ASTM A106 Gr.B Pipes
ASTM A106 Gr.B pipes are seamless pipes known for their seamless construction and pressure capabilities.
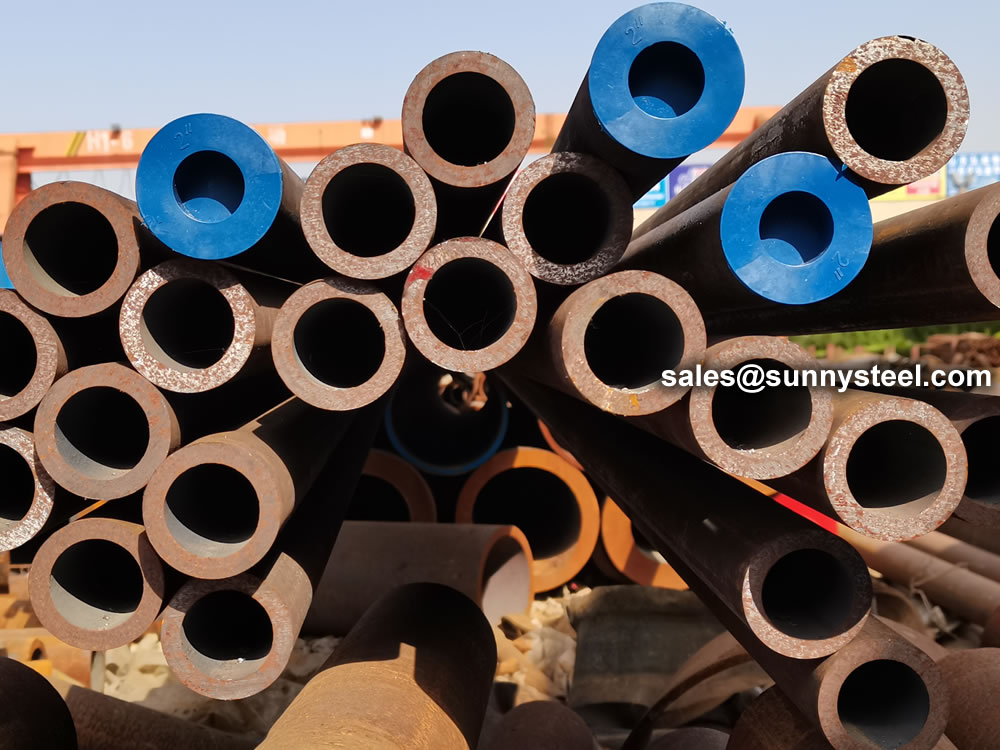

ASTM A210 Grade A1 boiler pipes are specifically designed for high-temperature service and are often used in hot water and steam systems.
Download PDFThey are corrosion-resistant which makes them last longer than other materials such as cast iron or copper which can corrode over time. Additionally, due to their material composition, they can withstand higher temperatures than other types of boilers; this makes them especially useful for applications that require high heat output.These ASTM A210 Grade A1 boiler pipes are much lighter than other materials which makes them easier to transport and install in various locations.
ASTM A210 Grade A1 specifies the requirements for seamless and welded carbon steel boiler tubes intended for high-temperature applications. These pipes are commonly utilized in power boilers, superheaters, and heat exchangers, where strength and reliability are crucial.
ASTM A210 Grade A1 boiler pipes are essential for applications requiring durability and reliability in high-temperature environments. Their carbon steel composition and availability in both seamless and welded forms make them suitable for various industrial applications, including power generation and heat exchange.
1.1 This specification2 covers minimum-wall-thickness, seamless medium-carbon steel, boiler tubes and boiler flues, including safe ends (see Note 1), arch and stay tubes, and superheater tubes.
NOTE 1: This type is not suitable for safe ending by forge welding.
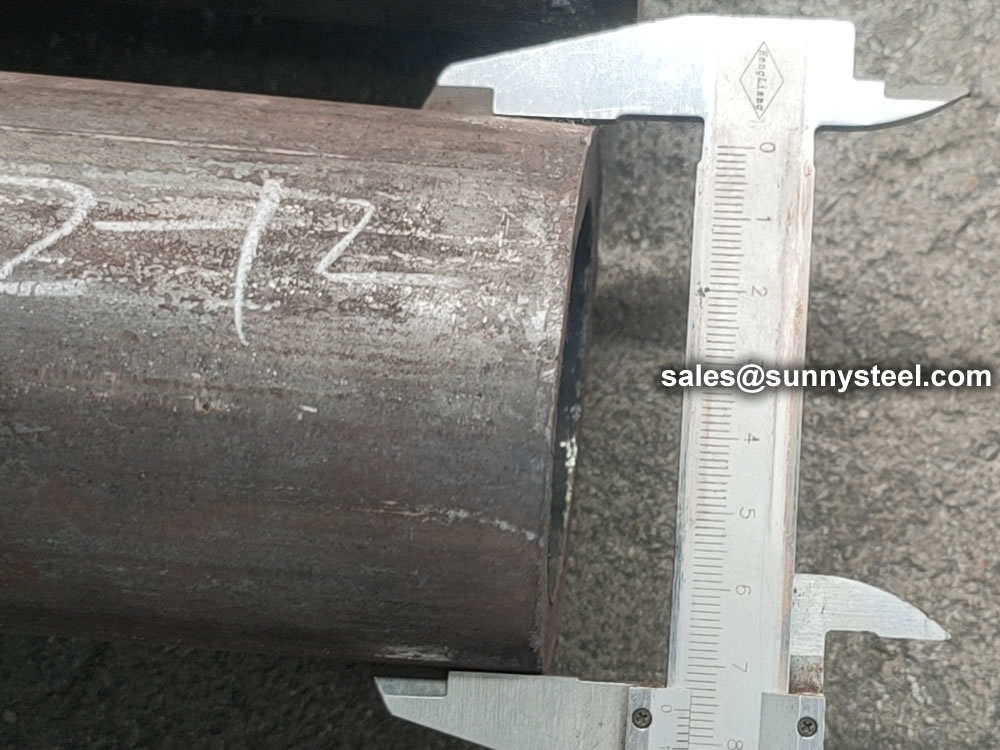
1.2 The tubing sizes and thicknesses usually furnished to this specification are 1/2 in. to 5 in. [12.7 to 127 mm] in outside diameter and 0.035 to 0.500 in. [0.9 to 12.7 mm], inclusive, in minimum wall thickness. Tubing having other dimensions may be furnished, provided such tubes comply with all other requirements of this specification.
