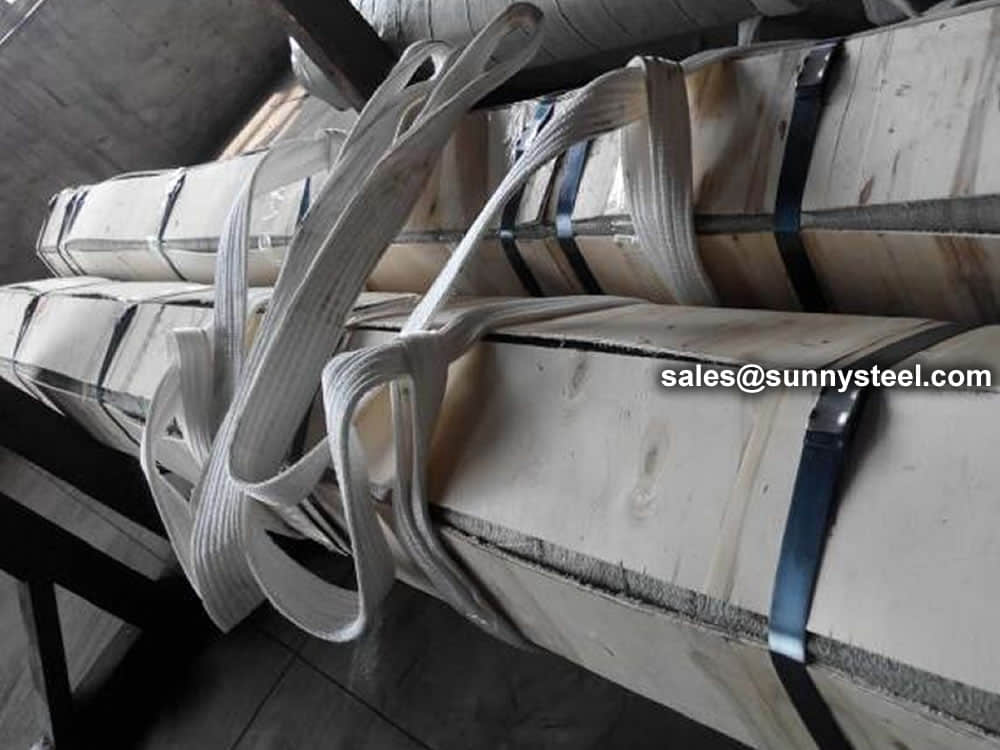
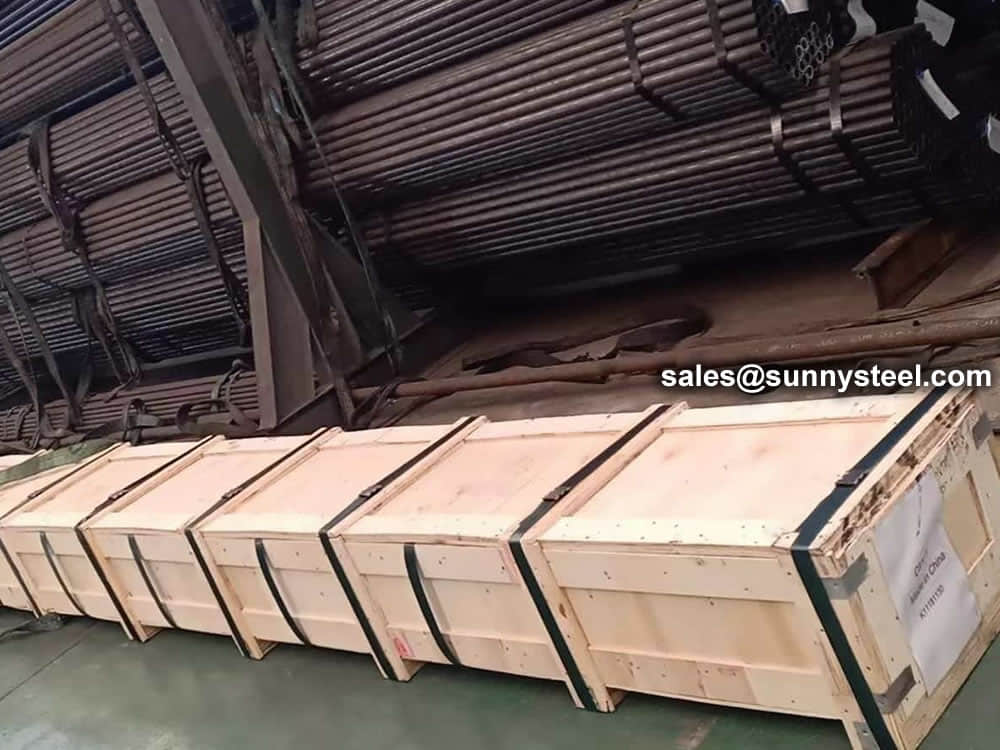
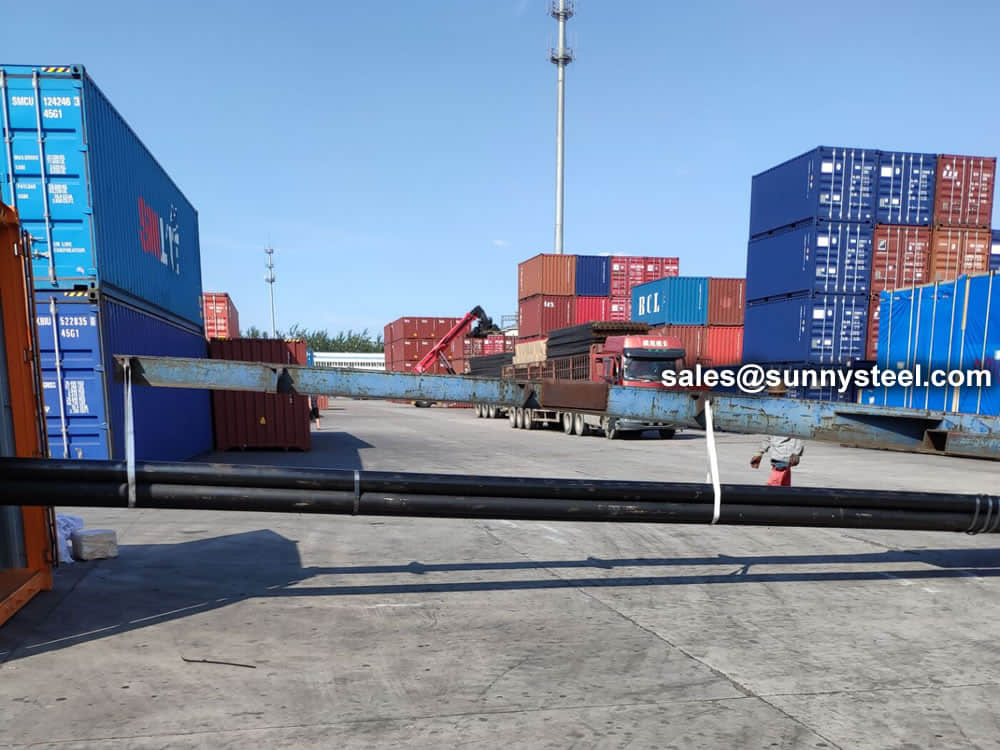
