Flexible Rubber Joint
Read more
Advanced production equipment + scientific management = reliable products
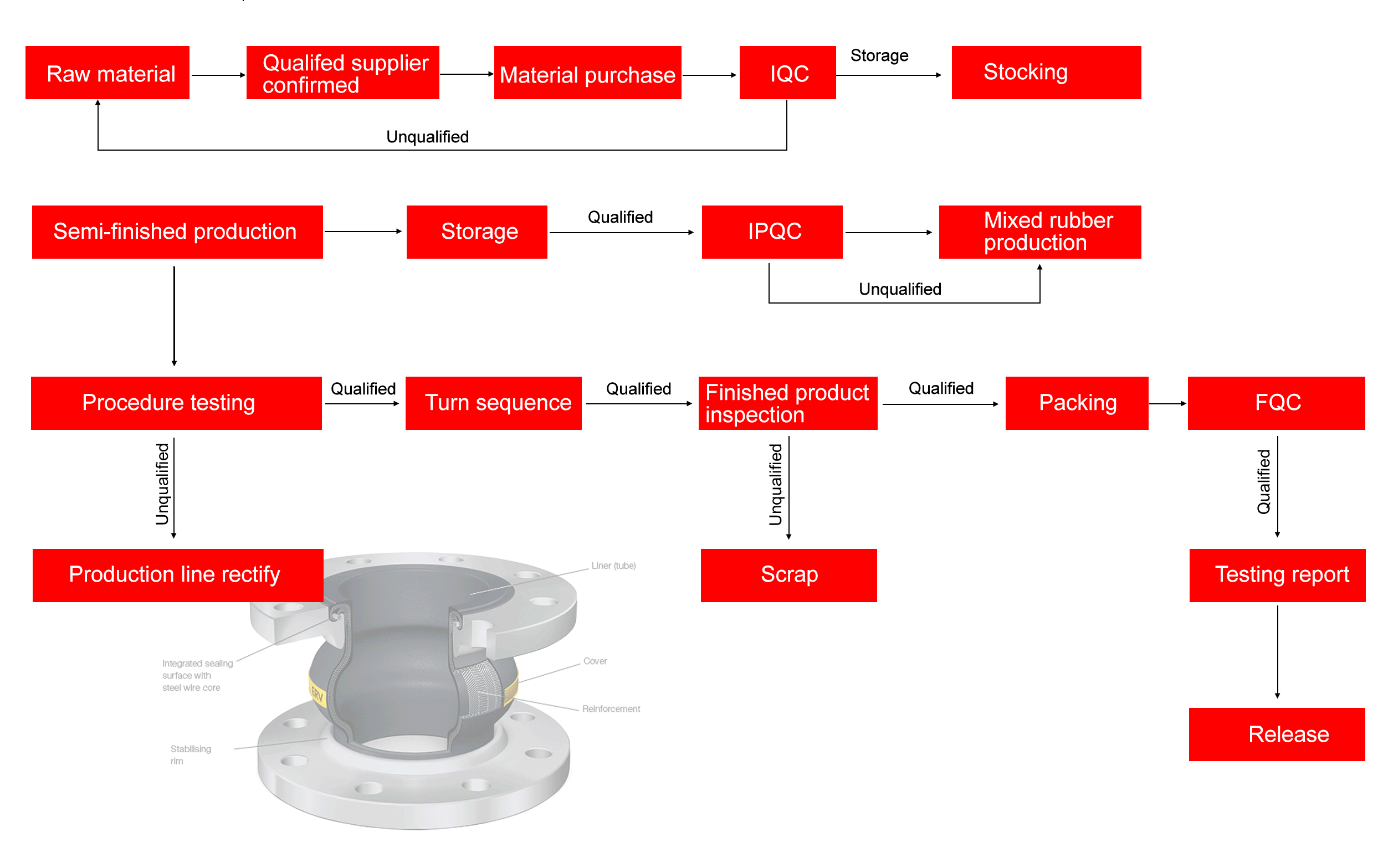
Rubber Expansion Joint Production Management involves several key processes that ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
Effective production management of rubber expansion joints involves a combination of planning, quality control, resource management, and process optimization. Given the critical role these components play in industrial applications, ensuring high-quality production is essential.
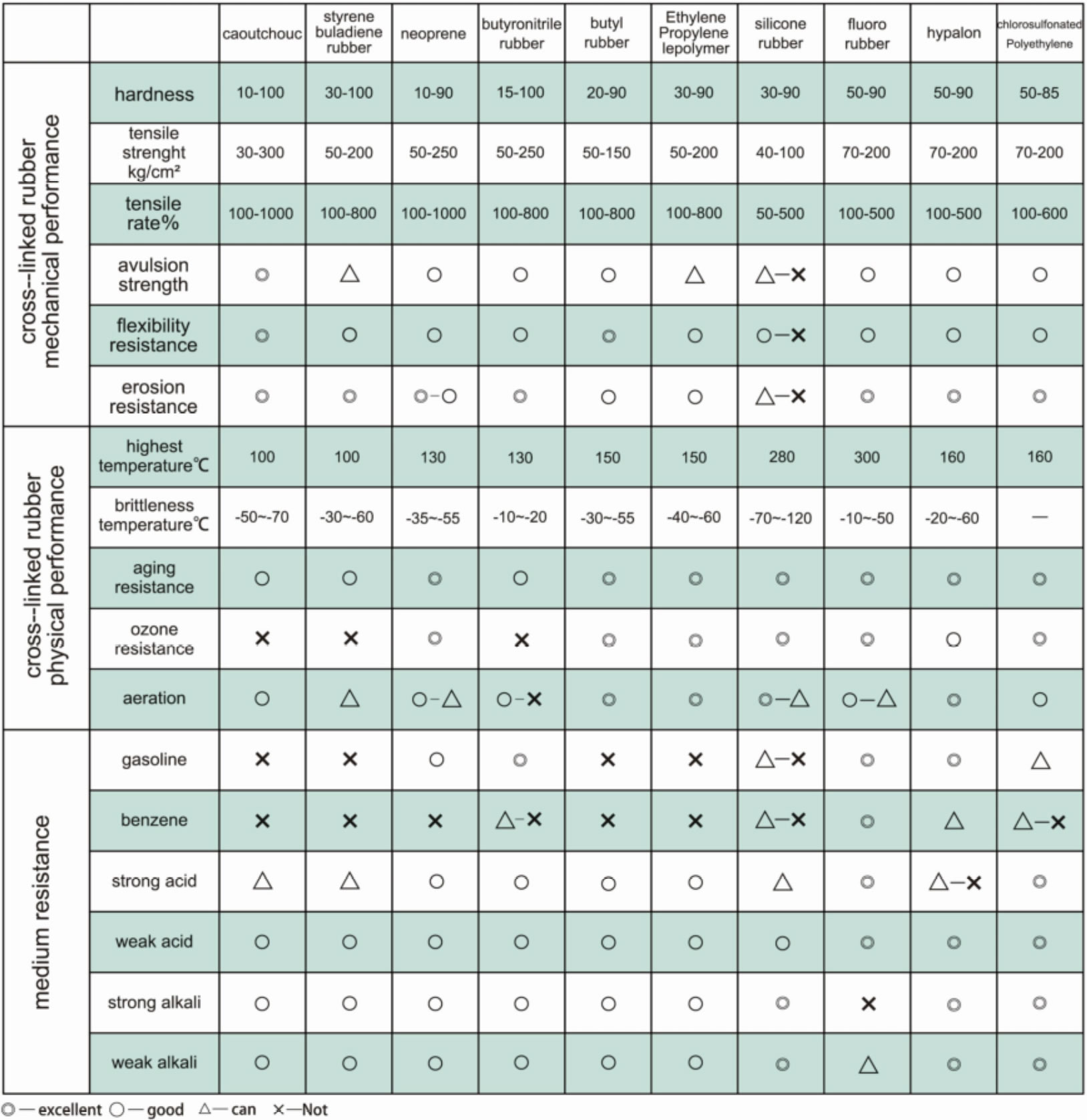
A Rubber Performance Form is typically a document or table used to evaluate and track the key performance characteristics of rubber materials in various applications. This form helps in assessing the suitability of different rubber compounds for specific industrial or product requirements.
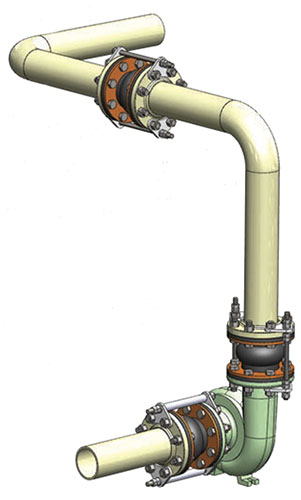
A rubber expansion joint is a vital component in piping and equipment systems designed to address various challenges like vibration, shock, noise, and the natural expansion and contraction that occurs due to temperature fluctuations.
These joints are made from rubber or elastomeric materials that provide flexibility and absorb movement, preventing damage to pipes and equipment while ensuring a smoother and quieter operation. Rubber expansion joints also help mitigate the stresses caused by thermal expansion and contraction, which can lead to leaks, cracks, or premature wear and tear. By absorbing these movements, they contribute to extending the service life of the entire system and maintaining its efficiency.
Rubber expansion joint can also be called flexible rubber joints, rubber soft connections, soft joints, flexible rubber joints, rubber expansion joints, shock absorbers, etc. They are pipeline joints with high elasticity, high air tightness, medium resistance and climate resistance.It can reduce the vibration and noise of pipeline, and compensate the thermal expansion and contraction caused by temperature change.
Expansion joints relieve stresses in piping systems, caused by temperature fluctuations, mechanical vibrations and movements.
Rubber expansion joint is also called rubber tube soft joint, flexible rubber joints, rubber soft joints, flexible rubber joints, high pressure rubber joints, rubber shock absorbers, compensators, etc.
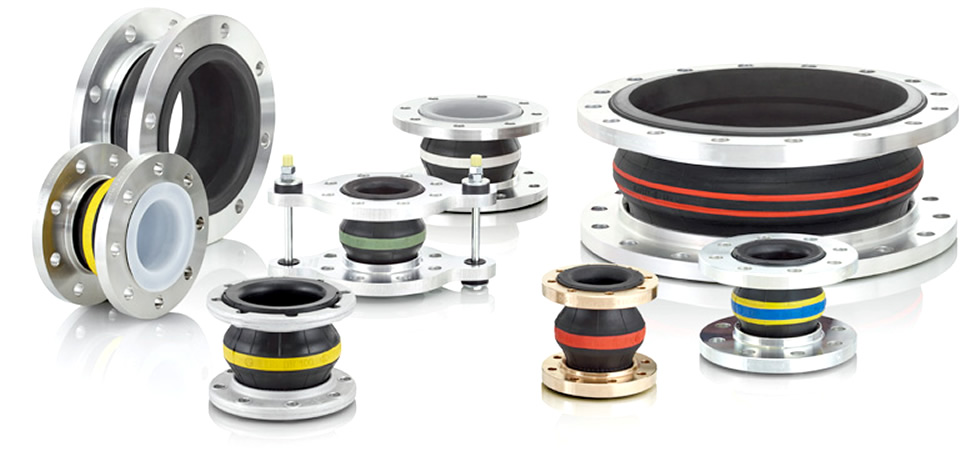