1.3 Mechanical property requirements do not apply to tubing smaller than 1/8 in. [3.2 mm] in inside diameter or 0.015 in. [0.4 mm] in thickness.
1.4 This specification covers grades A-1 and C of Seamless Medium-Carbon Boiler and Superheater Tubes with different chemical and tensile requirements. (Table 1, Table 3, and Section 11.)
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
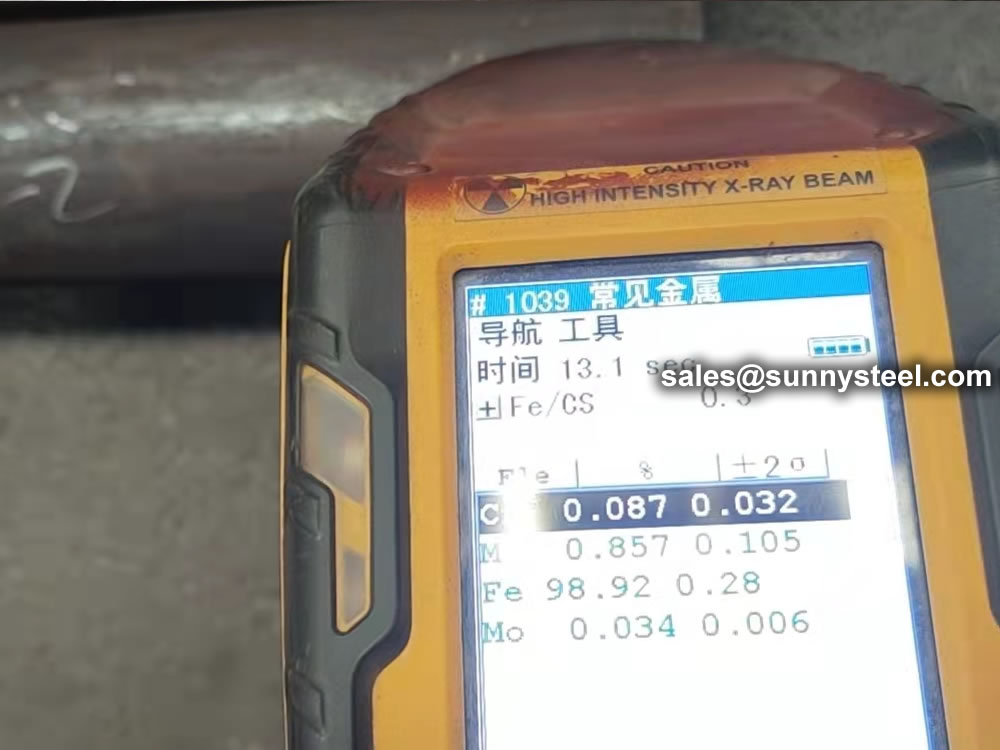
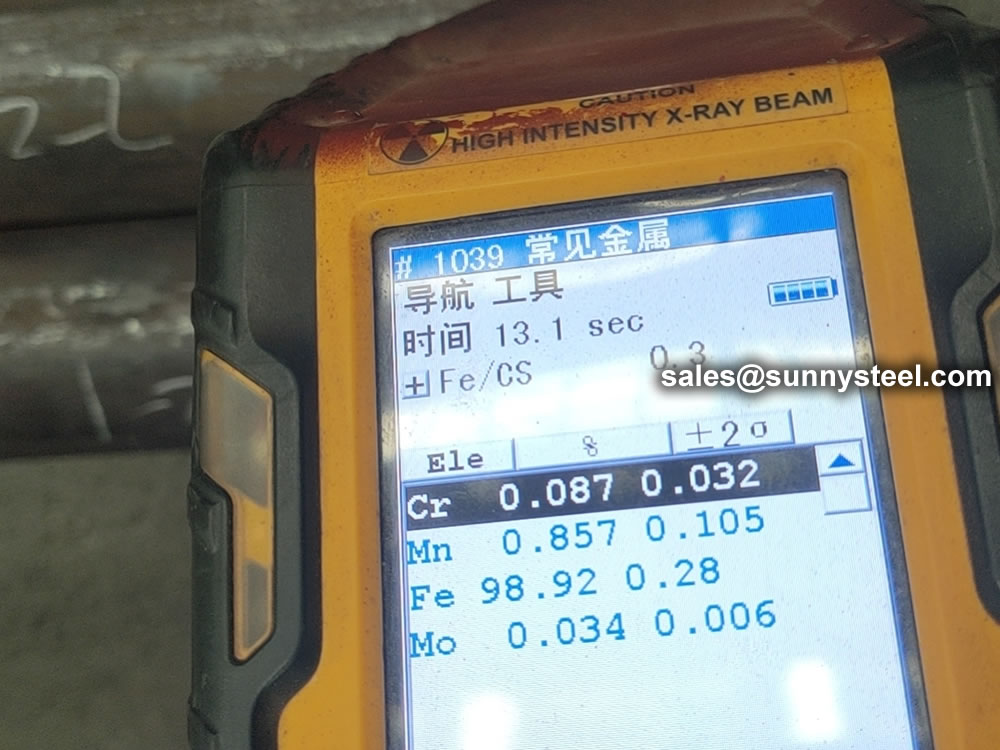







| Steel Grade | C | Si | Mn | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A210 A1/ SA-210A1 | ≤0.27 | ≥0.10 | ≤0.93 | 0.020 | 0.025 |
| A210C/ SA-210C | ≤0.35 | ≥0.10 | 0.29-1.06 | 0.020 | 0.025 |
| Grade | Tensile strength (Mpa) |
Yield point(Mpa) not less than |
Elongation(%) not less than |
Impact(J) not less than |
Hardness not less than |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A210 A1/ SA-210A1 | ≥415 | 255 | " | 79HRB | |
| A210C/ SA-210C | ≥485 | 275 | " | 89HRB |
| Hot rolled | Outside Diameter, mm | Tolerance, mm |
|---|---|---|
| OD≤101.6 | +0.4/-0.8 | |
| 101.6<OD≤127 | +0.4/-1.2 | |
| Cold Drawn | Outside Diameter, mm | Tolerance, mm |
| OD<25.4 | ±0.10 | |
| 25.4≤OD≤38.1 | ±0.15 | |
| 38.1<OD<50.8 | ±0.20 | |
| 50.8≤OD<63.5 | ±0.25 | |
| 63.5≤OD<76.2 | ±0.30 | |
| 76.2≤OD≤101.6 | ±0.38 | |
| 101.6<OD≤127 | +0.38/-0.64 |
| Hot rolled | Outside Diameter, mm | Tolerance, % |
|---|---|---|
| OD≤101.6, WT≤2.4 | +40/-0 | |
| OD≤101.6, 2.4<WT≤3.8 | +35/-0 | |
| OD≤101.6, 3.8<WT≤4.6 | +33/-0 | |
| OD≤101.6, WT>4.6 | +28/-0 | |
| OD>101.6, 2.4<WT≤3.8 | +35/-0 | |
| OD>101.6, 3.8<WT≤4.6 | +33/-0 | |
| OD>101.6, WT>4.6 | +28/-0 | |
| Cold Drawn | Outside Diameter , mm | Tolerance, % |
| OD≤38.1 | +20/-0 | |
| OD>38.1 | +22/-0 |
| Method of Manufacture |
Outside Diameter, in. [mm] |
Cut Length,in. [mm] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Over | Under | ||
| Seamless, hot-finished | All sizes | 3 ⁄ 16 [5] | 0 [0] |
| Seamless, cold-finished | Under 2 [50.8] | 1 ⁄ 8 [3] | 0 [0] |
| 2 [50.8] and over | 3 ⁄ 16 [5] | 0 [0] | |
| 2 [50.8] and over | 3 ⁄ 16 [5] | 0 [0] | |
Both ends of each crate will indicate the order no., heat no., dimensions, weight and bundles or as requested.
(1)Tension Test—One tension test shall be made on a specimen for lots of not more than 50 tubes. Tension tests shall be made on specimens from two tubes for lots of more than 50 tubes.
(2)Flattening Test—One flattening test shall be made on specimens from each end of one finished tube from each lot.
(3)Flaring Test—One flaring test shall be made on speci- mens from each end of the one finished tube from each lot.
(4)Hardness Test—Brinell or Rockwell hardness tests shall be made on specimens from two tubes from each lot.
(5)Hydrostatic or Nondestructive Electric Test—Each tube shall be subjected to the hydrostatic.
One flattening test shall be made on specimens from each end of one finished tube from each lot, but not the one used for the flaring test. Tears or breaks occurring at the 12 or 6 o’clock positions on Grade C tubing with sizes of 2.375 in. [60.3 mm] in outside diameter and smaller shall not be considered a basis for rejection.
One flaring test shall be made on specie- men from each end of the one finished tube from each lot, but not the one used for the flattening test.
Orders for ASTM A210 / A210M, ASME SA210 should include the following, as required, to describe the desired material adequately:

With years of expertise, we provide a diverse array of steel tube processing options. From sawing and machining tube blanks to intricate bending and upsetting operations, we actively assist you throughout your projects.