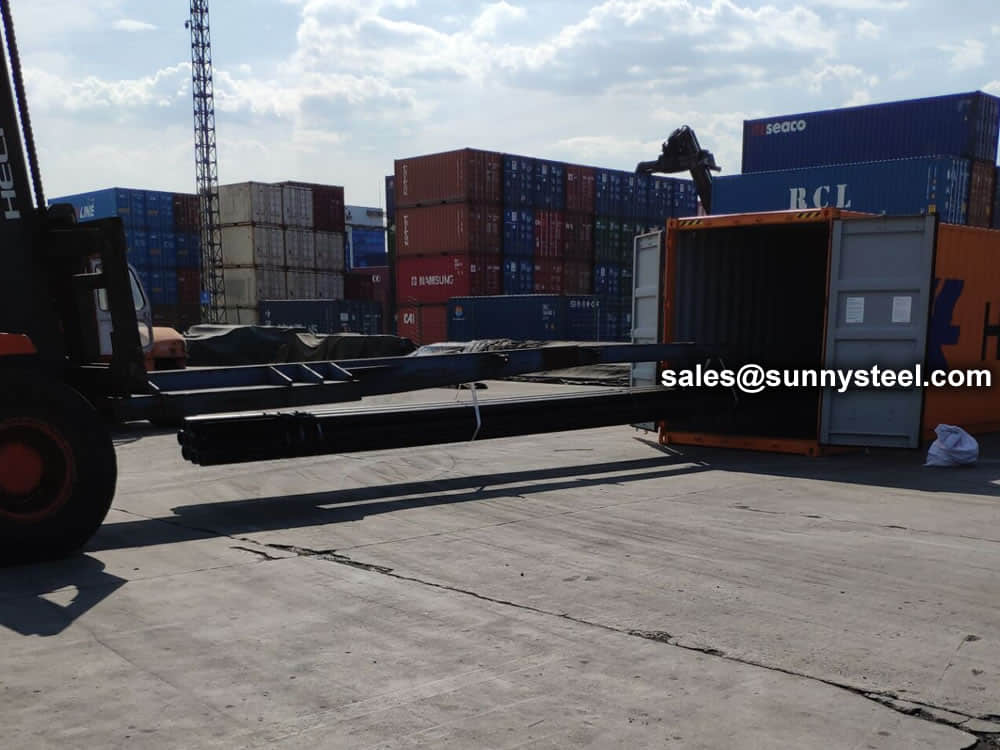
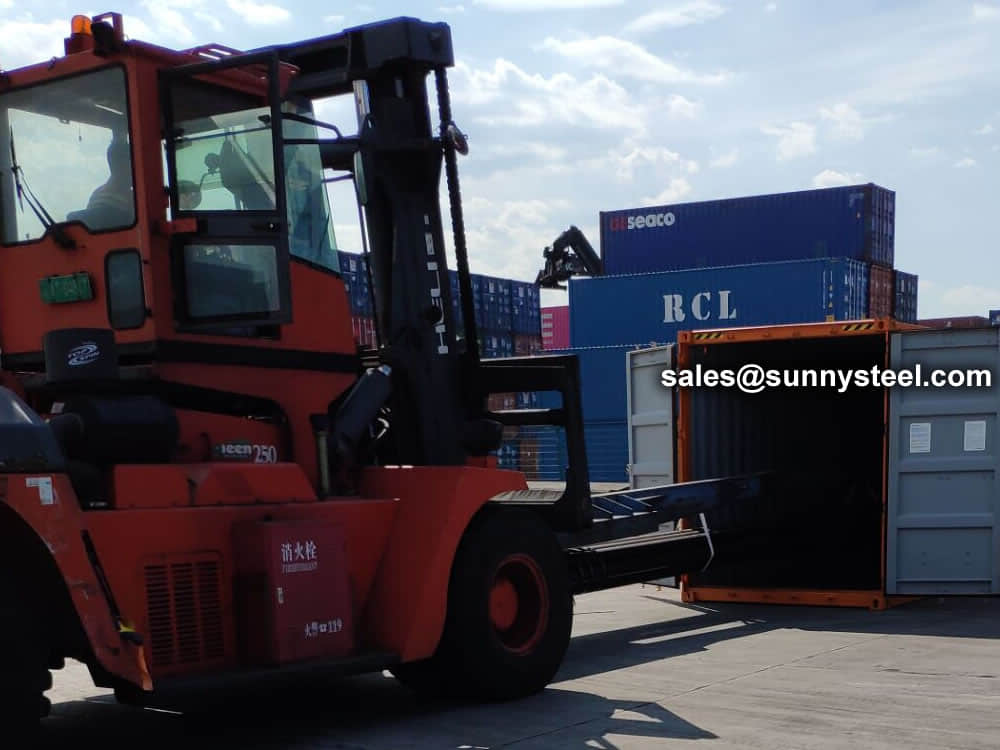
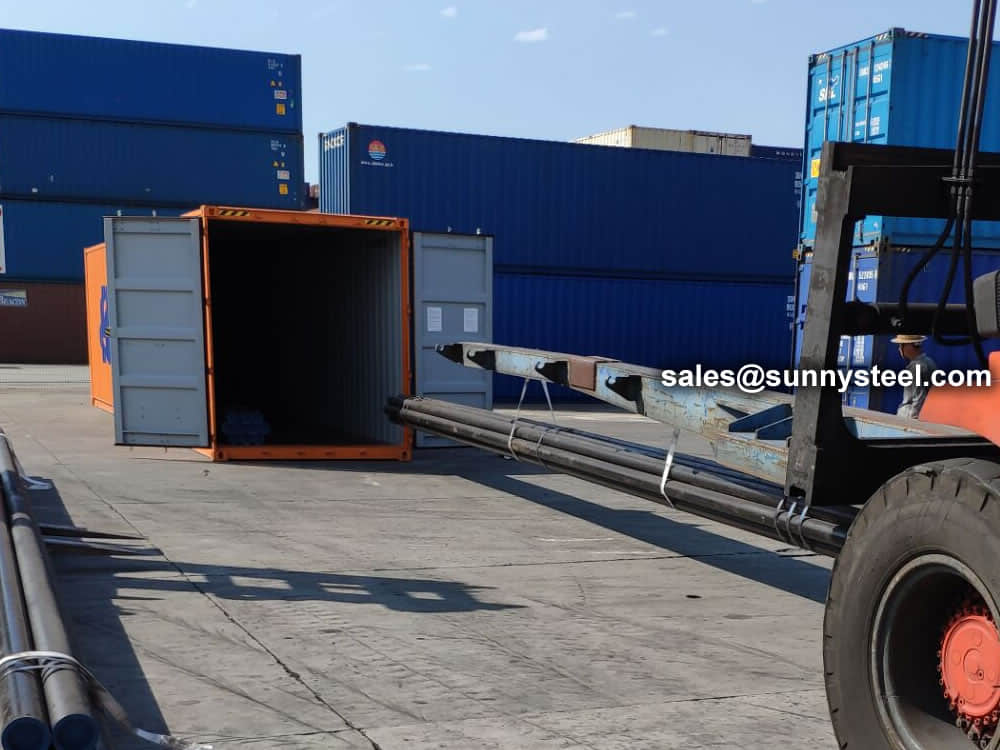