Ein Gummi-Kompensator ist ein flexibles Verbindungselement, das häufig in Rohrleitungs- und Anlagensystemen verwendet wird, um Vibrationen, Schocks, Geräusche sowie thermische Ausdehnung und Kontraktion zu verhindern. Sie tragen dazu bei, die Lebensdauer von Rohren und Anlagen zu verlängern.
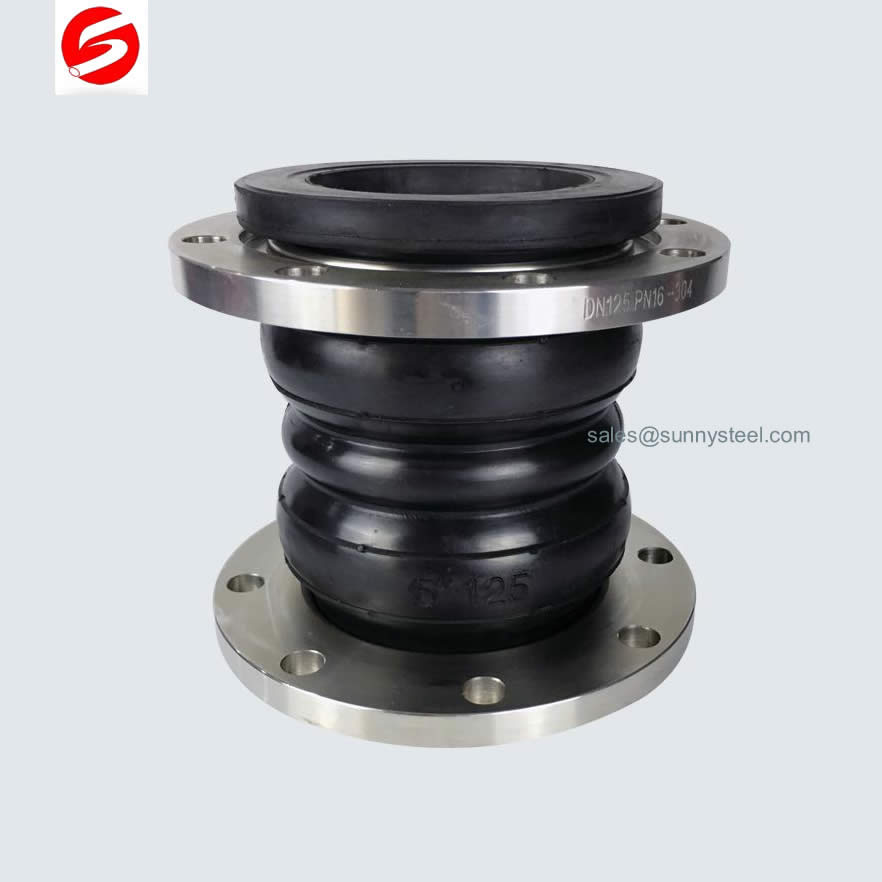
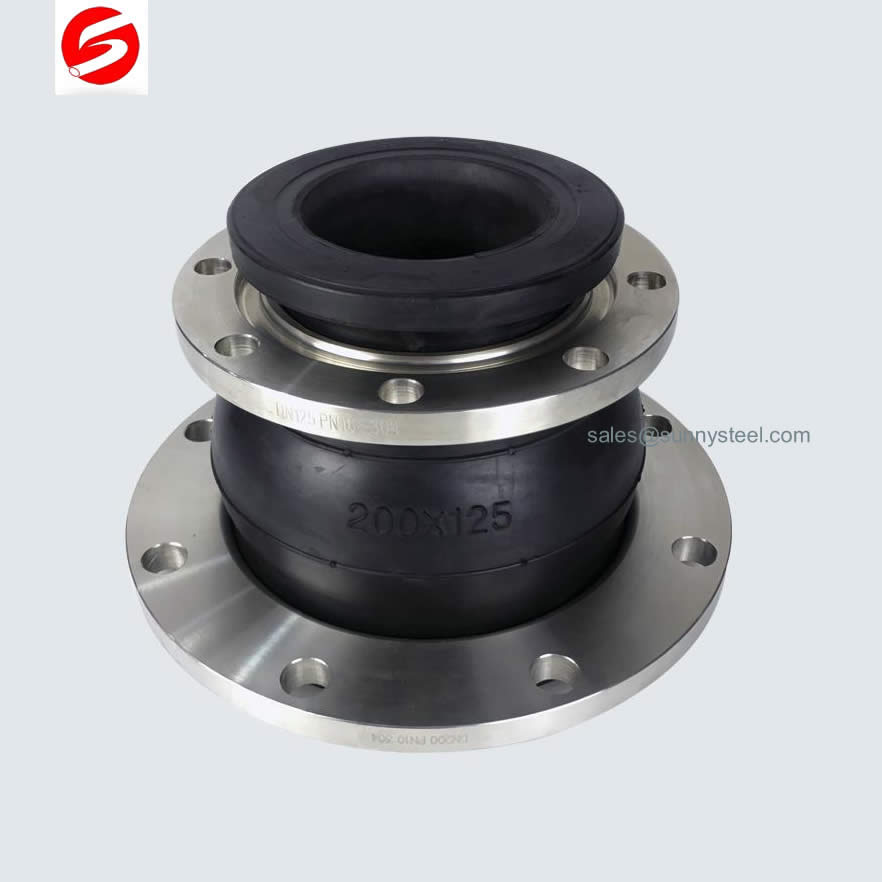



Ein Gummi-Kompensator, auch bekannt als Gummikompensator oder Gummiausgleichselement, ist ein flexibles Verbindungsstück in Rohrleitungssystemen. Es besteht aus Gummibelägen, die mit Stahlgewebe verstärkt sind, um Bewegung, Vibrationen und thermische Ausdehnung zu absorbieren. Die Hauptfunktion eines Gummi-Kompensators besteht darin, Spannungen und Belastungen zu minimieren, die in Rohrleitungen durch diese dynamischen Kräfte entstehen.
Die Flexibilität eines Gummi-Kompensators ermöglicht axiale, laterale und angulare Bewegungen, was ihn besonders nützlich in Anwendungen macht, in denen Rohrleitungen und Ausrüstungen Bewegungen unterworfen sind. In verschiedenen Industrien wie Chemie, Öl und Gas, Wasseraufbereitung und HLK (Heizung, Lüftung, Klimaanlage) finden sie breite Anwendung.
Gummi-Kompensatoren bieten viele Vorteile, darunter Schalldämpfung, Vibrationsabsorption und Stressentlastung, was zu einer erhöhten Langlebigkeit und Lebensdauer von Rohrleitungssystemen führt. Sie sind in verschiedenen Größen und Konfigurationen erhältlich, um den spezifischen Anforderungen verschiedener Anwendungen gerecht zu werden.
Gummi-Kompensatoren unverzichtbare Elemente für effiziente und zuverlässige Rohrleitungssysteme, da sie die Integrität und Leistung der Anlagen verbessern und gleichzeitig vor vorzeitigen Ausfällen schützen.

Sizes from DN25-DN3000 are all available, special sizes and lengths can also be customised, please contact us for exact data.
| Operation Condition | Details |
|---|---|
| Working temperature | -15-80℃(-30~150℃) |
| Working pressure | 6~40 bars (PN6~PN40) |
| Test pressure | 1.5 times of working pressure |
| Explosion pressure | 2 times of working pressure |
| Applicable media | Air, water, sewage, sea water, acid, alkali, oil etc. |




These joints are critical in absorbing movement, reducing stress, and compensating for misalignment in pipes.








