304 Stainless Snap Rings
304 Stainless Snap Rings provide secure fastening solutions for industrial and mechanical applications with high corrosion resistance and durability.
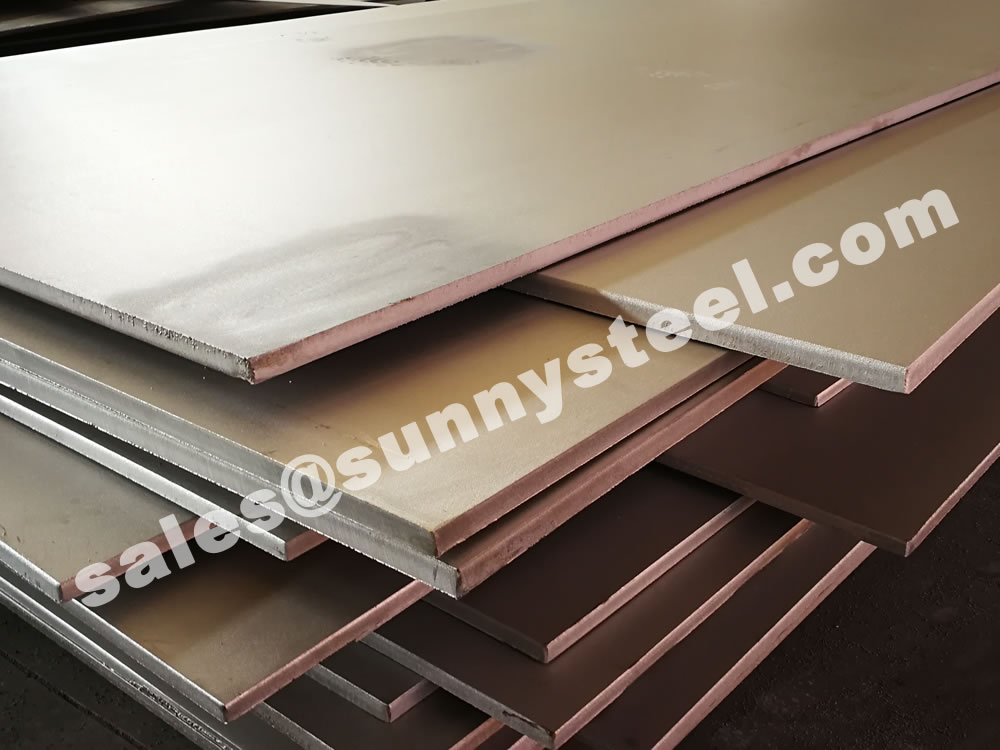

304 Stainless Steel Plate is a versatile and corrosion-resistant material used across industries for construction, food processing, medical equipment, and automotive applications.
304 stainless steel is one of the most widely used and versatile stainless steel grades due to its excellent corrosion resistance, high durability, and ease of fabrication.
It is commonly employed in various industrial, commercial, and household applications.
304 stainless steel plate is one of the most widely used materials in industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and ease of fabrication. It is popular in applications ranging from construction to food processing and medical equipment.
No. 1: Hot rolled, annealed, and pickled finish for industrial applications.
2B: Cold rolled and polished finish suitable for most general uses.
No. 4: Brushed finish for aesthetic purposes.
BA: Bright annealed finish offering a mirror-like appearance for decorative applications.