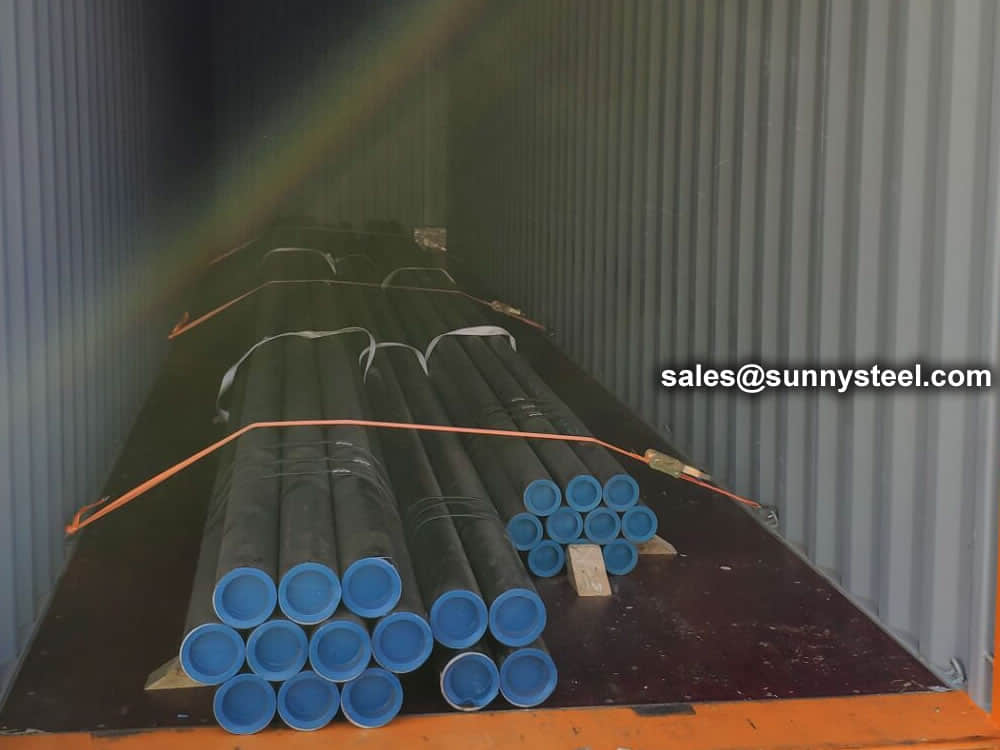
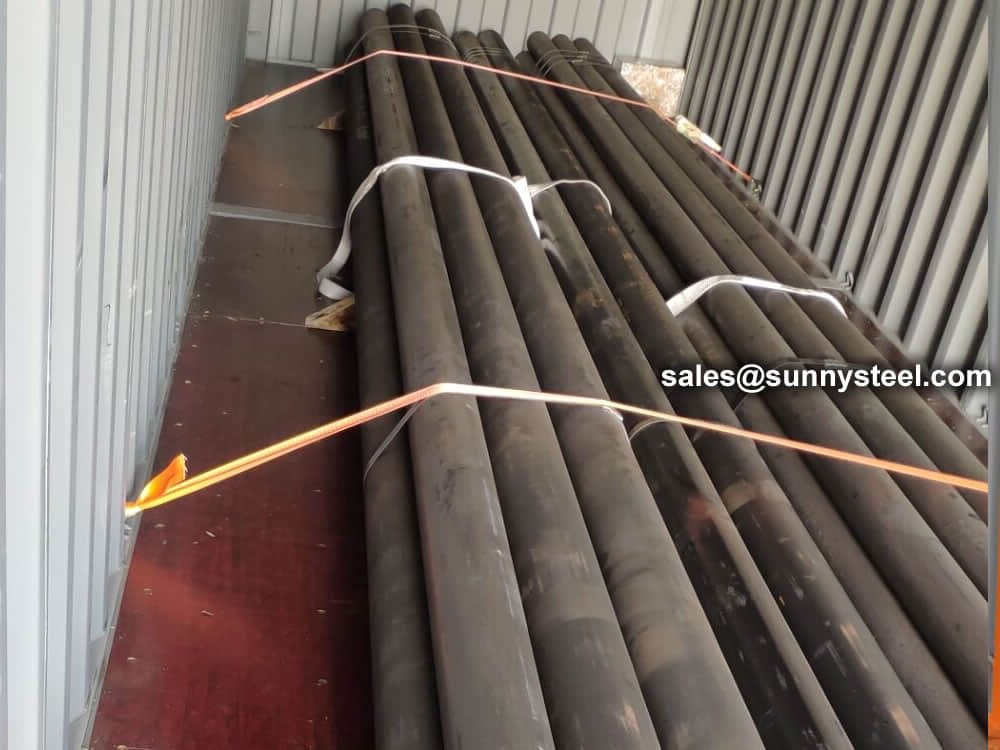












There are probably hundreds of different methods for packing a pipe, and most of them have merit, but there are two principles that are vital for any method to work prevent rusting and Sea transportation security.
Our packing can meet any needs of the customers.

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