Rubber compensators are widely applied in a variety of industrial pipelines, in power plants, in heating networks (heat transfer stations) and sanitary installations (sewage treatment plants and pumping stations, water treatment stations and machines). Basically, they are mounted near components that produce vibrations (pumps, engines, turbines, compressors etc.). They absorb different movements: axial, lateral and angular that result from thermal expansion of the pipelines or misalignment. They dampen vibration and noise and absorb the energy of pressure variations.
Rubber expansion joints offer flexibility allowing concurrent movements, isolation of vibration, reduction of noise, resistance to abrasion and chemical erosion within fluid systems.
Here are the key benefits of rubber expansion joints:
Rubber joints can absorb greater movements when compared to similar length metal expansion joints. Equipment such as pumps, compressors and piping can move out of alignment due to wear and settling of their supporting structures. Rubber expansion joints can routinely manage the resulting lateral, torsional and angular movements whilst strategically located rubber expansion joints can mitigate thermal expansion and contraction movements. Metal joints typically have a lower lateral movement capability and the allowance for movement offered by rubber expansion joints has positive benefits in extending system life and maintenance intervals.
Reducing vibration is important to prevent unbalanced forces building up to a level where they can damage a fluid system. Rubber pipe and expansion joints dampen these disturbances and provide resistance against shock stress from hydraulic surge and water hammer.
As systems age and wear, imbalances occur which cause unwanted noise. Rubber expansion joints dampen sound transmission with their rubber to steel interface. When compared to full metal joints, thick-walled rubber expansion joints offer a much higher reduction of sound transmission.
Metal joints are typically thin wall elements, having a wall thickness anywhere between 0.15mm to 2mm. Rubber joints are thicker, from 12mm to over 25mm. Metal expansion joints are susceptible to chemical erosion and abrasion whereas rubber joints are resistant to abrasion and erosion.
A wide variety of natural, synthetic, and special purpose elastomers and fabrics are available to create high performance rubber expansion joints to meet challenging operating conditions. Special polymers resist chemicals, oil, sunlight, acid fumes, ozone and external coatings can be added for further protection.
Expansion joints may use PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) and FEP (fluoroethylene propylene) liners within the joint body. When fluoroplastics are used in rubber expansion joints this results in better thermal stability, low friction and resistance to corrosive fluids, chemicals, abrasion and erosion.
The ability to flex and absorb gives rubber expansion joints a distinct advantage over metal joints since natural and synthetic elastomers are not subject to fatigue breakdown, loss of ductility or electrolytic reaction. This results in a long-lasting expansion joint.
Rubber expansion joints are light in weight compared to metal expansion joints, making them easy to handle and install. The vulcanized rubber and fabric flanges of elastomeric expansion joints are integrated and therefore do not require additional gaskets which also eliminates the need for ongoing gasket maintenance checking. Additionally, elastomeric expansion joints can equalize the uneven surfaces of the pipe flange to provide a gas tight seal.
Rubber expansion joints appear in all fluid systems. Rubber expansion joints relieve stress from movement, isolate vibration, reduce noise and compensate for misalignment in piping systems. Rubber expansion joints do not replace metal expansion joints in all applications but are recognized as the best choice for many applications involving high vibration and sound dampening.
Here are examples of applications that utilize rubber expansion joints:
Rubber expansion joints and connectors are the ideal choice for many piping situations, and they have several uses.
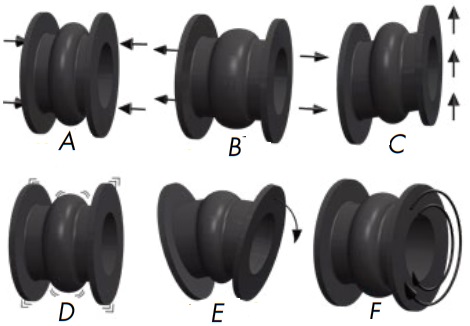
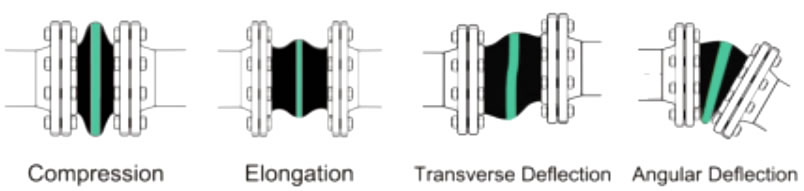
The function of a rubber expansion joint and the absorption of various movements:
A-axial compression, B-axial elongation, C-lateral or transverse movement, D-vibration, E-angular movement, F-torsional movement.
As illustrated in the picture, rubber expansion joints are primarily designed to absorb and compensate for various movements and vibration in a piping systems:
Rubber Expansion Joints for Piping Systems provide time-tested ways to accommodate pressure loads, relieve movement stresses, reduce noise, isolate vibration, compensate for misalignment after plants go on stream, and prolong the life of motive equipment. Rubber expansion joints are available in a variety of styles and are used to convey fluid under vacuum pressure conditions in piping systems. Flanged rubber expansion joints are most common and are available in single – and multi-arch designs. They can be custom-engineered to fit your application requirements. Our rubber expansion joints are particularly beneficial due to their flexible nature, which makes them suitable for many functions, including the absorption of sound, thermal energy and shock. They are specifically designed to reduce the need for maintenance, repair and manual assistance.
Flexible rubber expansion joints offer several benefits in piping systems, contributing to the overall performance, reliability, and longevity of the system. Here are some key advantages:
Changes in temperature and pressure in piping systems connected to pumps lead to thermal expansion and contraction within the pipes. Rubber expansion joints and connectors are the ideal choice for many piping situations, and they have several uses. Rubber expansion joints are most often used as a flexible connector between a vibrating piece of mechanical equipment and the pipeline. They can also be used to absorb pipe movements. Rubber connectors will also provide for a reasonable amount of pipe offset caused by equipment settling.
Available options include PTFE-lined, eccentric reducing, concentric reducing, filled arch, lightweight and off-set configurations. They can be designed to operate up to 200 psi and withstand temperatures up to 500º F. Sizes available from 1/2″ to 144″.
Careful selection of the expansion joint design and material for a given application, as well as properly engineered installation are important factors in determining performance. These factors should be fully evaluated by each person selecting and applying expansion joints for any application.
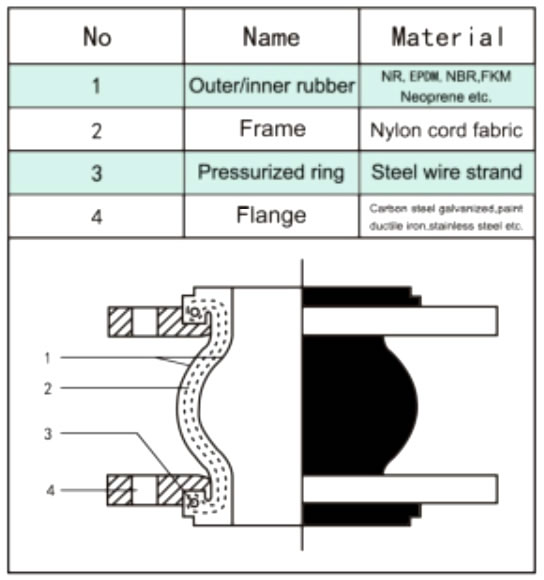
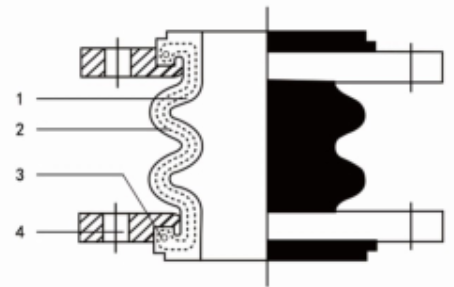
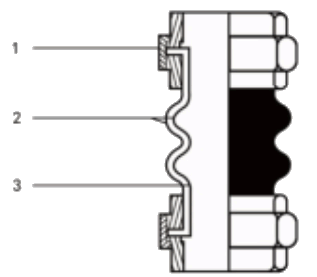
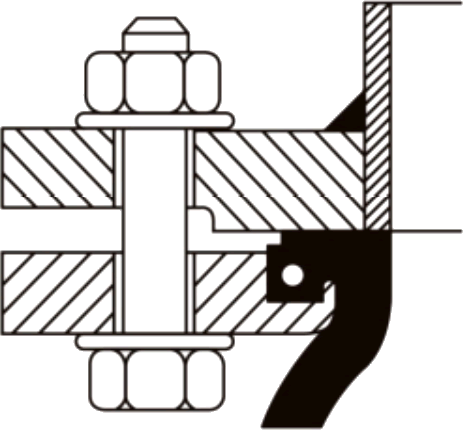
A rubber expansion joint generally consists of inner tube, cover and carcass. The inner tube shall be made of natural rubber, synthetic rubber, or blend of synthetic rubber. It is a seamless protective, leak-proof lining that extends through the bore to the outside edges of the joint. Since the inner tube is in direct contact with the flowing media, it shall be designed to cover service conditions for chemical, petroleum, sewage, gaseous and abrasive materials. The purpose of the tube is to eliminate the possibility of the materials being handled penetrating the carcass and weakening the fabric. The cover is the exterior surface of the joint that is formed from natural or synthetic rubber. The prime function of the cover is to protect the carcass from outside damage caused by atmospheric chemicals, oils, air, sunlight, vapor, etc. The carcass or body of the rubber expansion joint is the flexible and supporting member between the tube and cover. It is the structural framework of the joint and is made from multiple plies woven fabric or tire cord impregnated with synthetic rubber. Steel wires or solid metal rings are often embedded in the carcass to provide additional reinforcement to the body fabric.
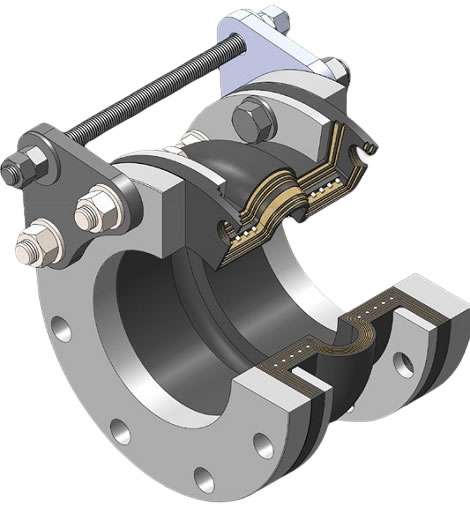
3-dimensional model of a spool arch type rubber expansion joint
(1) Integral Rubber Flanges – The end connection flanges of the joint are integrally formed as a part of the elastomeric bellows. It is also called “spool arch type rubber expansion joint”.
(2) Floating Metallic Flanges – The metal flanges shall have a groove to accept the molded bead in the body at each end of the expansion joint bellows.
(3) Spherical Type – Long radius arch, either single sphere or twin sphere, to provide better movement capability and strength.
(4) Control Units – Tie rods or control rods are provided to minimize possible damage to the expansion joint caused by excessive motion of the piping system.
(5) Custom Designs – rectangular flange connection, threaded union connection, tapered reducer type, no-arch U type, hinged type, gimbal type, sleeve type, PTFE lined type.
Carcass
The body of the expansion joint consisting of fabric and / or interior metal reinforcement.
Cover
The natural or synthetic rubber exterior of the joint which protects the carcass from damage.
Fabric Reinforcement
A synthetic or natural fabric between the tube and cover that flexibly supports the expansion joint for movement or pressure.
Metal Reinforcement
Solid rings or wire embedded in the carcass which strengthen the expansion joint to withstand high pressure or vacuum.
Tube
A protective, leak-proof lining tube that extends through the bore to the outside edges of the flanges to eliminate the possibility of the fluids penetrating the carcass and weakening the fabric.
| Single Sphere | Twin Sphere | Union Spherical |
| Spool Arch | Tie Rods | Special Design |
| Flange Drilling | Installation & Maintenance | Testing & Inspection |
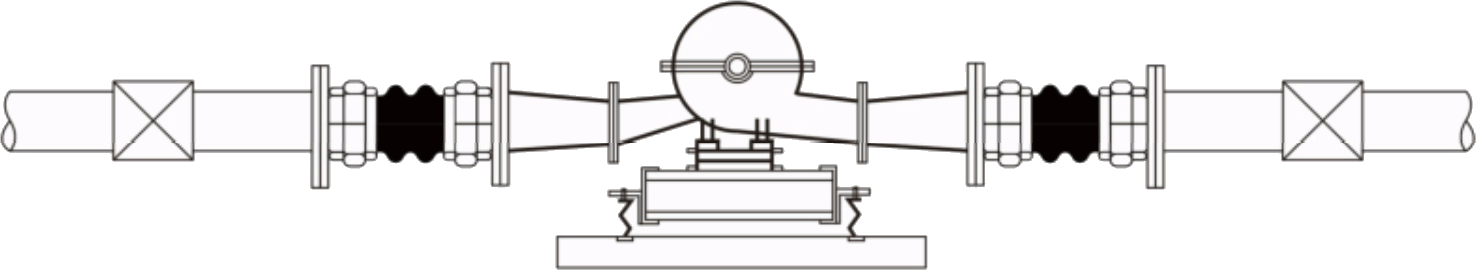
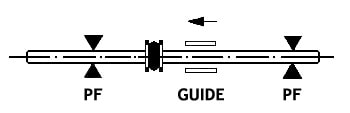
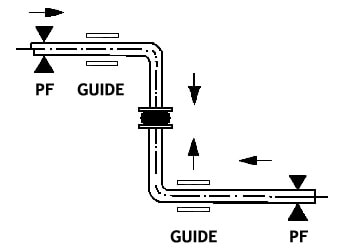
A rubber expansion joint can be used as a flex connector, to absorb noise and vibration from adjacent equipment. In this application, there are usually not anchors in the piping systems and the rubber expansion joint should employ control units to keep the product from expanding under pressure. Control unit nuts should be snug (using 1/4″ thick rubber washers. Alternately, these connectors can be used as a piping expansion joint to absorb thermal pipe growth or temporary pipe movements. Like metal bellows expansion joint systems, in these cases, this rubber product becomes part of the expansion joint system which includes main anchors and pipe alignment guides. Rubber expansion joints can also be used as both flex connectors and expansion joints in the same system. When using rubber connectors as an expansion joint in the piping system, they may or may not be located next to vibrating equipment. Control units can be used as a back-up safety device in the case of an main anchor failure, but nuts and washers should be loosened to allow for the full extension or contraction of the expansion joint.

(Above) Rubber connector used as an expansion joint to take up thermal growth and other pipe movements. There are anchors located on either side of the expansion joint, the joint is located as close to an anchor as possible, and pipe alignment guides are spaced out on the piping to prevent pipe bucking under column loads.
(Above) Rubber connectors used as flex connectors for noise and vibration. There are no piping anchors present and control units are installed on the rubber connectors.
Introducing a flexible product like an expansion joint to your piping system adds an aspect that must be taken into consideration when designing the piping system. Due to pressure thrust forces and spring loads, main anchors must be engineered to handle these increased loads. Unless restrained by control rods, expansion joints expand under pressure, creating pressure thrust forces on the anchors. In addition, the inherent stiffness of the expansion jointy must be overcome in order for these products to absorb thermal pipe growth. For each size and type of expansion joint, we can calculate the effective area of the joint. This figure is multiplied by the system pressure to determine the pressure thrust force. Each product and size also has a spring rate–the force required to compress, expand or offset the product by 1-inch. If we are expecting, for instance, 2-inches of pipe growth and the compression spring rate of our rubber expansion joint is 1000 lbs. per inch, our spring force is calculated to be 2000 lbs. This figure will be added to the pressure thrust force to determine the combined force on system anchors.