Our capabilities extend to eccentricity reduction and concentricity enhancement through turning and grinding. We excel in creating complex geometries using processes like rotary swaging and axial forming. Additionally, we offer property modifications via partial heat treatment, ensuring tailored solutions for your specific needs.
Variable wall thicknesses
Drilling / stamping / lasering
Peeling / roller burnishing
Cold forming
Cutting
Beveling
Deburring
Thread rolling / threading
Partial hardening
Turning / milling / grinding
Reducing / expanding
Swing

Alloy steel pipes are ideally suitable for chemical, petrochemicals, and other energy-related applications.
The alloy steel pipe adopts high quality carbon steel, alloy structural steel and stainless & heat resisting steel as raw material through hot rolling or cold drawn to be made.
Alloy steel can be used in process area where carbon steel has limitation such as
As an important element of steel products, alloy steel pipe can be divided into seamless steel pipe and welded steel pipe according to the manufacturing technique and tube billet shape.
Here you can see the common alloy steel grade that you will come across.
There are many kinds of materials used for transport in industrial production. Specifically we will have more choices and it is not limited to the use of alloy steel pipe. But even in the face of more choices, many people tend to choose alloy steel pipe. People make their own choices will have their own reasons. This means the alloy steel pipe application has its own advantages. Compared with transmission lines made of other materials, after it meets the basic application requirements, its quantity is lighter. Then in the practical application of alloy steel pipe, it will have more advantages because of this. Besides its physical characteristic advantage, it also has economic advantages. The wide application of alloy steel pipe is with kinds of reasons. So in practical usage, we can exploit the advantages to the full, in this way can we get more profits in these applications of alloy steel pipe.
The transportation of kinds of gases or liquids in production needs to rely on alloy steel pipe. This shows that the actual role of alloy steel pipe application is important. High temperature resistant and low temperature resistant is the tolerance of temperature. In the practical application of alloy steel pipe, there will be many materials need to be transported. However their temperatures are not the same. So this can be the basic requirement to alloy steel pipe. It needs more corrosion resistance. Corrosion resistant material is the best material during transporting, because it is corrosion resistant. So it can be used in more occasions. And it is definitely very convenient for users.
Can be 100% recycled, environmentally friendly, energy-saving, resource conservation, national strategy, national policy to encourage the expansion of the field of application of high-pressure alloy pipe. Of alloy steel pipe total consumption accounted steel in the proportion is only half of the developed countries, to expand the field of use of the alloy steel pipe to provide a wider space for the development of the industry. The future needs of the average annual growth of China’s high-pressure alloy steel pipe long products up to 10-12%.
Alloy Steel pipe contains substantial quantities of elements other than carbon such as nickel, chromium, silicon, manganese, tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium and limited amounts of other commonly accepted elements such as manganese, sulfur, silicon, and phosphorous.
Our team of experienced sales specialists proudly partners with gas and chemical processors, power generation plants, oil refineries, and related industries to offer piping components and value-added services.