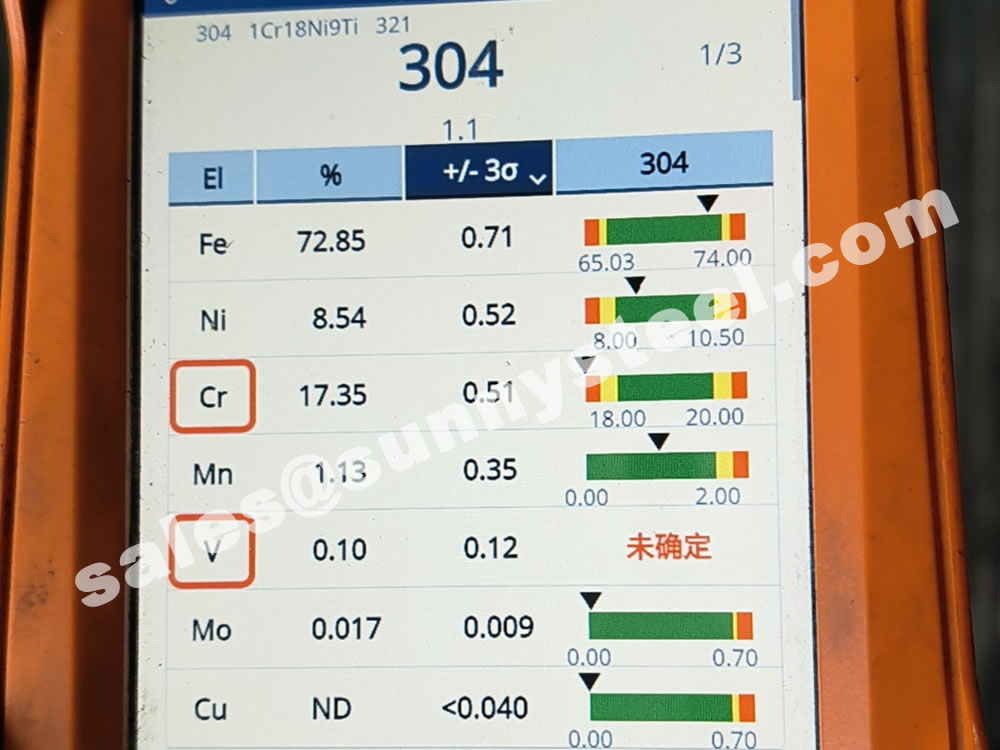
One of the most versatile and commonly used stainless steels on the market, Grade 304 stainless steel is the most standard used alloy of this type. Essentially, Grade 304 is an austenitic chromium alloy which is also known as an “18/8” stainless as the make-up of the steel is 18% chromium and 8% nickel.
The chromium content promotes the material’s considerable resistance to the effects of corrosion and oxidation. The stainless steel alloy resists most oxidizing acids and will withstand ordinary rusting though this does not mean that the steel will not tarnish over time. The steel needs to be cold worked to generate higher tensile strength. For stainless steel sections which are welded heavily, post-weld annealing may be necessary to provide maximum corrosive resistance.
Type 304 Stainless Steel has excellent welding and deep drawing characteristics – it is easy to fabricate, easy to clean and aesthetically pleasing to the eye.
304 Stainless Plate, the most widely used of the stainless and heat resisting steels. 304 stainless plate offers good corrosion resistance to many chemical corrodents as well as industrial atmospheres and marine environments Typical specifications for 304 Plate and 304L. Stainless Steel Plate are ASTM A-240, ASME SA -240 and A666.
304 Stainless Steel Plate has very good formability and can be readily welded by all common methods. 304/304L dual certified.
The composition typically consists of:
The alloy's lower carbon content is a real game-changer, minimising chromium carbide precipitation during welding and reducing its susceptibility to intergranular corrosion.Type 304's weldability and forming properties are nothing short of exceptional, and its machinability is more than satisfactory. But that's not all — this alloy boasts exceptional drawability, making it a breeze to work with.The combination of its low yield strength and high elongation is nothing short of remarkable, allowing for the formation of complex shapes with ease. And let's not forget, this material hardens at a rapid rate, making it incredibly versatile.
Type 304L, the low-carbon version of 304, is a real game-changer. It doesn't need any post-weld annealing, making it perfect for those heavy-duty projects, especially when used in components over 6 mm.
304 contains 18 - 20% Chromium (Cr). Chromium is the essential chemical in all stainless steel and it is that which forms the thin passive layer that makes the metal "stainless"
304 also contains 8-10.5% Nickel (Ni). This is added to make the Austenitic structure more stable at normal temperatures.