There are many choices of styles and configurations of rubber expansion joints. Rubber spheres are mainly used as flex connectors and connected to HVAC equipment to absorb noise and vibration. This type of connector is available in single sphere and double sphere flanged connectors, and double sphere threaded connectors. Flanges are made of plated steel and are able to rotate for easy alignment. Generally, these connectors are made of EPDM or Neoprene rubber. Spool or arch type rubber expansion joints are generally built for more specified applications. They are at least partially hand-built, with wrapped rubber covers, duck and rubber flanges, and a sharp arch configuration to absorb pipe movements. Consider these configuration choices:

Multiple arches

Reducing style

Enlarged flange

Filled arch

Metal liners

Sleeve type
Choosing the appropriate elastomer is crucial when your pipeline conveys liquids other than water. Different elastomers, fluoroelastomers, and fluoroplastics offer varying levels of compatibility with chemicals and abrasive slurries.
Expansion joint liners can be customized to handle a range of substances, including raw sewage, acids, alkaline solutions, hot air, drinking water, abrasive slurries, and more. Some popular elastomer choices include:
Note: Rubber expansion joints are not recommended for use with compressed gases, steam, or extreme temperature liquids.
For shipboard services on commercial vessels, we provide rubber expansion joints that meet U.S. Coast Guard and Federal Regulations standards. Additionally, our mil-spec joints for the U.S. Navy can be built with ANSI flange drilling or Navy drilling.
Carefully consider the maximum pressure your piping system may experience, especially during hydro-testing. Standard rubber expansion joints generally support working pressures from 150 to 225 PSI for most sizes, but higher-pressure options are available upon request. However, keep in mind that higher-pressure expansion joints tend to be heavier and more rigid.
Most rubber expansion joints are reinforced with polyester fabric layers along with steel hoops to enhance vacuum resistance. For even higher pressure ratings, Kevlar reinforcement might be recommended.
Rubber expansion joints are available in sizes ranging from 1-1/2 inches to 36 inches. Single and double rubber spheres, produced using hydraulic molds, come in sizes from 1-1/2 inches to 16 inches, with larger sizes (up to 20 inches) available by special order. Spool-type or arch-type expansion joints can be manufactured in larger diameters, from 1-1/2 inches up to 102 inches.
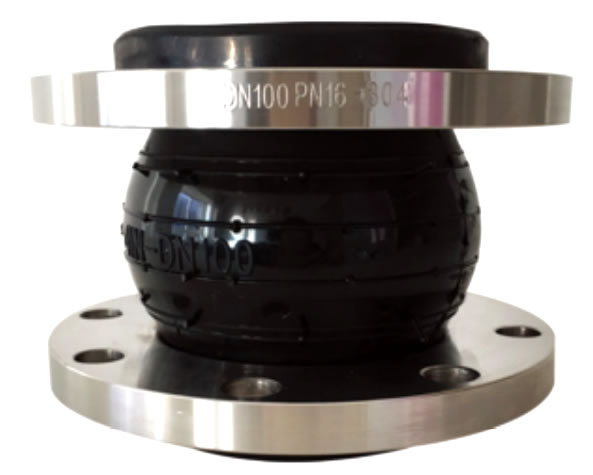
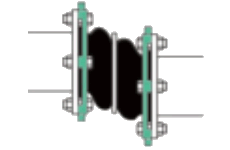
The Double Sphere Rubber Expansion Joint (REJ200) is a type of flexible connector used in piping systems to absorb movement, reduce stress, and compensate for misalignment. This type of expansion joint is designed with two spherical bellows, which enhance flexibility and allow for greater movement absorption compared to single sphere models.

| No. | Name | Material |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Outer/inner rubber | NR, EPDM, NBR, FKM, Necprnce etc. |
| 2 | Frame | Nylon cord fabric |
| 3 | Pressurized ring | Steel wire strand |
| 4 | Flange | Carbon steel/ Stainless |
|
||
| Nominal diameter | Length (mm) | Axial movement | Horizontal movement (mm) |
Defiection angle (a-a) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | inch | Extension |
Compression |
|||
| 40 | 1 | 165 | 30 | 50 | 45 | 35 |
| 50 | 2 | 165 | 30 | 50 | 45 | 35 |
65 |
2.5 | 170 | 30 | 50 | 45 | 35 |
| 80 | 3 | 175 | 35 | 50 | 45 | 35 |
| 100 | 4 | 225 | 35 | 50 | 40 | 35 |
| 125 | 5 | 225 | 35 | 50 | 40 | 35 |
| 150 | 6 | 225 | 35 | 50 | 40 | 35 |
| 200 | 8 | 325 | 35 | 50 | 40 | 35 |
| 250 | 10 | 325 | 35 | 60 | 35 | 30 |
| 300 | 12 | 325 | 35 | 60 | 35 | 30 |
| 350 | 14 | 350 | 35 | 60 | 35 | 30 |
| 400 | 16 | 350 | 35 | 60 | 35 | 30 |
| 450 | 18 | 350 | 35 | 60 | 35 | 30 |
| 500 | 20 | 350 | 35 | 60 | 35 | 30 |
| 600 | 24 | 400 | 35 | 60 | 35 | 30 |

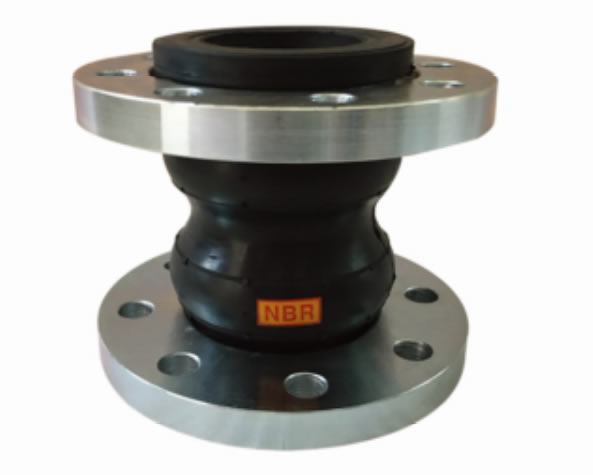
| No | Name | Material |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Union | Malleable iron, ss304 |
| 2 | Outer/inner rubber | NR, EPDM, NBR, FKM, Neoprene etc |
| 3 | Frame | Nylon and fabric |
|
||
| Nominal diameter | Length (mm) | Axial movement | Horizontal movement (mm) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | inch | Extension |
Compression |
||
| 15 | 1/2 | 200 | 22 | 5-6 | 22 |
| 20 | 3/4 | 200/220 | 22 | 5-6 | 22 |
| 25 | 1 | 200 | 22 | 5-6 | 22 |
| 32 | 1 1/4 | 200/220 | 22 | 5-6 | 22 |
| 40 | 1 1/2 | 200/220 | 22 | 5-6 | 22 |
| 50 | 2 | 200/220 | 22 | 5-6 | 22 |
| 65 | 2 1/2 | 240 | 22 | 5-6 | 22 |
| 80 | 3 | 280 | 22 | 5-6 | 22 |
| Content | Details |
|---|---|
| OEM and ODM service | Are supported by SunnySteel! |
| Packing | Usually it is packed by carton case, then put into export plywood case. |
| Normal working pressure | PN16 (Special pressure can be customized) |
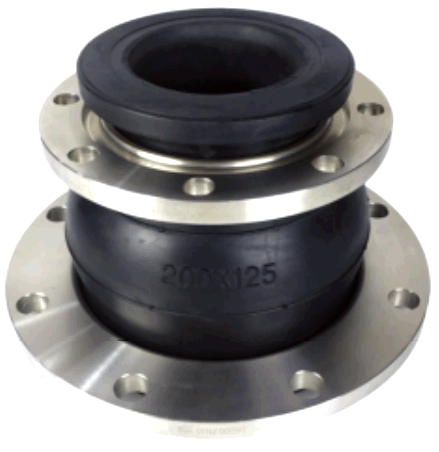
The Rubber Expansion Joint End Face Fully Sealed (REJ400) is a specialized type of rubber joint designed for sealing and protecting piping systems under high-pressure and temperature conditions.

| No. | Name | Material |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Outer/inner rubber | NR, EPDM, NBR, FKM, Necprnce etc. |
| 2 | Frame | Nylon cord fabric |
| 3 | Flange | Carbon steel, 304, 316L |
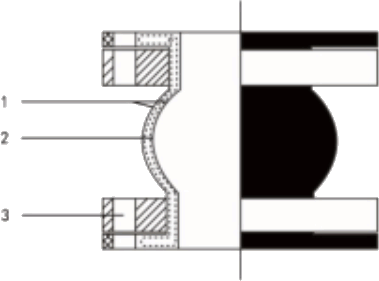
|
||

| Nominal diameter | Length (mm) | Axial movement | Horizontal movement (mm) |
Defiection angle (a-a) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | inch | Extension |
Compression |
|||
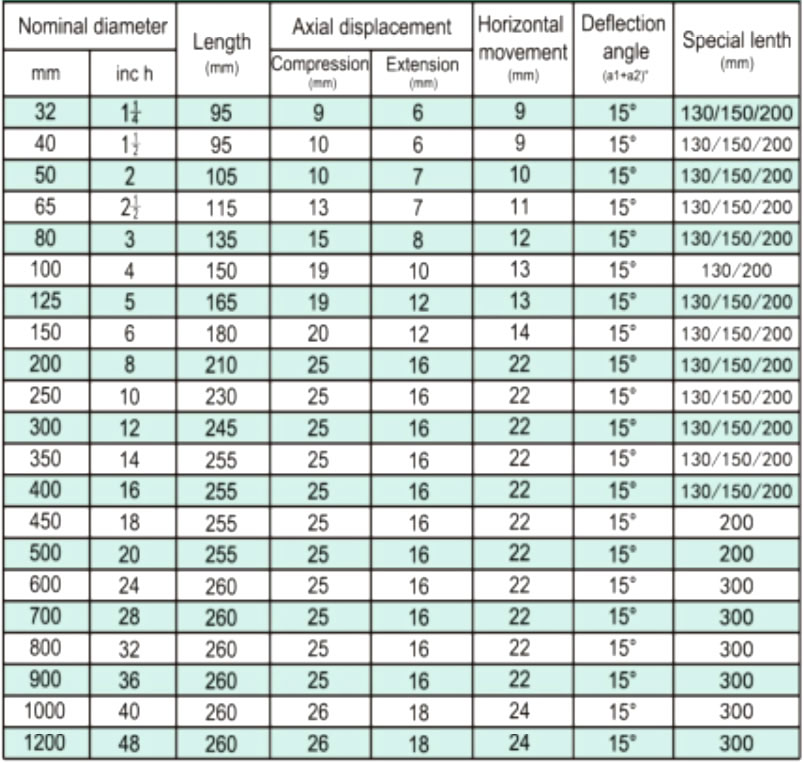
| 32 | 1 1/4 | 95 | 6 | 9 | 9 | 15° |
| 40 | 1 1/2 | 95 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 15° |
| 50 | 2 | 105 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 15° |
| 65 | 2 1/2 | 115 | 7 | 13 | 11 | 15° |
| 80 | 3 | 135 | 8 | 15 | 12 | 15° |
| 100 | 4 | 150 | 10 | 19 | 13 | 15° |
| 125 | 5 | 165 | 12 | 19 | 13 | 15° |
| 150 | 6 | 180 | 12 | 20 | 14 | 15° |
| 200 | 8 | 210 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 250 | 10 | 230 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 300 | 12 | 245 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 350 | 14 | 255 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 400 | 16 | 255 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 450 | 18 | 255 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 500 | 20 | 255 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 600 | 24 | 260 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 700 | 28 | 260 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 800 | 32 | 260 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 900 | 36 | 260 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 1000 | 40 | 260 | 18 | 26 | 24 | 15° |
| 1200 | 48 | 260 | 18 | 26 | 24 | 15° |