The biggest advantages of alloy steel pipe can be 100% recycled, environmentally friendly, energy-saving, resource conservation, national strategy, national policy to encourage the expansion of the field of application of high-pressure alloy pipe. Of alloy tube total consumption accounted steel in the proportion is only half of the developed countries, to expand the field of use of the alloy tube to provide a wider space for the development of the industry. According to the Chinese Special Steel Association alloy pipe Branch Expert Group, the future needs of the average annual growth of China’s high-pressure alloy pipe long products up to 10-12%.
Steel pipe delivery status(condition): cold / hard (BK), cold / soft (BKW), after cold stress relief annealing (BKS), annealing (GBK), normalized (NBK).
| Term | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-finished/hard (cold-finished as-drawn) | BK | No heat treatment after the last cold-forming process. The tubes therefore have only low deformability. |
| Cold-finished/soft (lightly cold-worked) | BKW | After the last heat treatment there is a light finishing pass (cold drawing) With proper subsequent processing, the tube can be cold-formed (e.g. bent, expanded) within certain limits. |
| Annealed | GBK | After the final cold-forming process the tubes are annealed in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
| Normalized | NBK | The tubes are annealed above the upper transformation point in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
The general cold strip mills, volume should go through continuous annealing (CAPL unit) to eliminate cold hardening and rolling stress, or batch annealing reach the mechanical properties of the corresponding standard specifies. Cold rolled steel surface quality, appearance, dimensional accuracy better than hot-rolled plate, and right-rolled thin product thickness is about 0.18mm, so the majority of users favor.