The nickel also improves high-temperature oxidation resistance makes the steel resistant to stress corrosion cracking.
Where the steel is to be stretched formed a lower percentage (8%) of nickel should be selected. If the steel is to be deep drawn a higher percentage is better (9% or more).
In addition a number of other chemicals may be present but these are expressed as maximum permited levels with the exception of the increased quantity of carbon required in 304H - i.e. a minimum of .04% and a maximum of 0.10%
*Maximum carbon content of 0.04% acceptable for drawn tubes
There are hundreds of different grades of stainless steel on the market. Each of these unique formulations of stainless steel offer some degree of corrosion resistance above and beyond that of plain steel.
The existence of these stainless steel variants can cause some confusion—especially when the names & formulations of two stainless steel alloys are almost the same. This is the case with grade 304 and 304L stainless steel.
| Element | Percentage by Weight Maximum Unless Range is Specified | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 304L | 304H | |
| Carbon | 0.08 | 0.030 | 0.04-0.10 |
| Manganese | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Phosphorus | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 |
| Sulfur | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Silicon | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Chromium | 18.00 20.00 |
18.00 20.00 |
18.00 20.00 |
| Nickel | 8.0 10.50 |
8.0 12.00 |
8.0 10.5 |
| Nitrogen | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |

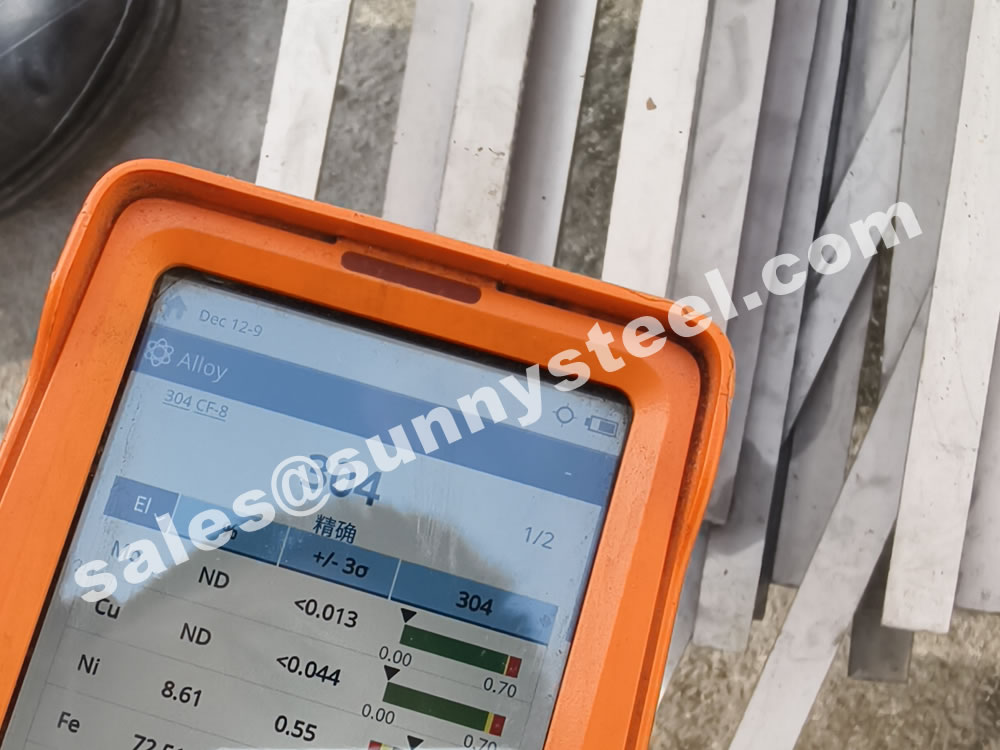
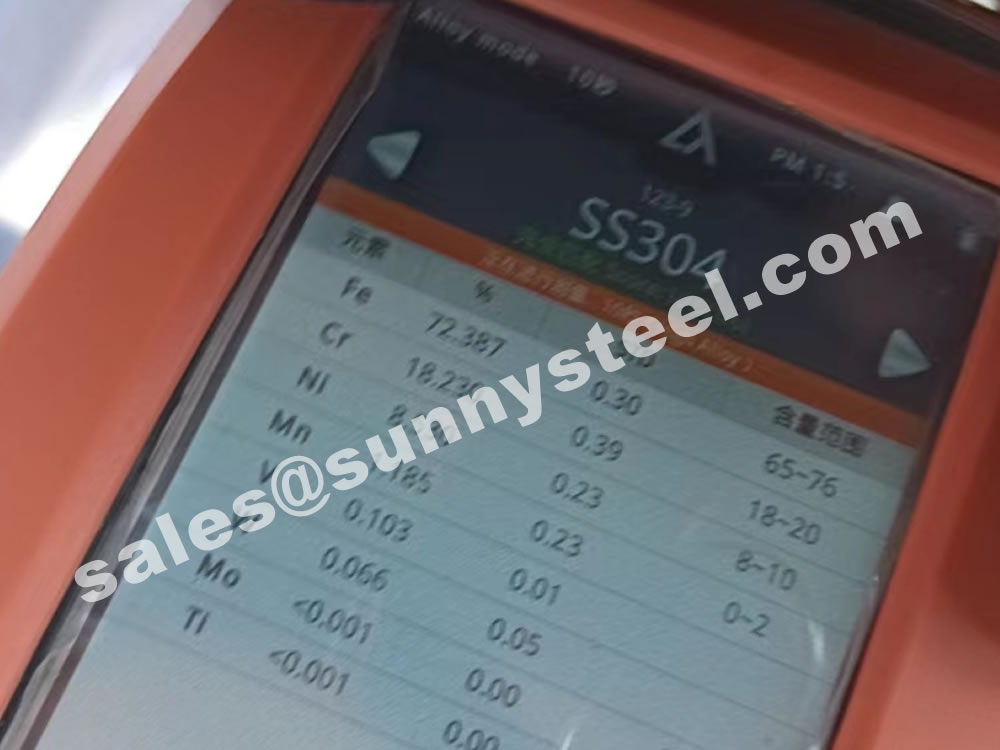
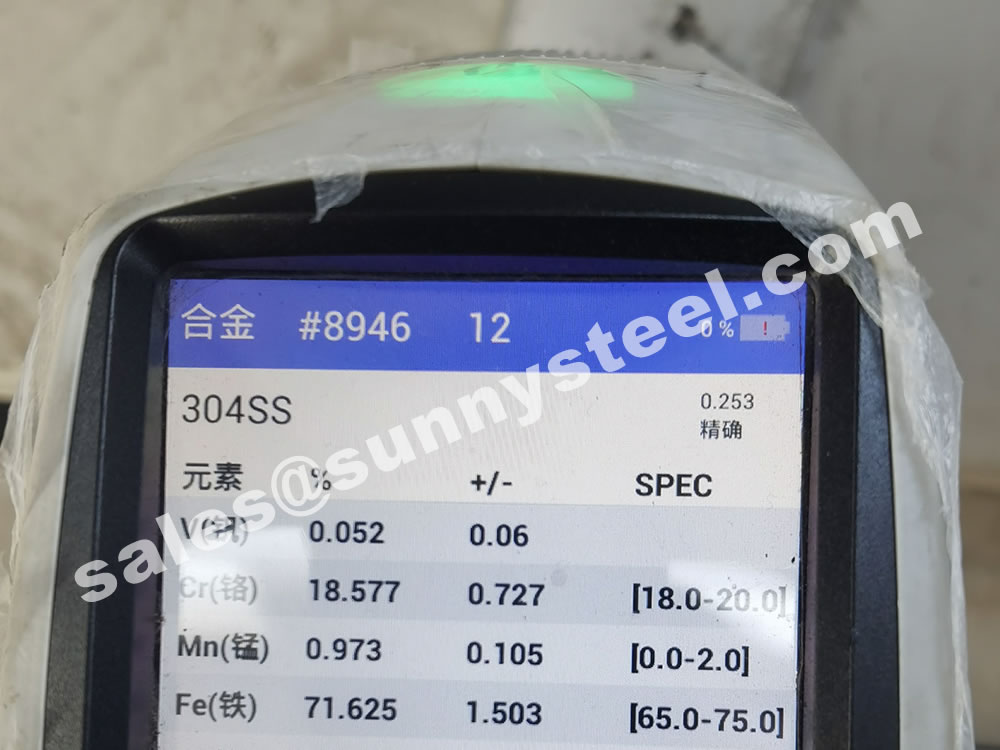
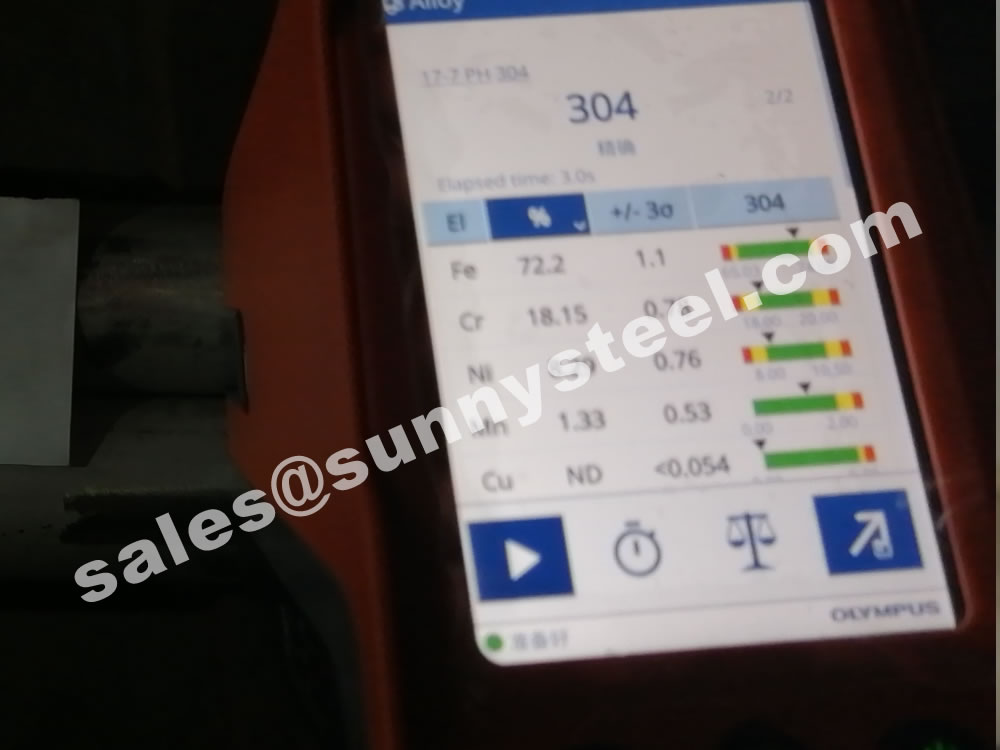
These three alloys are remarkably similar—but there is one key difference. In grade 304 stainless, the maximum carbon content is set at 0.08%, whereas grade 304L stainless steel has a maximum carbon content of 0.03%. The “L” in 304L can be interpreted as meaning extra-low carbon.