| No | Name | Material |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Outer/inner rubber | NR, EPDM, NBR, FKM, Necprnce etc. |
| 2 | Frame | Nylon cord fabric |
| 3 | Pressurized ring | Steel wire strand |
| 4 | Flange | Carbon steel/ Gal, Stainless |
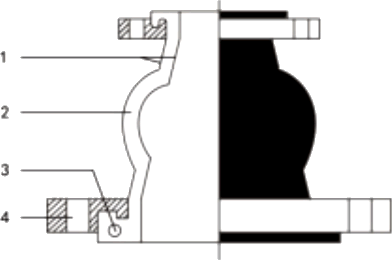
|
||
| DN x DN | Length (mm) | Axial displacement | Horizontal movement | Deflection angle | DN x DN | Length (mm) | Axial displacement | Horizontal movement | Deflection angle | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extension | Compression | (mm) | (a1 +a2) | Extension | Compression | (mm) | (a1 +a2) | ||||
| (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | ||||||||
| 32×25 | 115 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 35° | 125×100 | 200 | 22 | 30 | 40 | 35° |
| 40*25 | 115 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 35° | 150x50 | 200 | 22 | 30 | 40 | 35° |
| 40×32 | 115 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 35° | 150x125 | 200 | 25 | 35 | 40 | 30° |
| 50*32 | 180 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 35° | 200*80 | 200 | 25 | 35 | 40 | 30° |
| 50x40 | 180 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 35° | 200x150 | 200 | 25 | 35 | 40 | 30° |
| 65x32 | 180 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 35° | 250x100 | 220 | 25 | 35 | 40 | 30° |
| 65x50 | 180 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 35° | 300×250 | 220 | 25 | 35 | 40 | 30° |
| 80x40 | 180 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 35° | 350x300 | 240 | 25 | 35 | 35 | 30° |
| 80x65 | 180 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 35° | 400x350 | 240 | 25 | 38 | 35 | 30° |
| 100x40 | 180 | 22 | 30 | 40 | 35° | 500x300 | 240 | 28 | 38 | 35 | 26° |
| 100x80 | 180 | 22 | 30 | 40 | 35° | 500x400 | 240 | 28 | 38 | 35 | 26° |
| 125x50 | 180 | 22 | 30 | 40 | 35° | 600x400 | 240 | 28 | 38 | 35 | 26° |
Special size and length can be customized production for you.
According to the connection method, there are three kinds of flange type, fixed flange type and thread type; according to the structure, it can be divided into five types: single sphere, double sphere, different diameter body, curved sphere and wind pressure coil. The tubular rubber piece is composed of inner and outer rubber, ply and traveler, and is formed by vulcanization molding and loosening with metal flange or parallel joint. This product can reduce vibration and noise, and can compensate for thermal expansion and contraction caused by temperature changes, and is widely used in various piping systems.
| Nominal diameter(DN) | Length | Axial displacement(mm)
|
Horizontal displacement | Deflexion angle | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | inch | mm | Extension | Compression | mm | (a1+a2)° |
| 32 | 1 1/4 | 95 | 6 | 9 | 9 | 15° |
| 40 | 1 1/2 | 95 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 15° |
| 50 | 2 | 105 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 15° |
| 65 | 2 1/2 | 115 | 7 | 13 | 11 | 15° |
| 80 | 3 | 135 | 8 | 15 | 12 | 15° |
| 100 | 4 | 150 | 10 | 19 | 13 | 15° |
| 125 | 5 | 165 | 12 | 19 | 13 | 15° |
| 150 | 6 | 180 | 12 | 20 | 14 | 15° |
| 200 | 8 | 210 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 250 | 10 | 230 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 300 | 12 | 245 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 350 | 14 | 255 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 400 | 16 | 255 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 450 | 18 | 255 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 500 | 20 | 255 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
| 600 | 24 | 260 | 16 | 25 | 22 | 15° |
Material selection of rubber expansion joints are very variable and depends on the pressure, temperature, fluid etc. parameters. The common materials are, EPDM, IIR, NBR, PTFE and combined with these materials depends of usage area.
Rubber expansion joints are used in piping installations to compensate for thermal growth, relieve piping stress during operation, and reduce vibration and noise caused by rotating equipment.
The majority of expansion joints can be found off the suction and discharge side of every pump; however, they can also be found near boilers, tanks, cooling towers, heat exchangers and the middle of pipe runs. The average life span of a rubber expansion joint is roughly seven to 10 years.
Installing expansion joints and using a high-quality silicone-based sealant is one important step you can take to ensure that your work will last for years to come. Expansion joints allow space in which concrete can contract and expand without causing cracks.
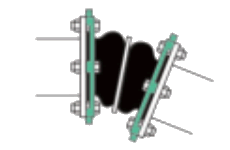
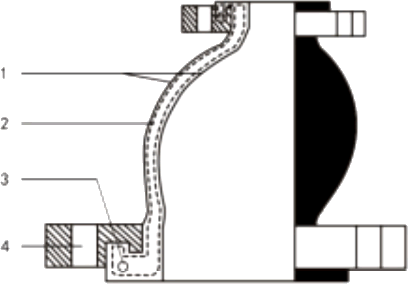
The Rubber Expansion Joint Eccentric Reducing REJ500-P is a specialized type of rubber joint designed to connect pipes of different diameters while accommodating movement, reducing stress, and absorbing vibrations within a piping system.
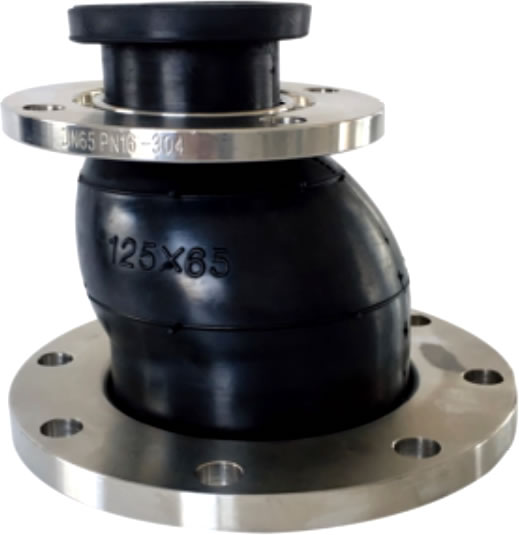

| No. | Name | Material |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Outer/inner rubber | NR, EPDM, NBR, FKM, Necprnce etc. |
| 2 | Frame | Nylon cord fabric |
| 3 | Pressurized ring | Steel wire strand |
| 4 | Flange | Carbon steel, 304, 316L |
|
||
| Nominal diameter | Length (mm) |
Tech nical parameters | Tech nical parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | D0 | n-φ | D | D0 | n-φ | ||
| 100×80 | 180 | 220 | 180 | 8-φ18 | 200 | 160 | 8-φ18 |
| 150×80 | 200 | 285 | 240 | 8-φ22 | 200 | 160 | 8-φ18 |
| 150×100 | 200 | 285 | 240 | 8-φ22 | 220 | 180 | 8-φ18 |
| 150×125 | 200 | 280 | 240 | 8-φ22 | 250 | 210 | 8-φ18 |
| 200×100 | 200 | 340 | 295 | 8-φ22 | 220 | 180 | 8-φ18 |
| 200×150 | 220 | 340 | 295 | 8-φ22 | 280 | 240 | 8-φ18 |
| 250×100 | 220 | 395 | 350 | 12-φ22 | 220 | 180 | 8-φ18 |
| 250×125 | 220 | 395 | 350 | 12-φ22 | 250 | 210 | 8-φ18 |
| 250×150 | 220 | 395 | 350 | 12-φ22 | 285 | 240 | 8-φ22 |
| 250×200 | 220 | 395 | 350 | 12-φ22 | 340 | 295 | 8-φ22 |
| 300×125 | 280 | 445 | 400 | 12-φ22 | 250 | 210 | 8-φ18 |
| 300×150 | 220 | 445 | 400 | 12-φ22 | 285 | 240 | 8-φ18 |
| 300×200 | 180 | 445 | 400 | 12-φ22 | 340 | 295 | 8-φ22 |
| 300×250 | 220 | 445 | 400 | 12-φ22 | 395 | 350 | 12-φ22 |
| 350×125 | 255 | 505 | 460 | 16-φ22 | 250 | 210 | 8-φ18 |
| 350×200 | 220 | 505 | 460 | 16-φ22 | 340 | 295 | 8-φ18 |
| 350×300 | 220 | 505 | 460 | 16-φ22 | 445 | 400 | 12-φ22 |
| 400×200 | 220 | 565 | 515 | 16-φ22 | 340 | 295 | 8-φ22 |
| 400×250 | 220 | 565 | 515 | 16-φ22 | 395 | 350 | 12-φ22 |
| 400×300 | 220 | 565 | 515 | 16-φ22 | 445 | 400 | 12-φ22 |
| 450×200 | 220 | 615 | 565 | 20-φ26 | 340 | 295 | 8-φ22 |
| 450×250 | 220 | 615 | 565 | 20-φ26 | 395 | 350 | 12-φ22 |
| 500×300 | 255 | 670 | 620 | 20-φ26 | 445 | 400 | 12-φ22 |

