316 Stainless Steel Elbow
Designed for durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for various industrial applications.
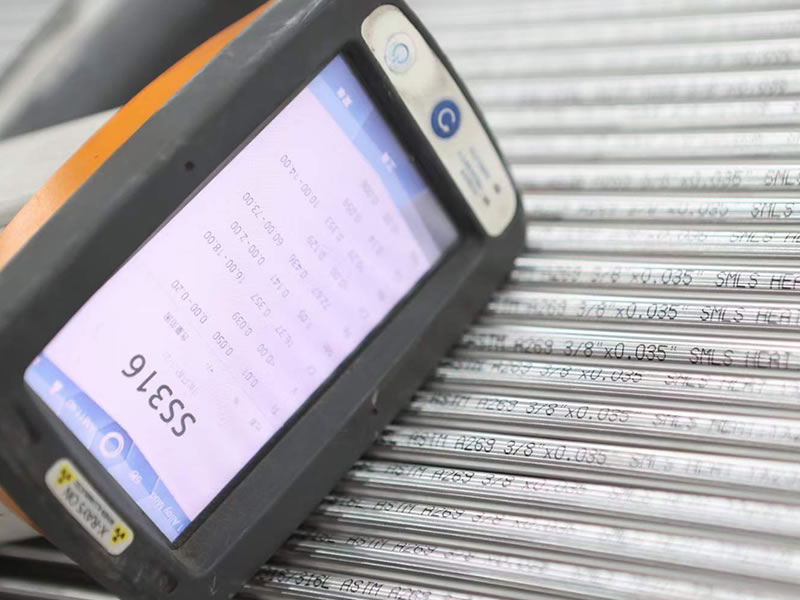

Stainless Steel Pipe 316/316L is a tubular shaped 316/316L Stainless Steel Alloy pipe.
316 Stainless Steel Alloy is a standard molybdenum-bearing grade, the second most commonly sought after grade next to grade 304 amongst the austenitic stainless steels.
The molybdenum gives 316 better overall corrosion resistant properties than Grade 304, particularly higher resistance in chloride environments.
Grade 316L (L= low carbon) ) is the same as 316 except it has an extra-low-carbon analysis, the advantage of which is that it precludes any harmful precipitation in the 800º F to 1500º F range that might result from welding heavier sections. Therefore 316L is extensively used in heavy gauge welded components.
316/316L stainless steel pipe can withstand elevated temperatures longer than grade 304/304L, has better corrosion resistance, and offers excellent weldability. It has many applications:
Alloy 316/316L is an austenitic alloy and similar to 304/304L is used in a wide range of applications. It is an important alloy when it comes to chloride environments and many other chemical process industries. The addition of Molybdenum significantly increases general corrosion resistance as compared to 304/304L and more importantly, increases the chloride pitting resistance.
316/316L has excellent forming and welding characteristics. Due to its superior chloride pitting resistance, it is commonly used in applications involving chlorides or halides. That property is also useful in marine environments.
It also has an excellent resistance to intergranular corrosion in as-welded condition. Dual grade becomes important if heavy gauge welding is performed. This is where intergranular corrosion comes into picture and having a lower carbon version makes it difficult for Chromium Carbide to precipitate in the 797 to 1580 degF (425 to 860 degC) range when the welding is going on for a long time due to the heavy gauge.
It has excellent creep and rupture strength at higher temperatures compared to 304/304L. Finally, it has excellent strength and toughness at cryogenic temperatures.
In addition, it provides excellent elevated temperature tensile, creep and stress-rupture strengths.