This difference of 0.05% carbon content produces a slight, but marked, difference in the performances of the two alloys.
| Grade | Tensile Strength Rm N/mm² |
Yield Strength Rp 0.2, N/mm² | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Annealed | 500-700 | 195 | 40 |
| 304L Annealed | 460-680 | 180 | 40 |
| Data | Metric | English |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8 g/cc | 0.289 lb/in³ |
| Hardness, Brinell | 123 | 123 | Converted from Rockwell B hardness. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness, Knoop | 138 | 138 | Converted from Rockwell B hardness. |
| Hardness, Rockwell B | 70 | 70 | |
| Hardness, Vickers | 129 | 129 | Converted from Rockwell B hardness. |
| Tensile Strength, Ultimate | 505 MPa | 73200 psi | |
| Tensile Strength, Yield | 215 MPa | 31200 psi | at 0.2% offset |
| Elongation at Break | 70 % | 70 % | in 50 mm |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 193 - 200 GPa | 28000 - 29000 ksi | |
| Poissons Ratio | 0.29 | 0.29 | |
| Charpy Impact | 325 J | 240 ft-lb | |
| Shear Modulus | 86 GPa | 12500 ksi |
| Electrical Resistivity | 7.2e-005 ohm-cm | 7.2e-005 ohm-cm | at 20°C (68°F); 1.16E-04 at 650°C (1200°F) |
| Magnetic Permeability | 1.008 | 1.008 | at RT |
Grade 304L has a slight, but noticeable, reduction in key mechanical performance characteristics compared to the “standard” grade 304 stainless steel alloy.
Typical specifications for 304 Plate and 304L Stainless Steel Plate are ASTM A-240, ASME SA -240 and A666.
304 stainless steel,also known as 18/8 stainless steel, European norm 1.4301, is the most common stainless steel. The steel contains both chromium (usually 18%) and nickel (usually 8%) metals as the main non-iron constituents. It is an austenite steel. It is not very electrically or thermally conductive, and is non-magnetic. It has a higher corrosion resistance than regular steel and is widely used because of the ease in which it is formed into various shapes.
Grade 304L is the low carbon version of 304. It does not require post-weld annealing and so is extensively used in heavy gauge components.
Design Features - Stainless Steel 304/304L
Typical Applications - Stainless Steel 304/304L
Tensile Requirements - Stainless Steel 304/304L
304 Stainless Steel Plate has very good formability and can be readily welded by all common methods.
Our precision machinery and state of the art facilities enables us to produce these 304 tube shield in superior quality and precise dimensions. All these years have enhanced our capabilities and enabled us to produce all kinds of standard tube shield as well as custom snap rings as per customer’s specifications. We have numerous combinations of sizes readily available in large number of stocks and can fabricate custom sizes according to customer’s requirement.
In common with other austenitic stainless steels, 304 grade has strong work hardening characteristics. Clearly, in some cases, this can be an advantage, but generally, it is an issue to be considered carefully.
If it is likely to be an issue, discussion with the producer can be valuable as minor variations to the precise composition and process can have benefits.
Where heavy sections have to we welded, post-weld annealing may be necessary to restore corrosion resistance.
The cross-sectional shape of boiler tube erosion shields is mostly semi-circular (180 degrees), and there are also 120-160 degrees. It is mainly used on finned tubes (water-cooled walls); boiler tubes erosion shields are divided into direct wear-resistant shields, in-curve anti-wear shields, outer-curve anti-wear shields, side-curve anti-wear shields, s-curve anti-wear shields, etc. The length of the straight anti-wear shields ranges from 20mm to 3000mm, and the general length of 1000-2000mm is commonly used. The anti-wear shields with bends generally requires a processing, drawing and the following parameters should be on the drawing: outer diameter of the pipe used, bending of the pipe radius r (to the centre of the pipe), the degree of bending angle, and the length of the straight sections on both sides of the arc segment of the wear-resistant shields.
The most basic parameter of boiler tube erosion shields is the outer diameter of the tube used (that is, the inner diameter of boiler tubes erosion shields). The main specifications of the tube are: 32, 38, 42, 44.5, 48, 51, 57, 60, 63.5 , 76, 89mm, etc .; the inner diameter of the boiler tubes erosion shields is usually 1-3mm larger than the outer diameter of the tube used, depending on the actual requirements.