Cold rolled steel coil substrate products deep processing of high value-added products. Such as electro-galvanized, hot dip galvanized, electro-galvanized fingerprint resistant, painted steel roll damping composite steel, PVC laminating steel plates, etc., so that the excellent quality of these products has a beautiful, high resistance to corrosion, has been widely used.
Cold rolled steel coil finishing after annealing, cut the head, tail, trimming, flattening, smooth, heavy volume, or longitudinal clipboard. Cold-rolled products are widely used in automobile manufacturing, household electrical appliances, instruments, switches, buildings, office furniture and other industries. Steel plate strapping package weight of 3 to 5 tons. Flat sub-volume typically 3 to 10 tons / volume. Coil diameter 6m.
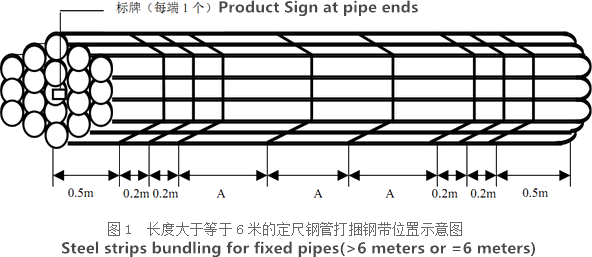
Bare packing/bundle packing/crate packing/wooden protection at the both sides of tubes and suitably protected for sea-worthly delivery or as requested.
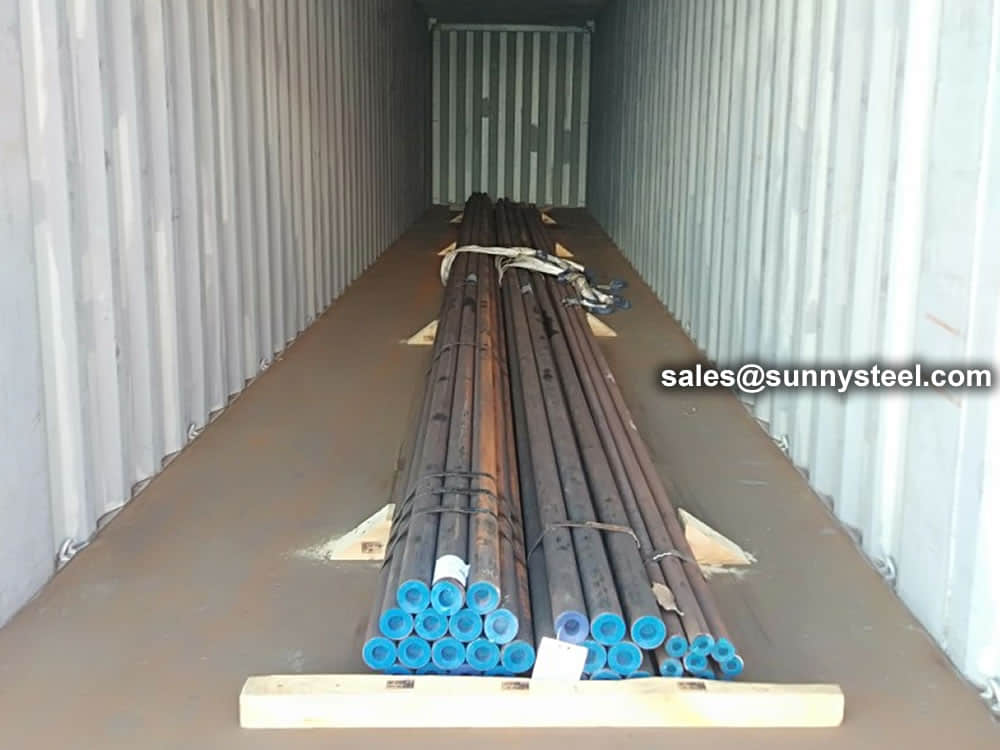
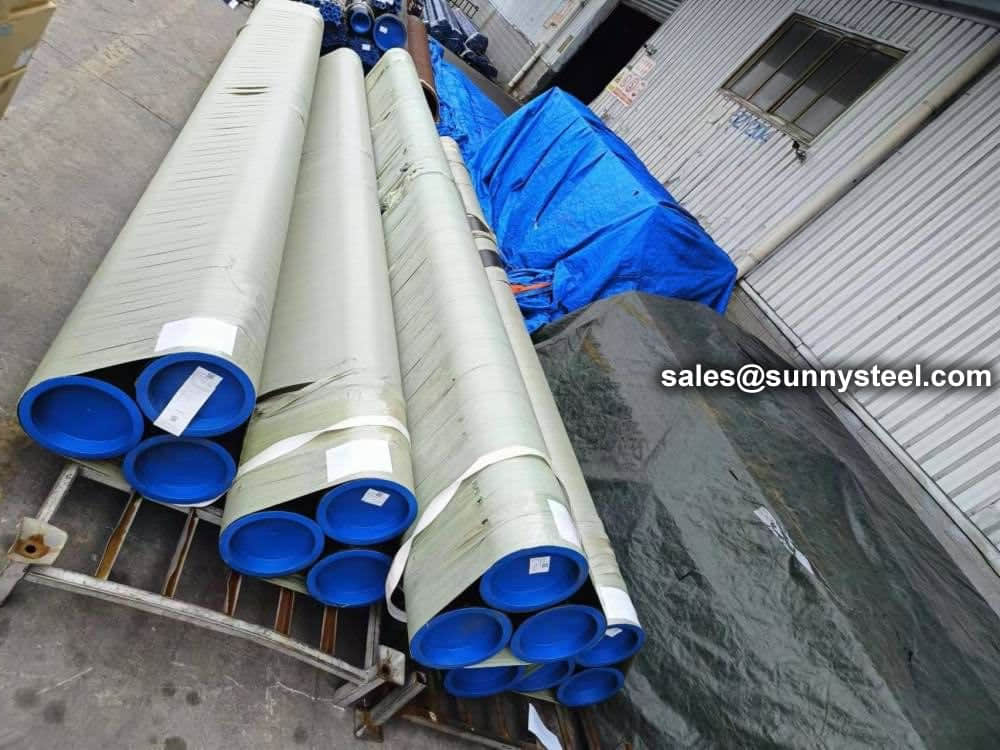