| Grade | 316 | 316L |
|---|---|---|
| UNS Designation | S31600 | S31603 |
| Carbon (C) Max. | 0.08 | 0.030* |
| Manganese (Mn) Max. | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Phosphorous (P) Max. | 0.045 | 0.045 |
| Sulphur (S) Max. | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Silicon (Si) Max. | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 16.0 – 18.0 | 16.0 – 18.0 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 10.0 – 14.0 | 10.0 – 14.0 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2.0 – 3.0 | 2.0 – 3.0 |
| Nitrogen (N) | — | — |
| Iron (Fe) | Bal. | Bal. |
| Other Elements | — | — |
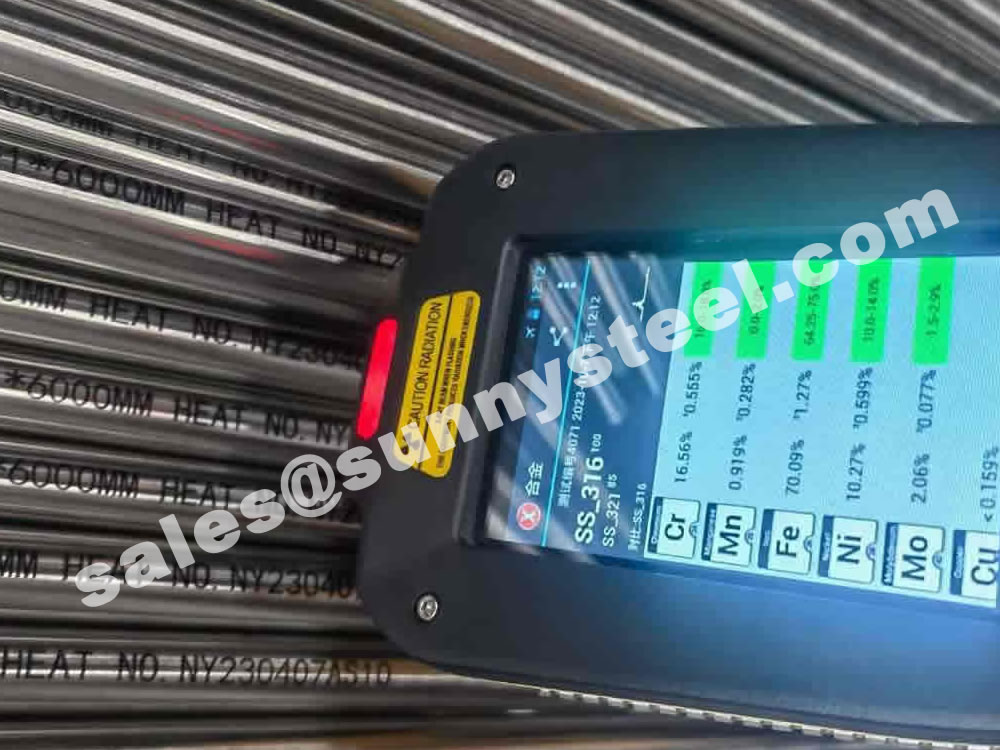
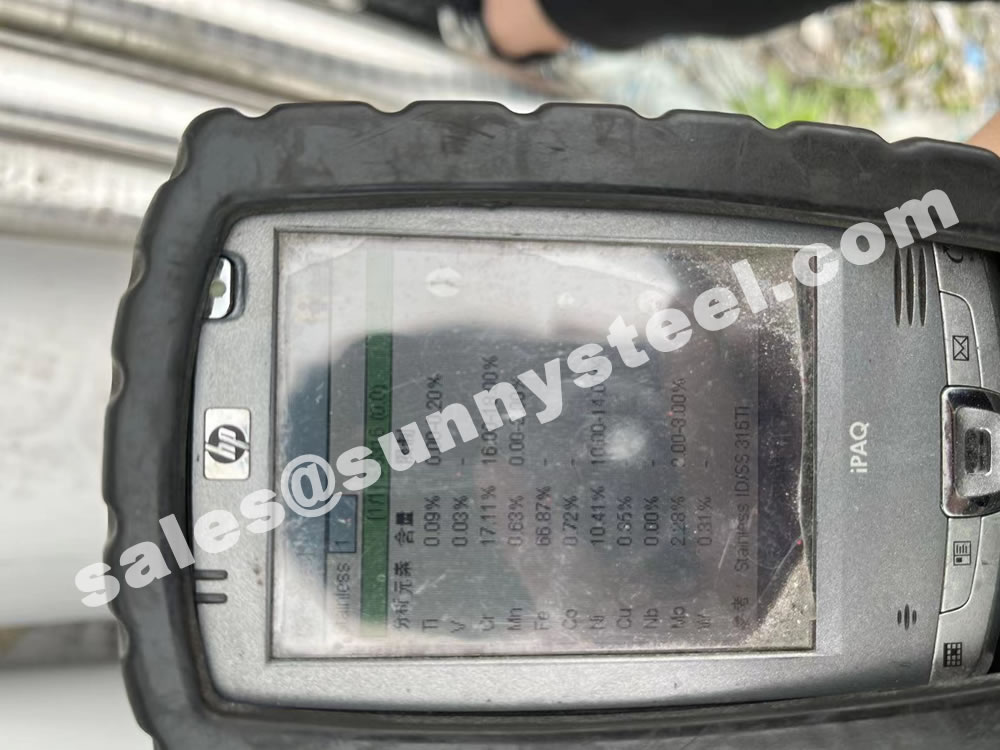

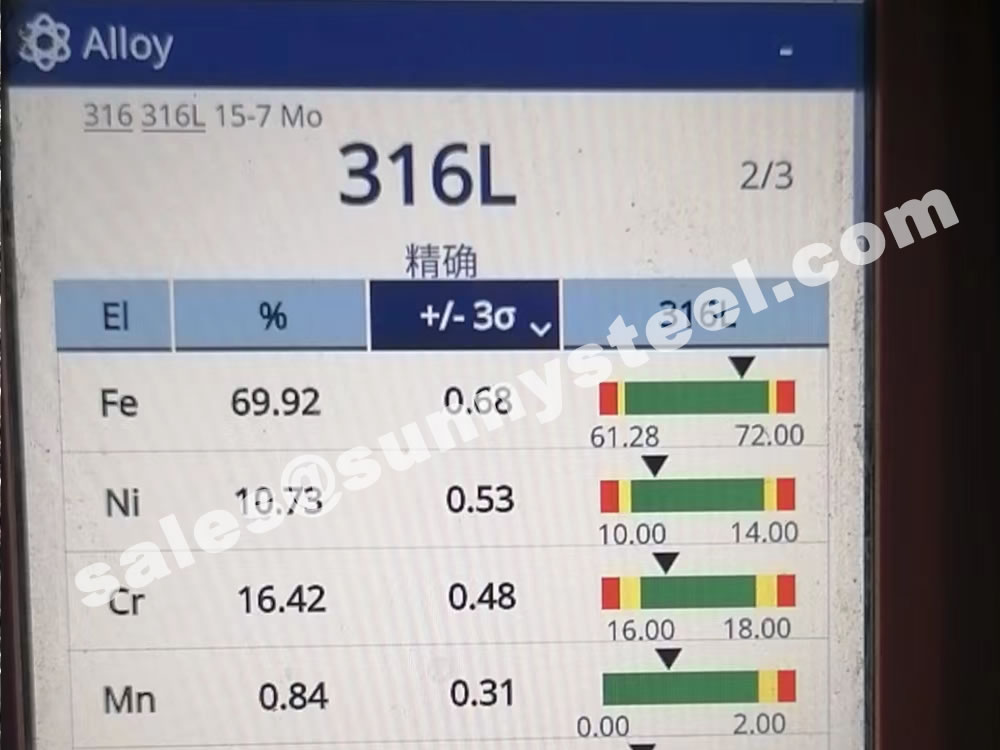

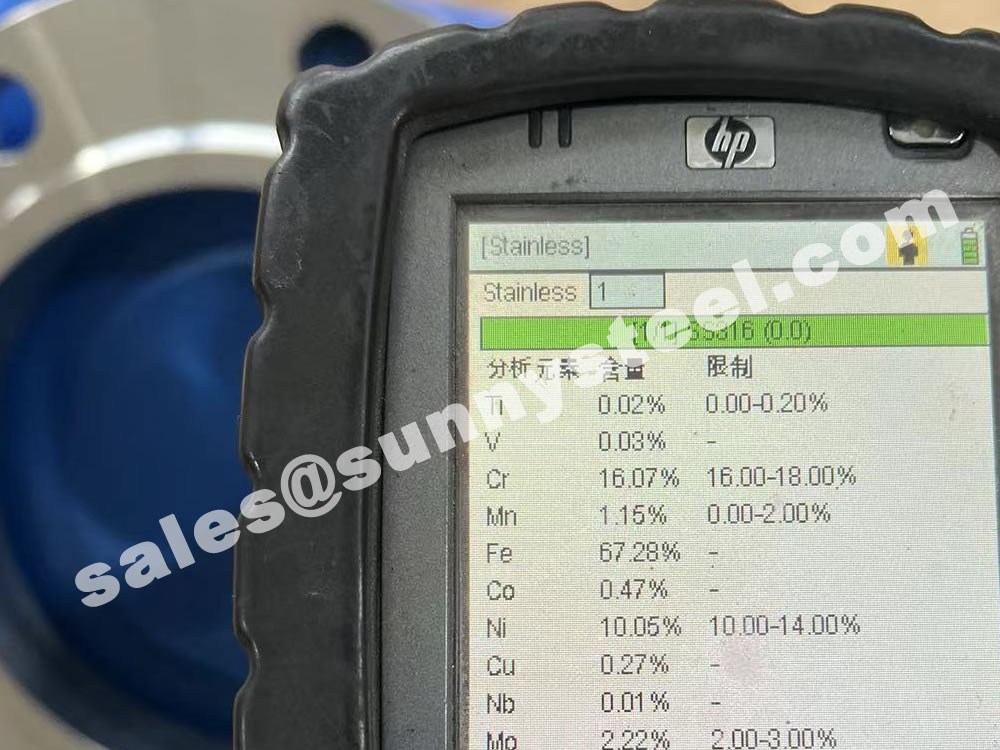

The main constituents of 316 stainless steel - other than iron - are Chromium and Nickel. However, it is the addition of 2% Molybdenum that provides the increased corrosion resistance.