Alloy 304 a T-300 series stainless steel austenitic, which has a minimum of 18% chromium and 8% nickel. Type 304 has a maximum carbon of 0.07% . It is the standard “18/8 stainless” that is commonly found in pans and cooking tools. Alloy 304 is the most versatile and widely used alloy in the stainless steel family. Ideal for a wide variety of home and commercial applications, Alloy 304 exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and has a high ease of fabrication, outstanding formability. The austenitic stainless steels are also considered to be the most weldable of the high-alloy steels and can be welded by all fusion and resistance welding processes.
Specifications: UNS S30400
Each alloy represents an excellent combination of corrosion resistance and fabricability. This combination of properties is the reason for the extensive use of these alloys which represent nearly one half of the total U.S. stainless steel production. The 18-8 stainless steels, principally Alloys 304, 304L, and 304H, are available in a wide range of product forms including sheet, strip, and plate. The alloys are covered by a variety of specifications and codes relating to, or regulating, construction or use of equipment manufactured from these alloys for specific conditions. Food and beverage, sanitary, cryogenic, and pressure-containing applications are examples.
Alloy 304 is the standard alloy since AOD technology has made lower carbon levels more easily attainable and economical. Alloy 304L is used for welded products which might be exposed to conditions which could cause intergranular corrosion in service.
Alloy 304H is a modification of Alloy 304 in which the carbon content is controlled to a range of 0.04-0.10 to provide improved high temperature strength to parts exposed to temperatures above 800°F.
For example, the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 304L is roughly 85 ksi (~586 MPa), less than the UTS of standard grade 304 stainless, which is 90 ksi (~620 MPa). The difference in yield strength is slightly greater, with 304 SS having a 0.2% yield strength of 42 ksi (~289 MPa) and 304L having a 0.2% yield strength of 35 ksi (~241 MPa).
This means that if you had two steel wire baskets and both baskets had the exact same design, wire thickness, and construction, the basket made from 304L would be structurally weaker than the standard 304 basket.
So, if 304L is weaker than standard 304 stainless steel, why would anyone want to use it?
The answer is that the 304L alloy’s lower carbon content helps minimize/eliminate carbide precipitation during the welding process. This allows 304L stainless steel to be used in the “as-welded” state, even in severe corrosive environments.
If you were to use standard 304 stainless in the same way, it would degrade much faster at the weld joints.
Basically, using 304L eliminates the need to anneal weld joints prior to using the completed metal form—saving time and effort.
In practice, both 304 and 304L can be used for many of the same applications. The differences are often minor enough that one isn’t considered massively more useful over the other. When stronger corrosion resistance is needed, other alloys, such as grade 316 stainless steel, are usually considered as an alternative.
ASTM A213 / ASME SA213 is a America specification for stainless steel boiler, super heater, heat exchanger tubes, executed by most world stainless steel seamless tubes mills and factories, minimum wall thickness required in A213 seamless tube, or average wall thickness as customers requirement, tight tolerance of outside and wall thickness stated as A213 standard or A1016
Cold rolling steel is a method that is used to provide a dense, dimensionally precise piece of steel. The most commonly used grade of stainless steel is 304. All stainless steels are a specific alloy mix.
Cold rolled steel, also called CRS, is a process used to finish steel. Hot rolled steel is steel that is still warm enough to be malleable and run through pressure rollers. After cleaning, when the steel has cooled and is no longer elastic, the steel is then put through power rollers and cold rolled. This produces a product that has a fine, smooth finish.
The most commonly used grade of stainless steel is 304. Another name for 304 is 18/8 because it is 18 percent chromium and 8 percent nickel. These additions make it resistant to corrosion.
The difference between CRS and 304 stainless steel is that CRS is a process and 304 is an alloy. Steel, hot or cold rolled, will rust and corrode. It is used in applications where that is not a consideration. Stainless steel is an alloy with chromium and nickel that prevents rust and corrosion. It is used where rust and corrosion will be a problem. It is possible to buy 304 cold rolled stainless steel.