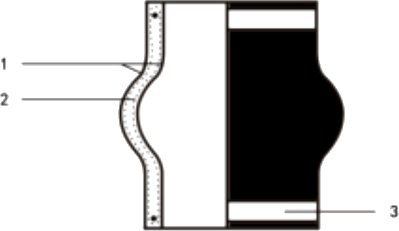
| No. | Name | Material |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Outer/inner rubber | NR, EPDM, NBR |
| 2 | Key frame | Nylon cord fabric |
| 3 | Clamp | Stainless 304 |
|
||

| DN | O.D. of pipe (mm) | Length (mm) | Axial movement | Horizontal movement (mm) |
Deflexion angle (a+ a1)o | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extension (mm) |
Compression (mm) |
|||||
| 50 | 60.3 | 180 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 20 |
| 65 | 76 | 180 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 20 |
| 80 | 89 | 180 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 20 |
| 100 | 114 | 180 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 20 |
| 125 | 133 | 180 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 20 |
| 150 | 159 | 180 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 15 |
| 200 | 219 | 200 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 10 |
| 250 | 273 | 200 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 10 |
| 300 | 325 | 200 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 8 |
| 350 | 327 | 200 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 8 |
| 400 | 426 | 200 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 8 |
| 500 | 530 | 200 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 6 |
| 600 | 630 | 200 | 20 | 25 | 15 | 6 |
Compensation of axial movement with a compensator without tie rods
Compensation of axial and lateral movement with compensators without tie rods
Compensation of lateral and axial movement with compensators without tie rods on each pipe
Compensation of a large axial movement with two hinge compensators
Compensation of movements in 2 planes with 3 angular compensators. The advantages are the absorption of large movements, weak adjustment force, weak movement resumption
Compensation of lateral and axial movement with compensators without tie rods on each pipe
Cracking:
Exterior surface cracking is most commonly the result of aging or elevated temperature. Because of rubber ages, it becomes hard and brittle and loses inherent flexibility and resilience. Cracking or crazing may not be serious if only the outer cover is involved and the fabric is not exposed. If necessary, repair onsite with rubber cement where cracks are minor. Carefully inspect cracks to determine if underlying fabric reinforcing plies are compromised.
Exposure of Metal Reinforcement:
If the metal reinforcement of an flexible rubber expansion joint is visible through the cover, the rubber expansion joint should be replaced ASAP.
Dimensions:
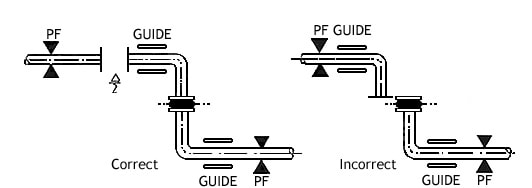
Any inspections should verify that the installation is correct; no excessive misalignment between the flanges exists; and the installed face-to-face dimension is correct. Check for over-elongation, over compression, lateral or angular misalignment. If incorrect installation has caused the expansion joint to fail, adjust the piping and order a new expansion joint to fit the existing installation.
Rubber Deterioration:
If the joint feels soft or gummy, plan to replace the flexible rubber expansion joint as soon as possible. Chemical attack is the most likely cause.
Leakage:
It is most important to determine where the leak originated prior to implementing any corrective action. If leakage or weeping is occurring from any surface of the expansion joint, except where flanges meet, replace the joint immediately.
Rubber expansion joints have been specified and successfully used for many years to accommodate pressure loads, relieve movement stresses, reduce noise, isolate vibration, compensate for misalignment after plants go on stream and prolong the life of pumps and other motive equipment.
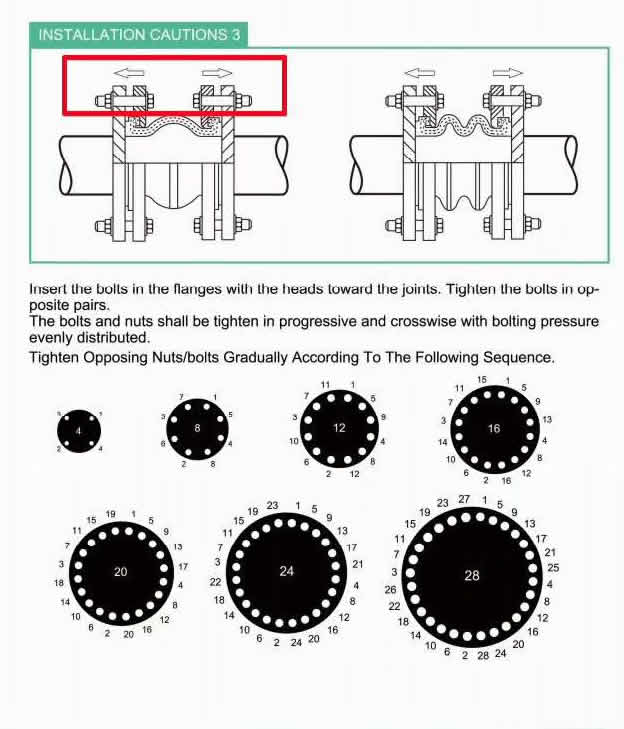
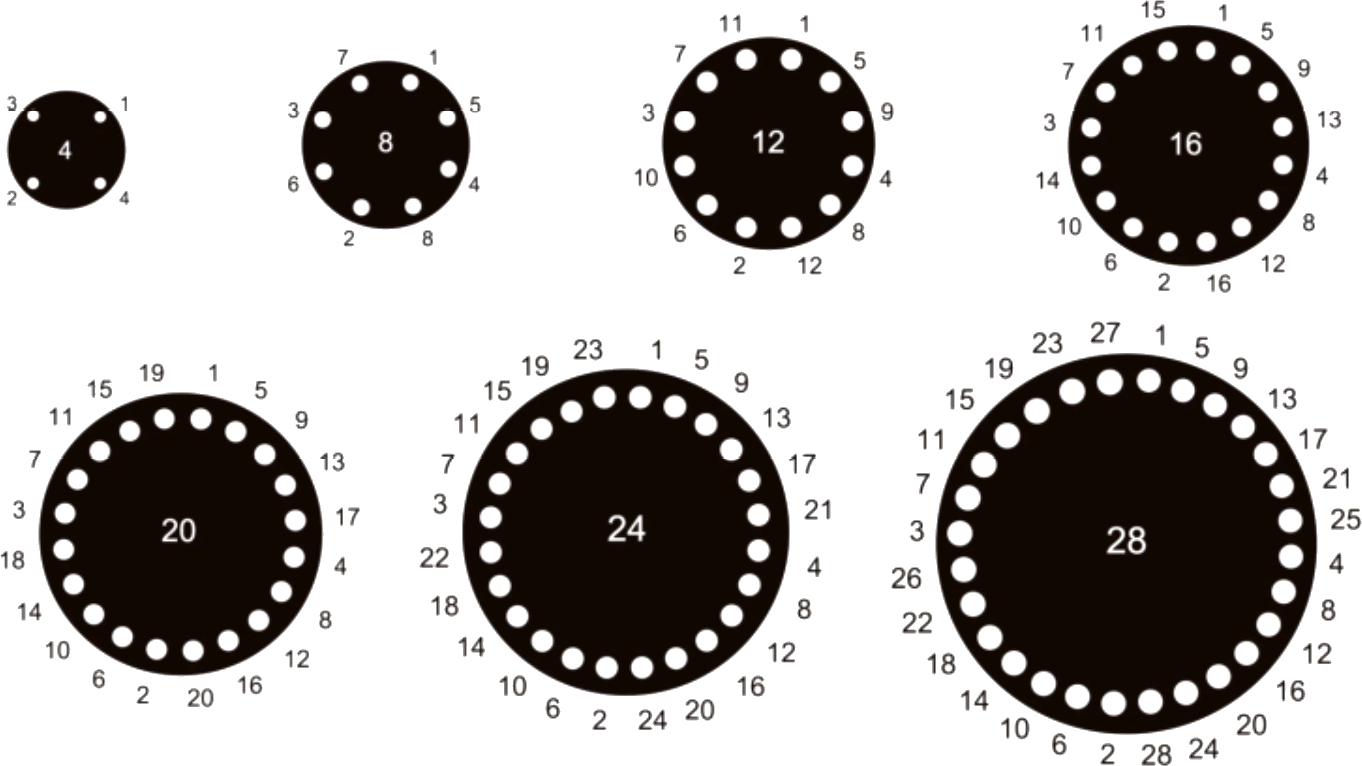
Insert the bolts in the flanges with the head loward the joints. Tighten the bolts in opposite pairs. The bolts and nuts shall be tighten in progressive and crosswise with bolting pressure evenly distributed. Tighten opposing Nuts/bolts gradually according to the fullwing sequence.
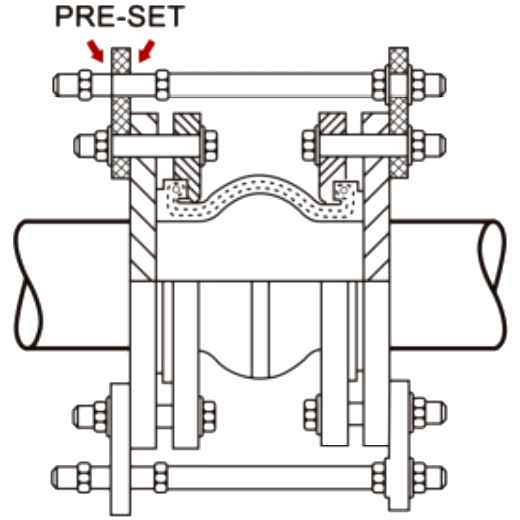
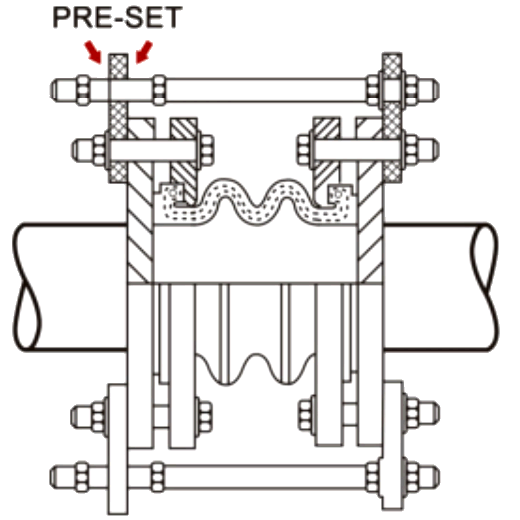
The control rod assemblies are pre-set at the maximum allowable expansion and/or contraction of the joint during the commissioning or operating. It is strictly recommended for unanchored/unsupported systems and also spring-mounted pumps or equipment. Control rod joints must be strictly used when the movement/pressure exceeds the permissible limit.
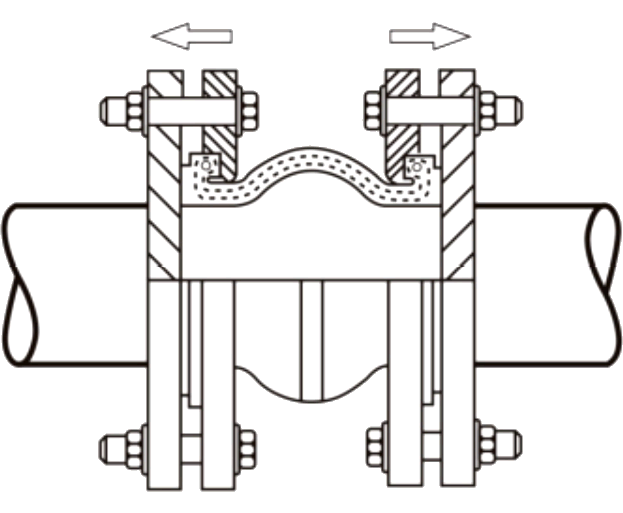
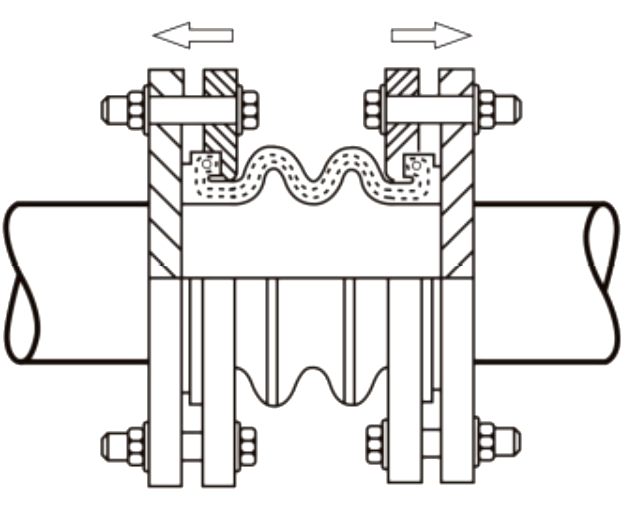
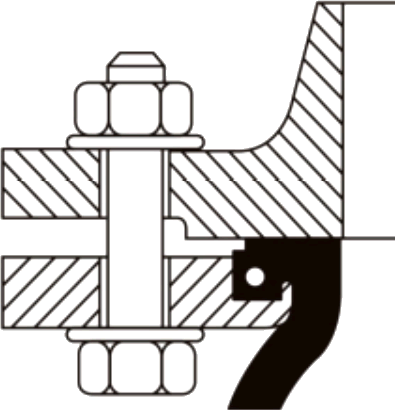
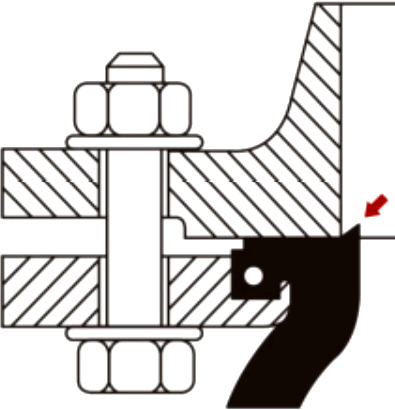
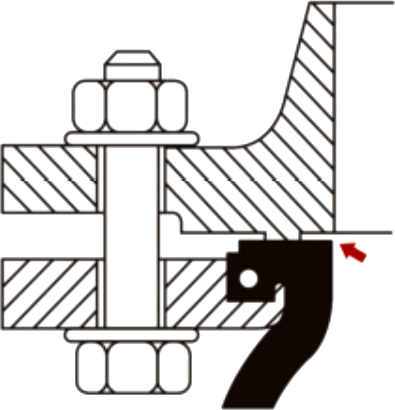
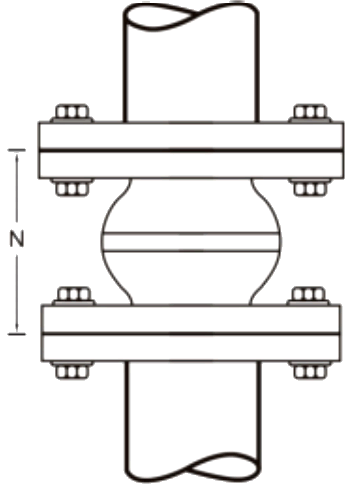
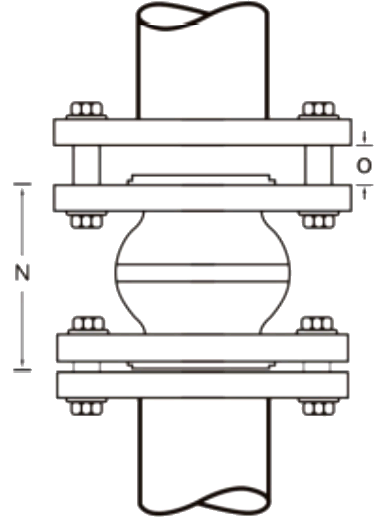
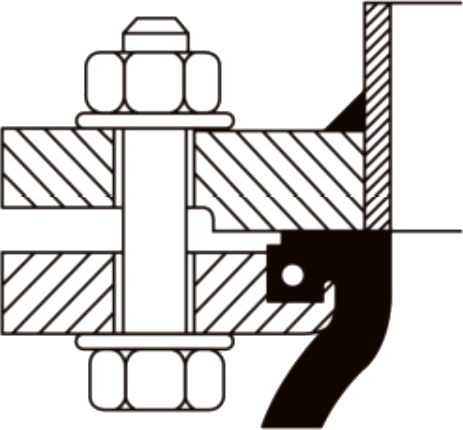
Installation of the SunnySteel joint shall be carried out while maintaining the existing state. Do not use force to tighten the distance in order to fill the reserved gap.
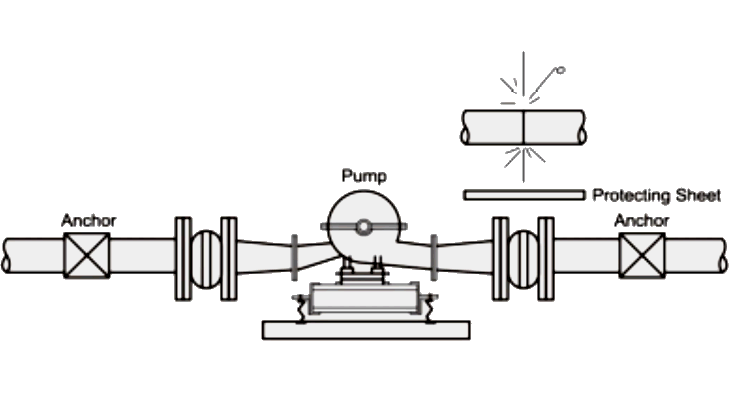
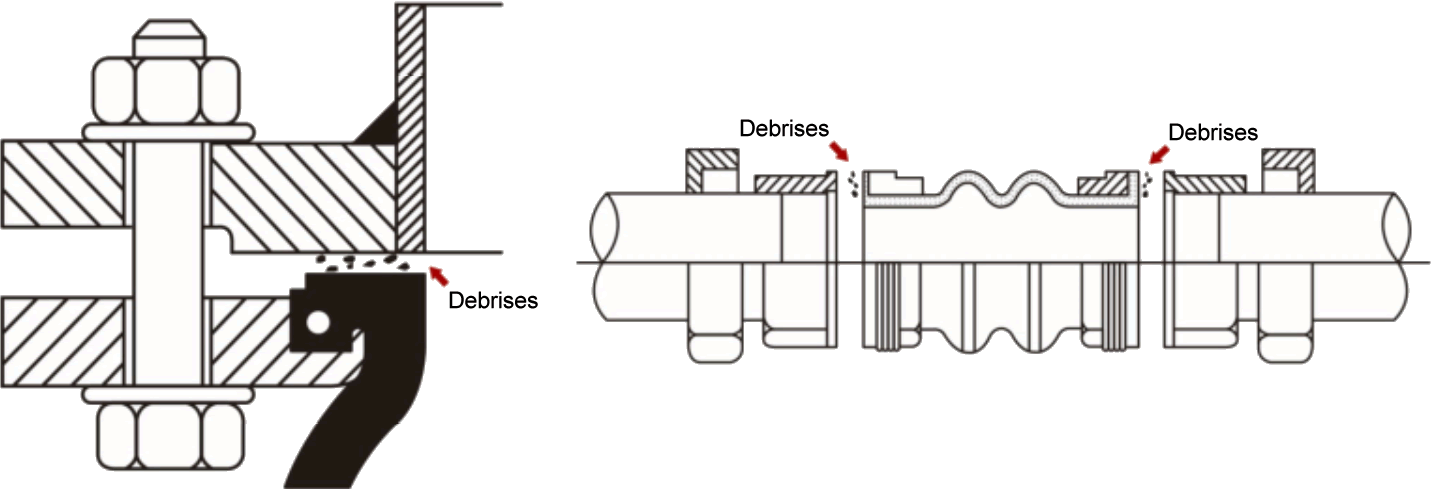
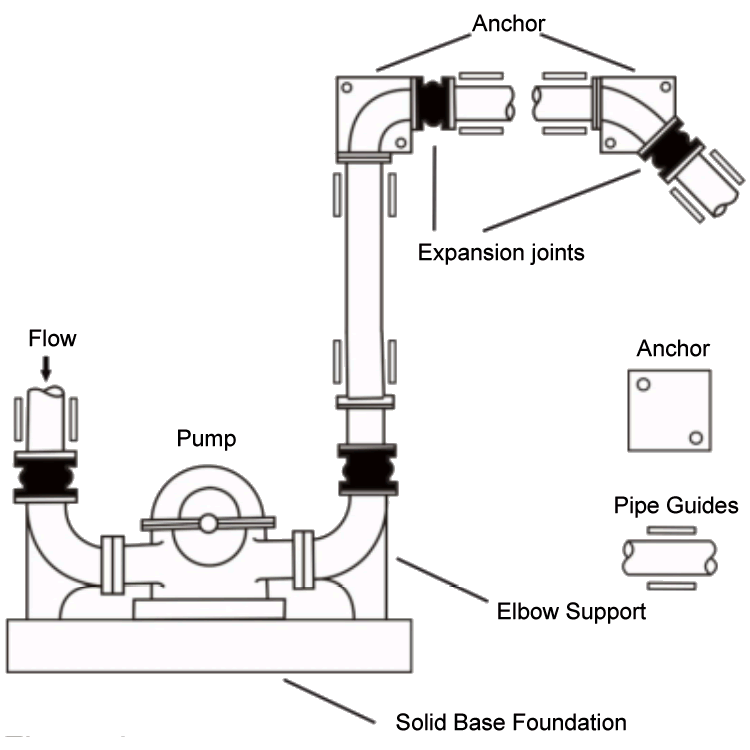
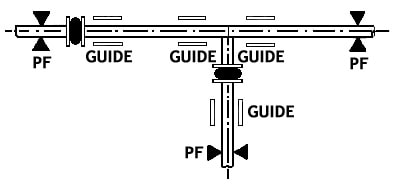
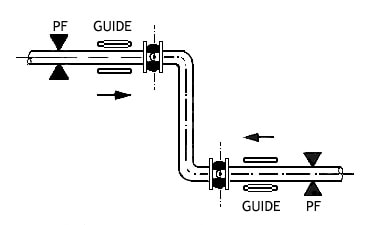
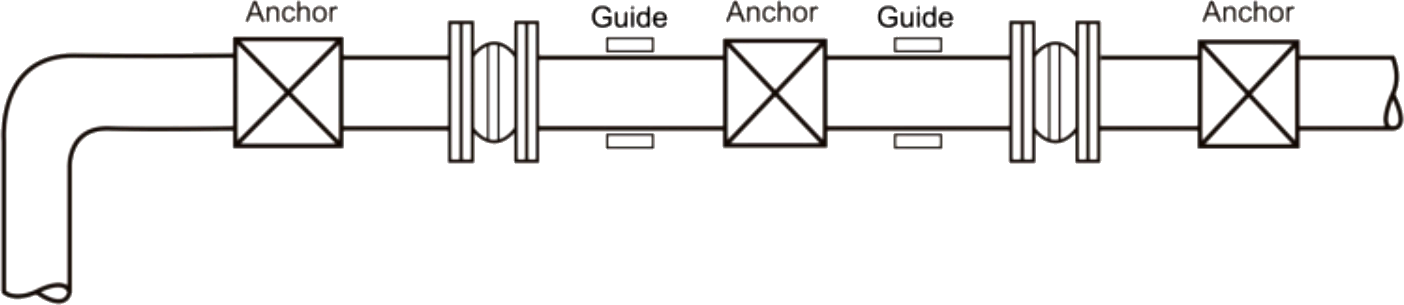
Typical Piping Layout Utilizing Expansion Joints When Equipment And Piping Are Properly Anchored.
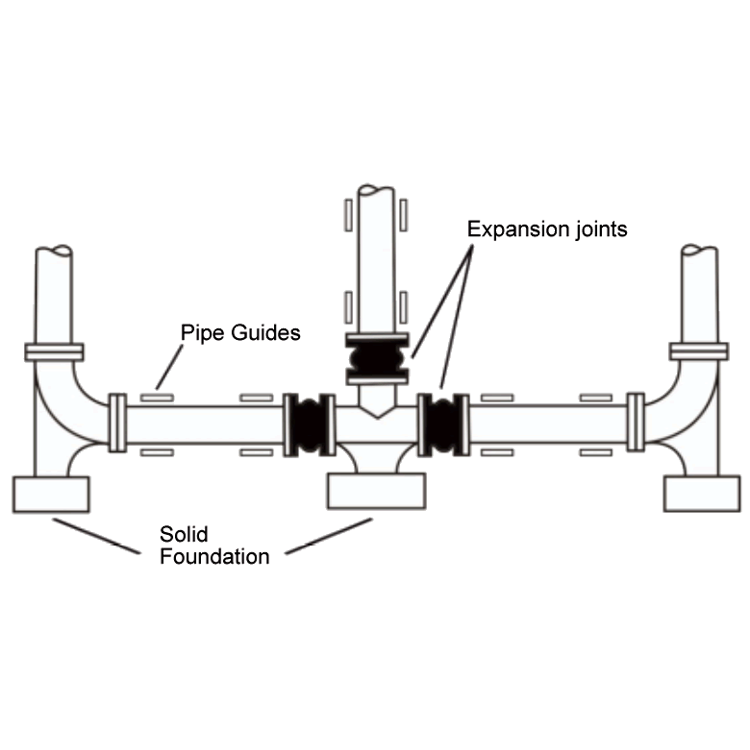
Typical Piping Layout Utilizing Expansion Joints and the Proper Use of Anchors in Branch Locations.
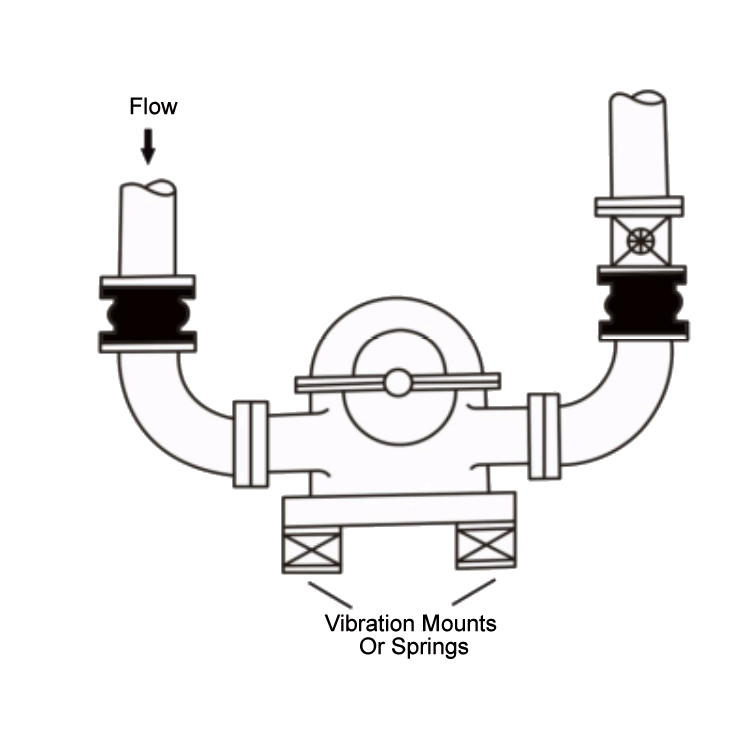
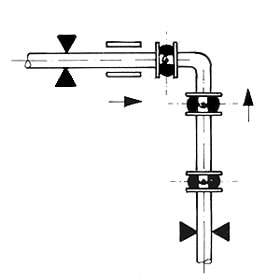
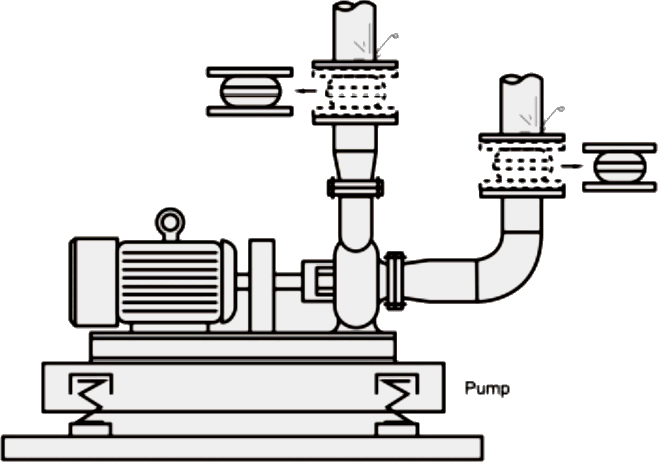
Typical Pump Installation With SunnySteel Expansion Joints Utilizing Vibration Mounts.
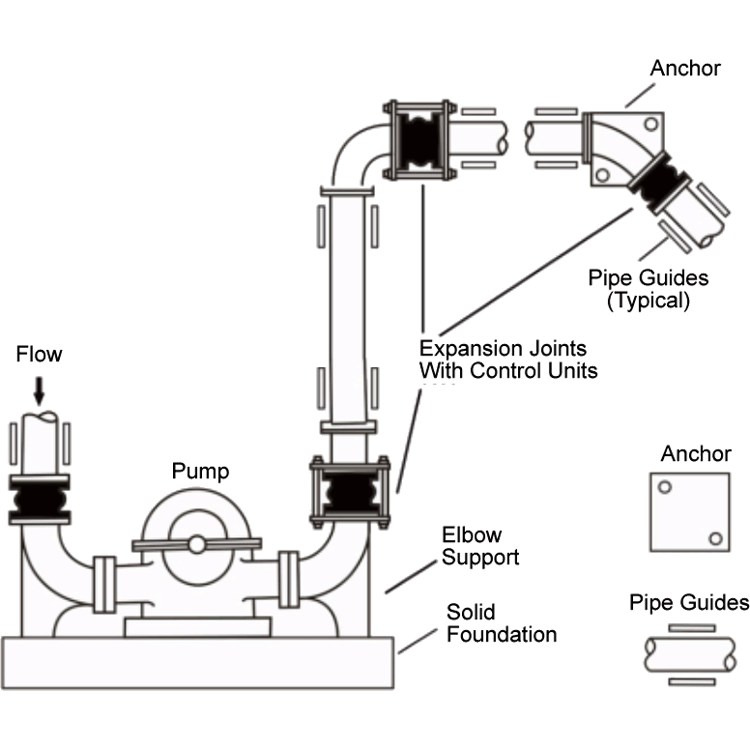
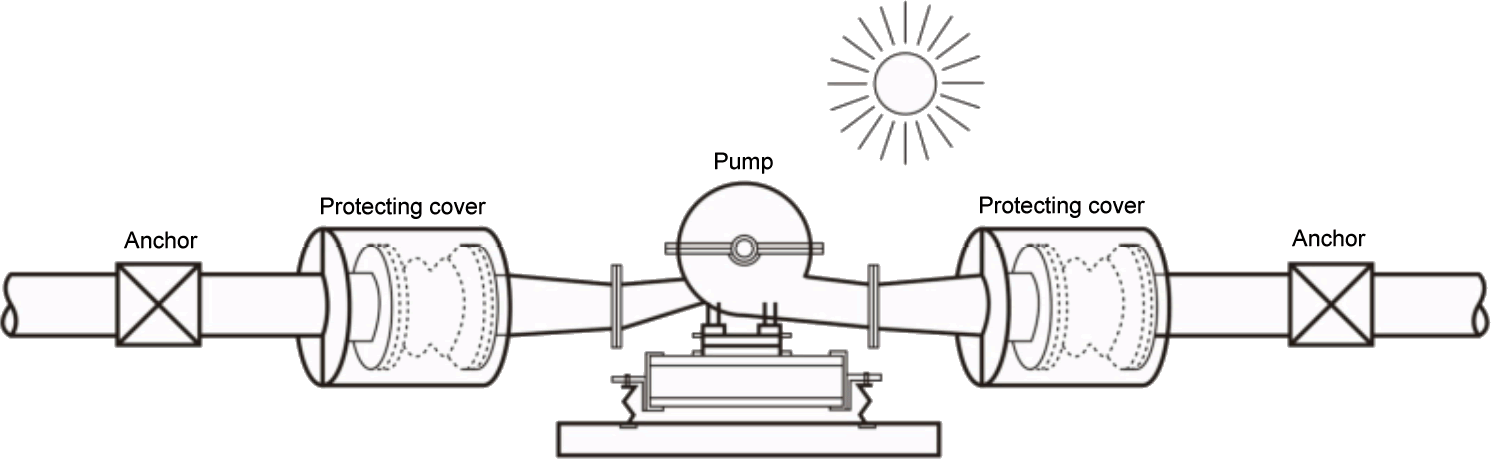
Typical Piping Layout Showing The Use Of SunnySteel When Proper System Anchoring Is Limited.
Rubber expansion joints are vital components in various industries, providing essential flexibility to piping systems. These versatile connectors can accommodate movement, vibration, and thermal expansion, preventing stress and damage to pipelines and equipment. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of rubber expansion joints, exploring their uses, benefits, installation, maintenance, and much more.
Rubber expansion joints are flexible connectors used in piping systems to absorb movement, vibrations, and thermal expansion. Their unique design allows for axial, lateral, and angular movement, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Explore the different types of rubber expansion joints available, such as single sphere, twin sphere, and more. Each type has specific features that cater to diverse requirements.