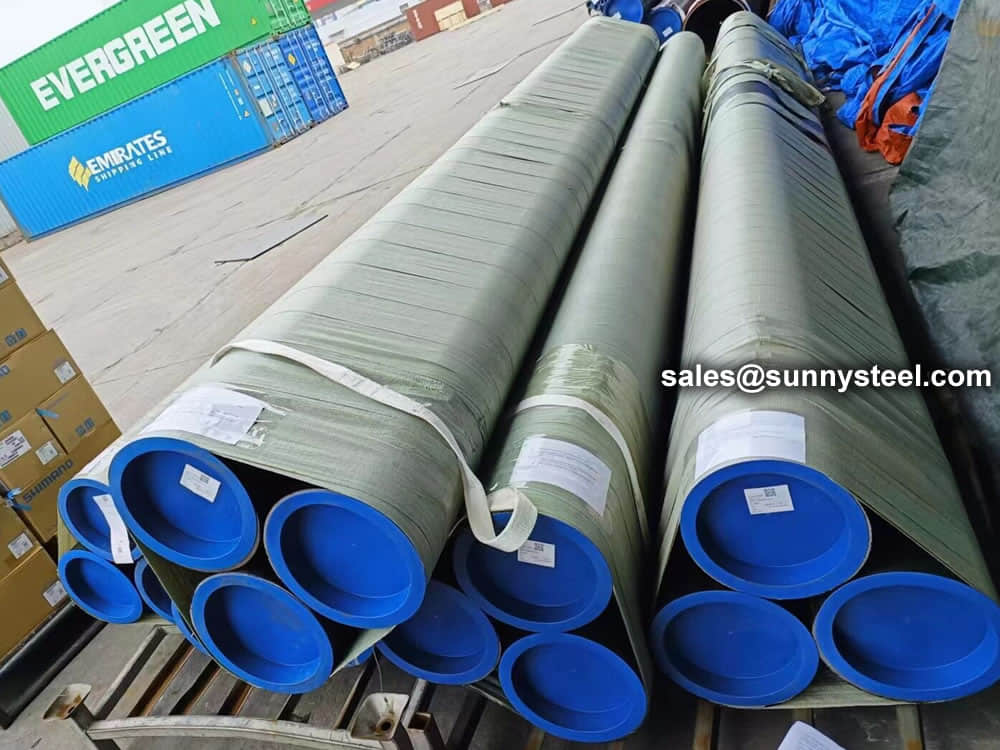
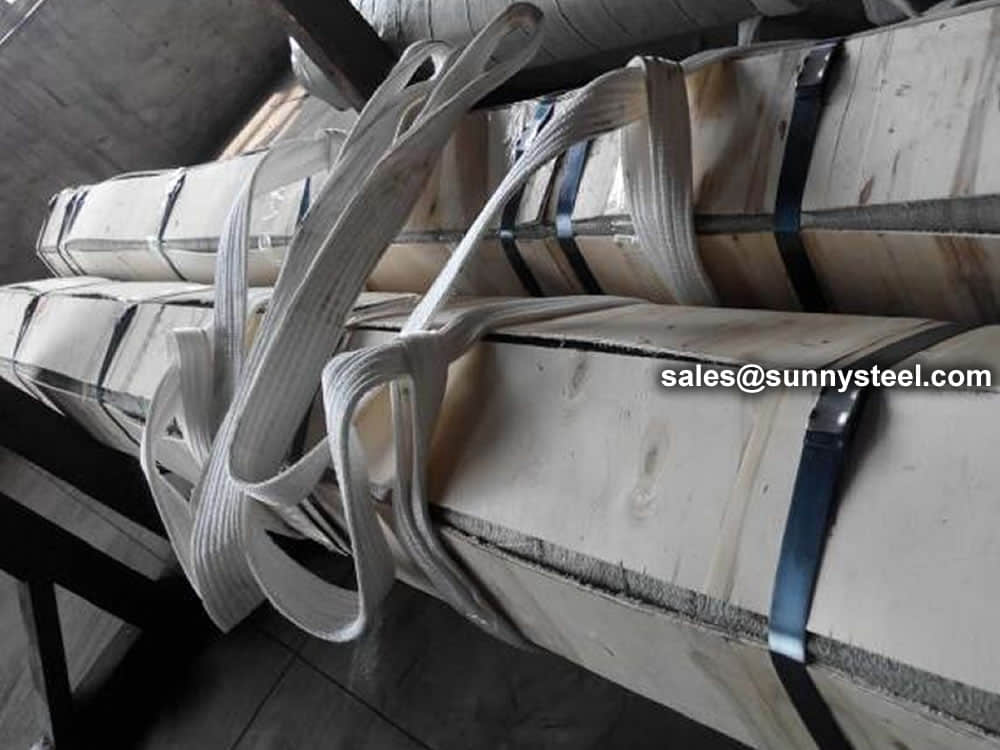
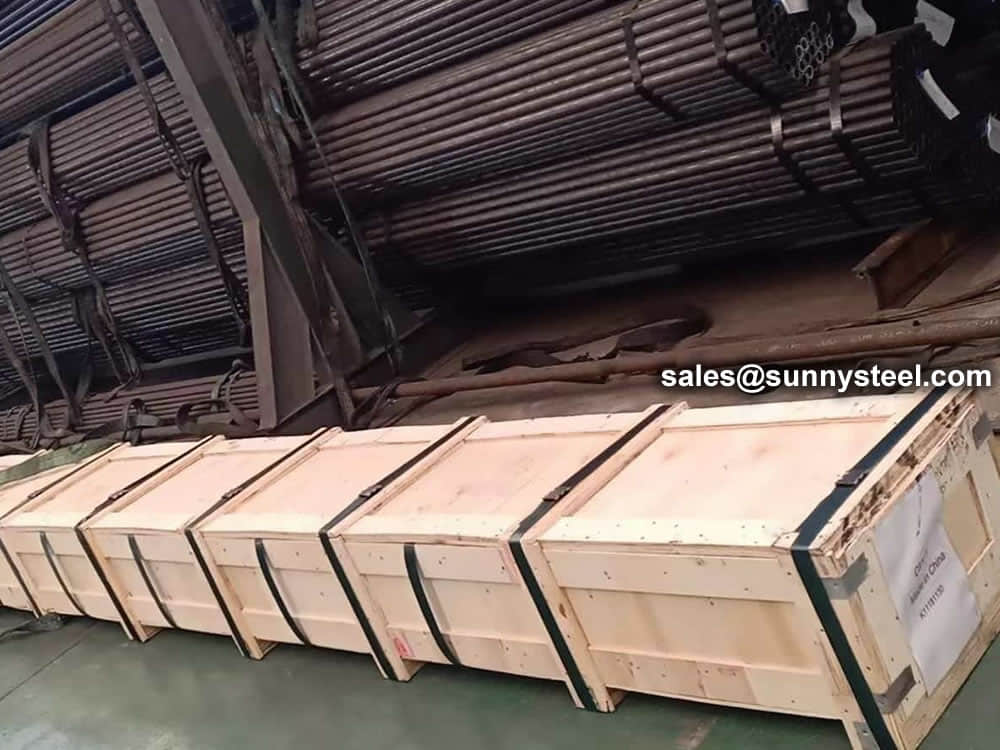
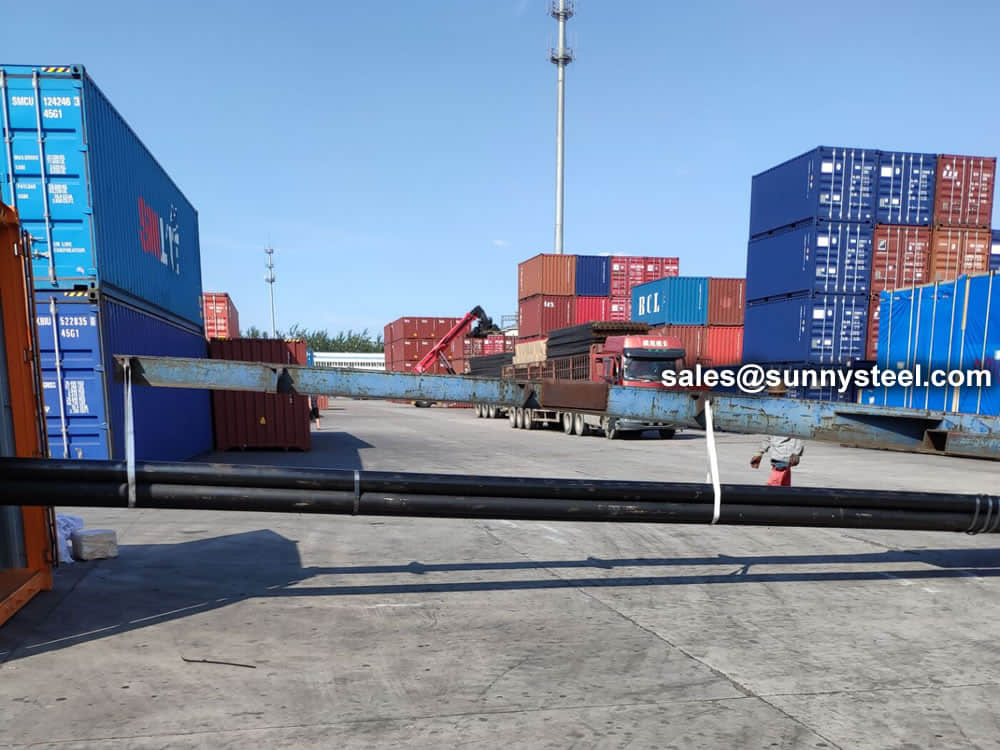
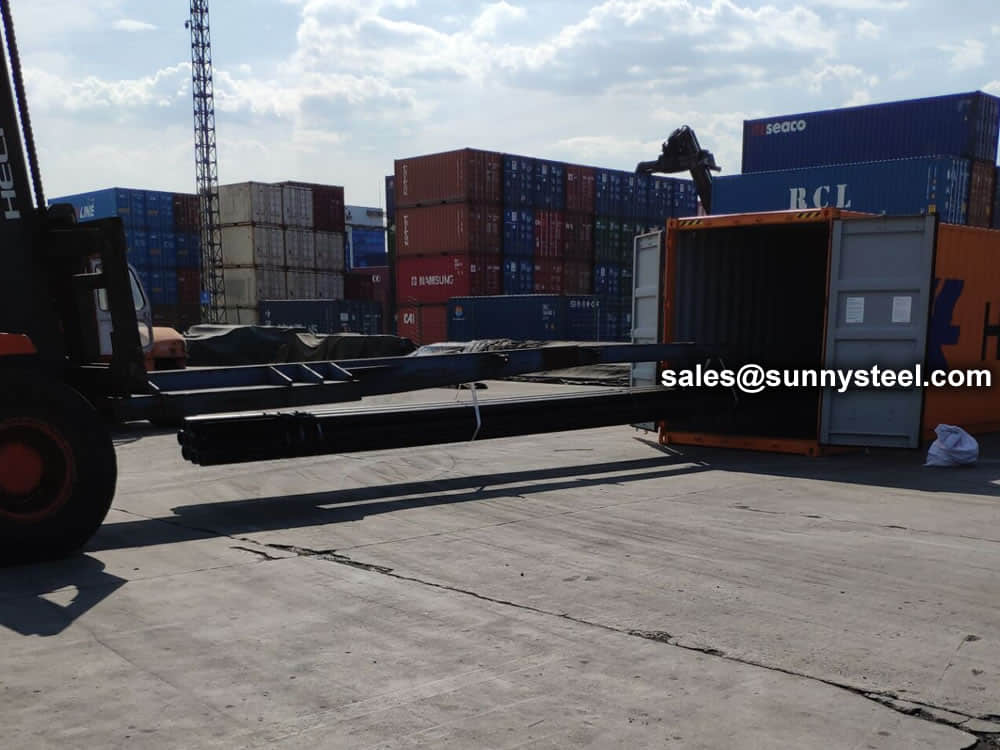
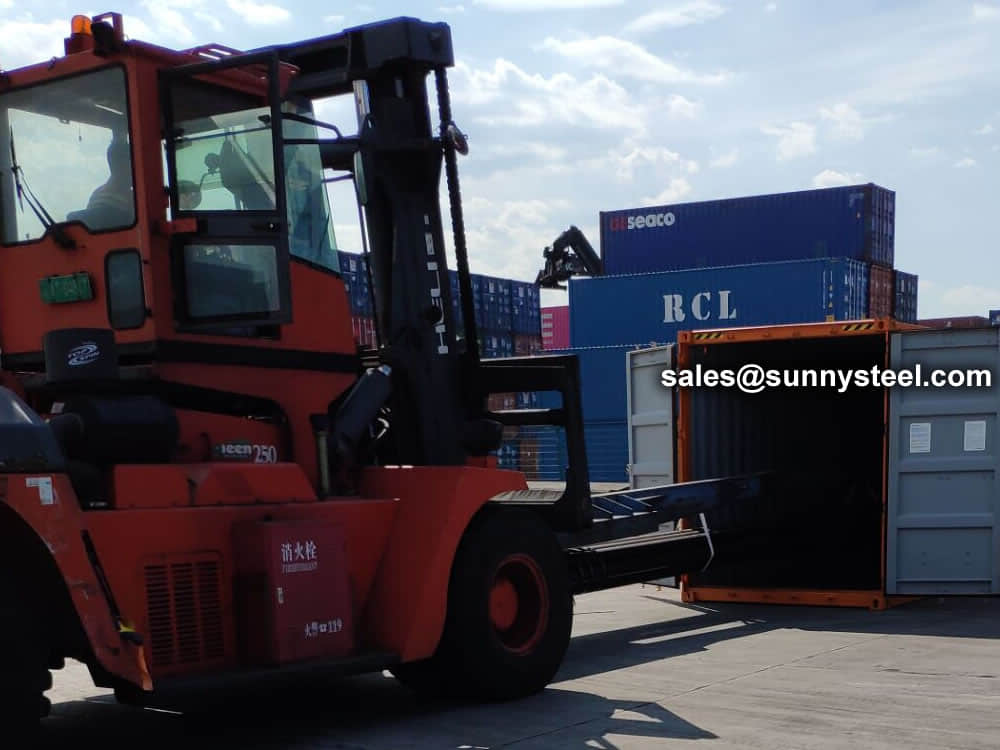
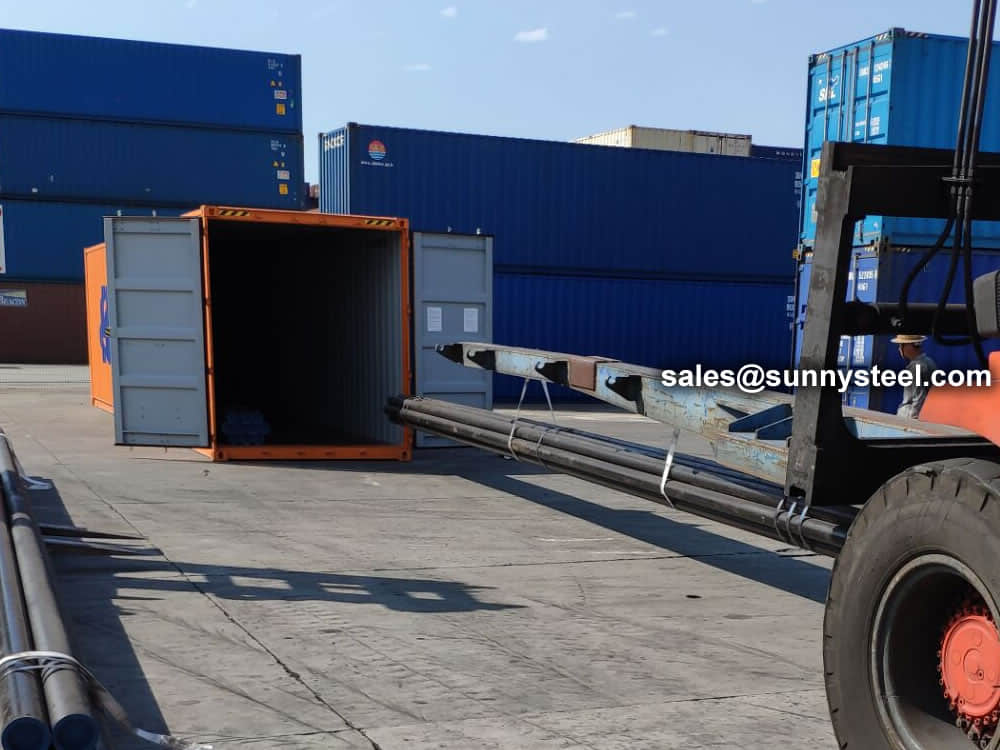
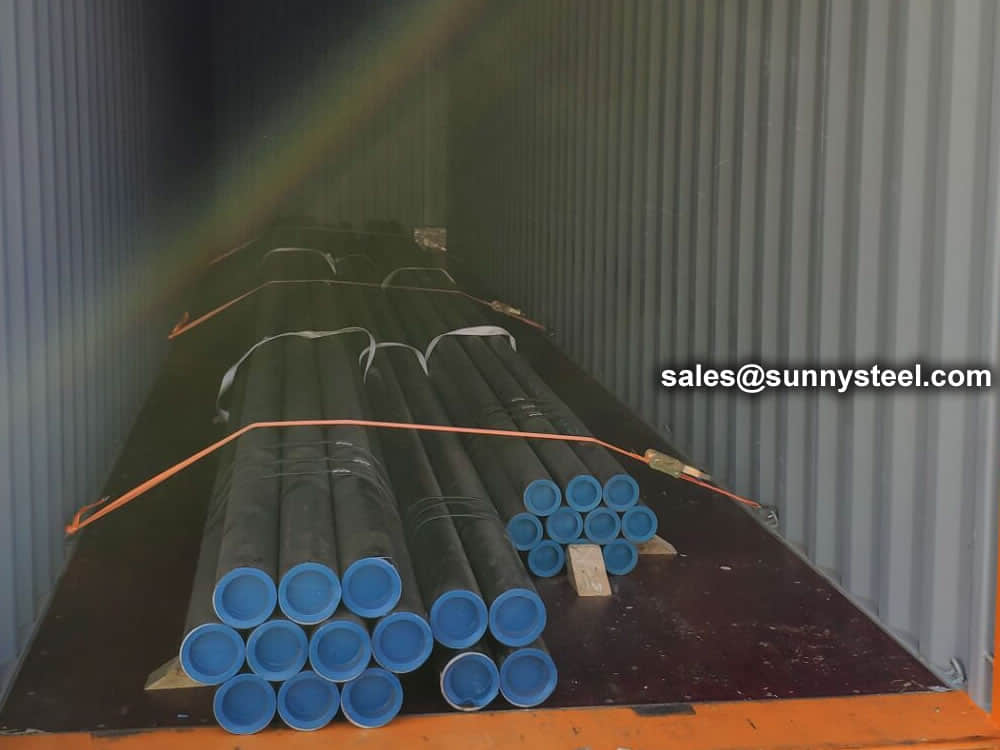
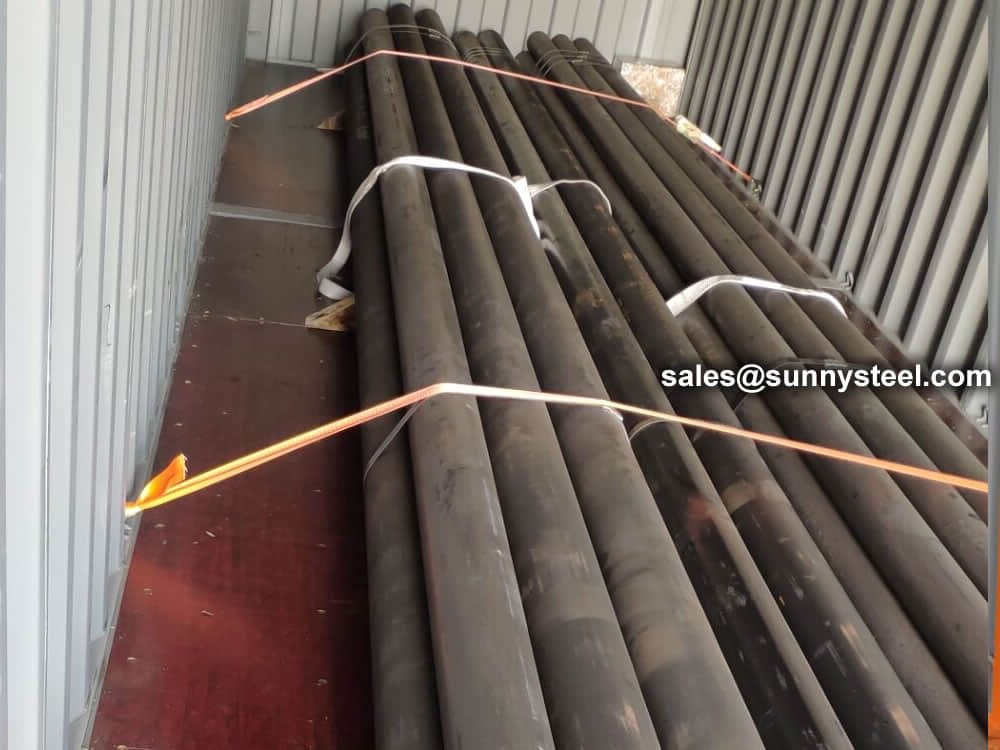












There are probably hundreds of different methods for packing a pipe, and most of them have merit, but there are two principles that are vital for any method to work prevent rusting and Sea transportation security.
Our packing can meet any needs of the customers.
Commonly used alloying elements and their effects are listed in the table given below.
| Alloying Elements | Effect on the Properties |
|---|---|
| Chromium | Increases Resistance to corrosion and oxidation. Increases hardenability and wear resistance. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Nickel | Increases hardenability. Improves toughness. Increases impact strength at low temperatures. |
| Molybdenum | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Enhances the effects of other alloying elements. Eliminate temper brittleness in steels. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Manganese | Increases hardenability. Combines with sulfur to reduce its adverse effects. |
| Vanadium | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Improves fatigue resistance. |
| Titanium | Strongest carbide former. Added to stainless steel to prevent precipitation of chromium carbide. |
| Silicon | Removes oxygen in steel making. Improves toughness. Increases hardness ability |
| Boron | Increases hardenability. Produces fine grain size. |
| Aluminum | Forms nitride in nitriding steels. Produces fine grain size in casting. Removes oxygen in steel melting. |
| Cobalt | Increases heat and wear resistance. |
| Tungsten | Increases hardness at elevated temperatures. Refines grain size. |

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