316 contains 16 - 18% Chromium (Cr). Chromium is the essential chemical in all stainless steel and it is that which forms the thin passive layer that makes the metal "stainless"
316 also contains 10-14% Nickel (Ni). This is added to make the Austenitic structure more stable at normal temperatures.
The nickel also improves high-temperature oxidation resistance makes the steel resistant to stress corrosion cracking.
Where the steel is to be stretched formed a lower percentage (8%) of nickel should be selected. If the steel is to be deep drawn a higher percentage is better (9% or more).
In addition a number of other chemicals may be present but these are expressed as maximum permited levels with the exception of the increased quantity of carbon required in 316H - i.e. a minimum of .04% and a maximum of 0.10%
| Electrical Resistivity | Magnetic Permeability |
|---|---|
| 7.2e-005 ohm-cm | 1.008 |
| 7.2e-005 ohm-cm | 1.008 |
| at 20°C (68°F); 1.16E-04 at 650°C (1200°F) | at RT |
| Material | Form | Tensile Strength (ksi) |
Yield Strength (ksi) |
Elongation % |
Hardness HB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy 316L | 316L Sheet AMS 5507 | 100 max | - | 45 | - |
| Alloy 316 | 316 Sheet AMS 5524 | 75 min | 30 | 45 | 207 max |
316/316L/316H stainless steel in the Annealed Condition at -20°F to +100°F
| Alloy | UNS Designation | Spec. | Tensile Strength (psi) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (ksi) | Yield Strength (psi) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (ksi) | Elongation in 2 inches (min.) % | Grain Size Req. | Max. Hardness | Modulus of Elasticity (x106 psi) | Mean Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (IN./IN./°F x 10-6) | Thermal Conductivity (BTU-in/ft2-h-°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | S31600 | A249, A312 | 75,000 | 515 | 75 | 30,000 | 205 | 30 | 35 | — | 90 Rb | 28.0 | 9.2 | 116 |
| 316L | S31603 | A270, A312 | 70,000 | 485 | 70 | 25,000 | 170 | 25 | — | — | 90 Rb | 28.0 | 9.2 | 116 |
| 316H | S31609 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 7 or coarser | — | — | — | — |
| Alloy | UNS Designation | Werkstoff NR. | Specifications* |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | S31600 | 1.4401 | A269, A/SA249, A/SA312, A1016, A632, A/SA688 |
| 316L** | S31603 | 1.4404 | A269, A/SA249, A/SA312, A1016, A632, A/SA688 |
*Note: The specifications noted including ASTM, ASME, or other applicable authorities are correct at the time of publication. Other specifications may apply for use of these materials in different applications.
Type 316L is the low carbon version of 316 stainless. With the addition of molybdenum, the steel is popular for use in severe corrosion environments due to the materials immunity from boundary carbide precipitation (sensitisation).
The material is widely used in heavy gauge welded components and weld annealing is only required where the material is for use in high stress environments. 316L has an extensive variety of uses especially in marine applications due to the materials high corrosion resistance.
Type 316H is a higher carbon variant of 316 making the steel more suitable for use in applications where elevated temperatures are present.
Stabilised Grade 316Ti offers similar qualities.
The increased carbon content delivers a greater tensile and yield strength. The austenitic structure of the material also gives this grade excellent toughness, even down to cryogenic temperatures.
We support our stainless steel stock with a wide range of shapes and sizes to suit your engineering applications.
We hold thirteen different types of shapes to support the grades of material we stock, including bars, sheets and plates.

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