Stainless Steel is a chromium-based alloy known for its incredible anti-rust properties. But along with this, Stainless Steel alloys are also used due to their incredible strength. Stainless Steel 304 has incredible strength and durability. Its strength is one of the most sought-after traits of grade 304 SS. Stainless Steel 304L Pipes and 304 Pipes are solid and retain their strength at extreme temperatures.
Stainless Steel 304, 304 L, and almost every grade of Stainless Steel is brilliant at repelling corrosion. As a result of this property, Stainless Steel grade 304 Pipes also have the property of repelling the growth and spread of microbes and dirt on the surface of the Pipes. Hence, it is often used in applications that have a primary need for sanitization and monitoring cleanliness. Additionally, Stainless Steel 304 Pipes are incredibly easy to maintain. They can be cleaned very easily. Hence, Stainless Steel 304 Pipes are used at hospitals, kitchens, food processing localities, etc., where cleanliness is a requisite.
AS its name suggests, Stainless Steel is a material that prohibits rusting and corrosion even in extreme temperature and weather conditions, including high-pressure areas. The chromium present in stainless Steel reacts with oxygen to create a chromium oxide film or layer that settles on the surface of the metal. This layer is what protects the Pipes from corroding. It is a self-reparatory layer that does not require maintenance or refurbishing.
But what sets grade 304 apart is the addition of molybdenum to the alloying composition making it an austenitic grade of stainless Steel. Austenitic Steel has enhanced corrosion resistance. Hence, for applications in extreme conditions, Stainless Steel 304 Pipes are an ideal choice.
Stainless Steel 304 Pipes are entirely recyclable. Once its utility purposes have been outlived or fulfilled, it can be recycled and re-forged. When stainless Steel is recycled, it does not lose any of its properties. All of its chemical, physical, and mechanical properties remain intact. About 70% of existing Stainless Steel artifacts are made out of recycled material.
Even though Stainless Steel 304 Pipes are lightweight, they are solid. They won’t succumb to external weights and pressure. Hence, it is said that it is one of the most durable materials. Stainless Steel 304 Pipes can withstand extreme temperatures as well as extreme pressures.

304 stainless steel is an austenitic stainless steel that contains chromium and nickel as its major alloying elements.
Stainless steel is synonymous with strength, durability and aesthetics. From kitchen knives to electrical enclosures and beyond, stainless steel is a material that keeps our world and our tools cleaner, safer and more functional.
But not all stainless steel is the same. There are many different types of stainless steel in use today, and it can be difficult to remember which is which. But it's important to do your research, because different types of stainless steel have very different properties that affect their suitability for different applications.
In this article, we'll talk about what those benefits are and what kind of performance you can expect from 304 stainless steel enclosures.
Like all steels, stainless steel is an alloy of iron, carbon and small amounts of other metals. However, stainless steel is different because its composition also includes a substantial amount of chromium.
The addition of chromium gives stainless steel its desirable properties, including its resistance to corrosion and its brilliant appearance. When normal steel comes into contact with a source of oxidation, such as water, the iron that’s present in the steel starts giving away its electrons, forming iron oxide—better known as rust. In contrast, the chromium in stainless steel helps create a protective layer that makes the steel much less reactive and helps protect it from corrosion.
Stainless steel comes in many different types that vary by composition. Carbon content, chromium content and the content of other metals like nickel and molybdenum set the different types of stainless steels apart and make them suitable for different functions.
304 stainless steel is one of the most popular types of stainless steel. It’s a member of the austenitic family of stainless steels, which means that 304 stainless also contains nickel in addition to chromium.
The defining features of 304 stainless steel are its inclusion of at least 18 percent chromium and 8 percent nickel, which is why it’s also known as 18/8 steel. This is a uniquely well-balanced combination that produces a number of desirable material qualities. Some of the positive qualities of 304 stainless steel include:

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