Discover how rubber expansion joints find applications in industries like chemical processing, oil and gas, water treatment, HVAC, and more. Their versatility makes them indispensable in handling various fluid mediums.
Rubber expansion joints offer numerous advantages, including noise reduction, vibration absorption, and stress alleviation, leading to enhanced durability and longevity of piping systems.
Consider critical factors like pressure ratings, temperature range, movement capability, and chemical compatibility when selecting the appropriate rubber expansion joint for a specific application.
Follow detailed step-by-step instructions for the correct installation of rubber expansion joints to ensure optimal performance and prevent potential issues.
Learn about the importance of regular maintenance and inspection to detect potential problems early and extend the service life of rubber expansion joints.
Address common problems that may occur with rubber expansion joints, including leaks, premature wear, and abnormal noises. Find effective solutions to troubleshoot these issues.
Compare rubber expansion joints with other types of expansion joints, such as metal and fabric, and understand their specific advantages and limitations.
Examine the eco-friendliness and recyclability of rubber expansion joints, making them a sustainable choice for various industries.
Explore the various industry standards and certifications that rubber expansion joints must meet to ensure their reliability and safety in critical applications.
Stay up-to-date with the latest technological advancements and innovations in the field of rubber expansion joints, ensuring continuous improvement and enhanced performance.
Gain valuable insights from industry experts and real-life case studies, providing practical applications and success stories of rubber expansion joints.
Q: What are the primary uses of rubber expansion joints?
A: Rubber expansion joints are widely used in piping systems to compensate for movement, absorb vibrations, and reduce stress, ensuring the smooth operation of various industries.
Q: Can rubber expansion joints withstand high temperatures?
A: Yes, rubber expansion joints are designed to withstand a wide temperature range, making them suitable for both high-temperature and low-temperature applications.
Q: How long do rubber expansion joints typically last?
A: The lifespan of rubber expansion joints depends on factors like operating conditions, maintenance, and quality. Well-maintained rubber expansion joints can last for several years.
Q: Are rubber expansion joints resistant to chemicals?
A: Yes, rubber expansion joints are available in various elastomers, each with specific chemical resistance properties, making them suitable for a wide range of fluid mediums.
Q: Can I install rubber expansion joints myself?
A: While some installations can be straightforward, it is recommended to have a professional handle the installation to ensure proper fitting and performance.

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
